XLS, XLSX
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
-
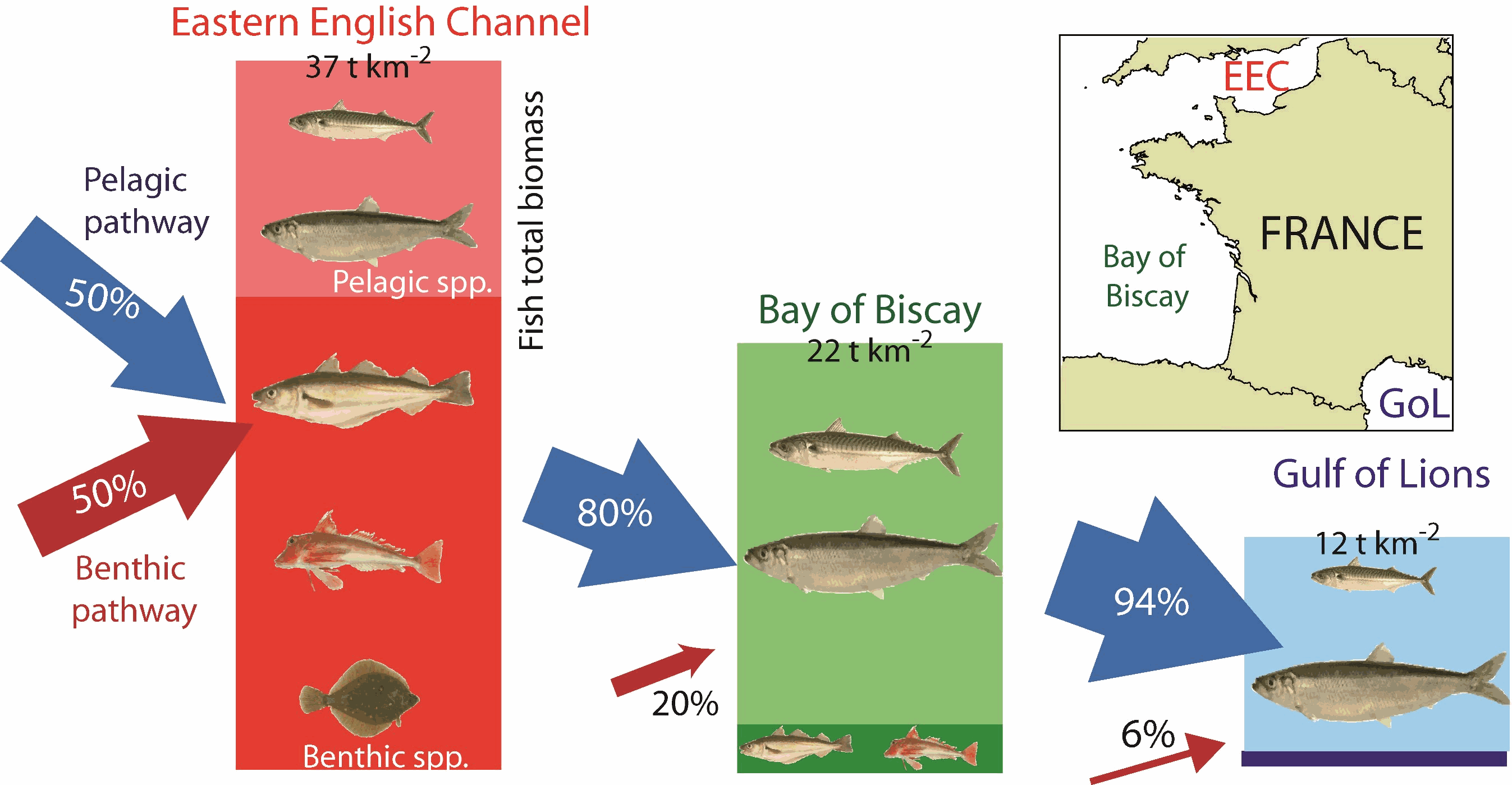
This dataset gathers data used to infer the trophic structure and functioning of fish assemblages in the Eastern English Channel, the Bay of Biscay and the Gulf of Lions : - Biomass data, resulting from accoustic monitoring for pelagic species, or bottom trawling for demersal species, after extrapolation based on stratification scheme - Individual C and N isotopic ratios, length and mass, for all individuals considered - Individual energetic density values
-
The Mediterranean Sea is generally described as an oligotrophic area where primary productivity is limited to a few coastal environments with nutrient-enriched fluvial input. However, several studies have revealed that the hydrology of the western Mediterranean has major seasonal productive patterns linked either to significant riverine input or to seasonal upwelling cells. This study aims to: i) discuss organic microfossils (i.e. pollen and dinoflagellate cyst assemblages, as well as other non-pollen palynomorphs) from two different productive areas of the western Mediterranean Sea, and ii) examine the importance of the interconnections between marine and continental influences responsible for modern palynomorph distributions. Based on 25 samples from the Gulf of Lion (GoL) and Algerian Margin, this study key findings are: i) that GoL marine productivity is driven by the combination of discharges from the Rhône River and seasonal upwelling mechanisms, ii) that the strong productive pattern of the northern African coast is driven by water density front mixings and related upwellings. These two patterns are discussed in the light of major links that provide a better understanding of the signatures of marine and continental bio-indicators. The dinocyst Lingulodinium machaerophorum can be considered as a tracer of Rhône River plume influence in the GoL. Brigantedinium taxa are shown to be upwelling-sensitive in both studied areas. Typical differences in vegetation across the north–south climate gradient in the western Mediterranean Basin are highlighted by the larger ratio of Euro-Siberian to Mediterranean pollen taxa in the northern sector. Synoptic maps also illustrate the complex interactions of environmental drivers determining the distributions of continental and marine palynomorphs in the western Mediterranean Sea.
-

Good Environmental Status assessment (GES) for descriptor 8 (contaminants, D8) of the Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD) is reached when concentrations of contaminants are at levels not giving rise to pollution effects. It is described by 4 criteria among which the first one focus on the concentration of the contaminants in the environment (criteria 1 of the D8, D8C1). The environmental status for D8 in France includes assessment of contaminant concentrations in sediment, bivalves, fish, birds, mammals to cover the French marine area the continental shelf from the coast line). The 8 tables below present the assessment of the chemical contamination in sediment and bivalves on the coastal area of the 4 French marine subregions for D8 as part of the 2024 GES assessment. These tables report the status and temporal trends of each station x matrice x substance triplet in each of the 4 French marine subregions. Explanation on how to read the cells is given in the “read file”. The environmental assessment for D8 in France can be found in Mauffret al., 2023 (DOI:10.13155/97214). It includes 17 national indicator assessments, 4 OSPAR indicators and integrated assessment in selected assessment units at the level of the criteria 1 and 2.
-
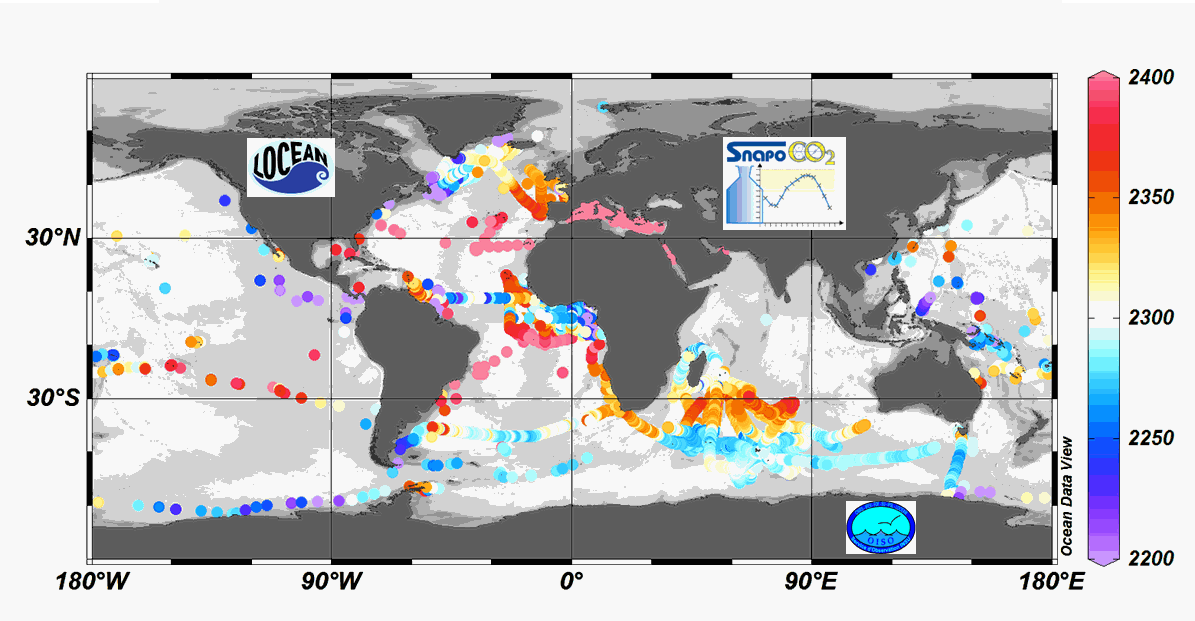
Since 2004, the Service facility SNAPO-CO2 (Service National d’Analyse des Paramètres Océaniques du CO2) housed by the LOCEAN laboratory (Paris, France) has been in charge for the analysis of Total Alkalinity (AT) and Total dissolved inorganic carbon (CT) of seawater samples on a series of cruises or ships of opportunity conducted in different regions in the frame of French projects. More than 44000 observations are synthetized in this work. Sampling was performed either from CTD-Rosette casts (Niskin bottles) or collected from the ship’s seawater supply (intake at about 5m depth). After completion of each cruise, discrete samples were returned back at LOCEAN laboratory and stored in a dark room at 4 °C before analysis generally within 2-3 months after sampling (sometimes within a week). AT and CT were analyzed simultaneously by potentiometric titration using a closed cell (Edmond, 1970). Certified Reference Materials (CRMs) provided by Pr. A. Dickson (Scripps Institution of Oceanography, San Diego, USA) were used to calibrate the measurements. The same instrumentation was used for underway measurements during OISO cruises (https://doi.org/10.18142/228) and OISO AT-CT data for 1998-2018 in the South Indian Ocean added in this synthesis. The synthesis is organized in two files (one for Global ocean and the Coastal Zones, one for the Mediterranean Sea) with the same format: Cruise name, Ship name, day, month, year, hour, minute, second, latitude, longitude, depth, AT (µmol/kg), Flag-AT, CT (µmol/kg), Flag-CT, Temperature (°C), Flag-Temp, Salinity (PSU), Flag-Salinity, nsample/cruise, nsample on file, sampling method.
-
Key physico-chemical parameters (salinity, temperature, turbidity and dissolved oxygen) were measured in surface water during longitudinal transects in the Loire and Gironde estuaries in summers 2017 and 2018. This objective of this work was to determine the distribution of the dissolved oxygen and to detect potential severe desoxygenation. The transects were scheduled in order to begin the measurements at high tide from a site located upstream of an area where severe deoxygenation have been already been reported. Then, the transect was realised by sailing at low speed downstream with a multiparameter probe SAMBAT, maintained at 0.5 m below the surface, that collected a measurement every 2 minutes.
-
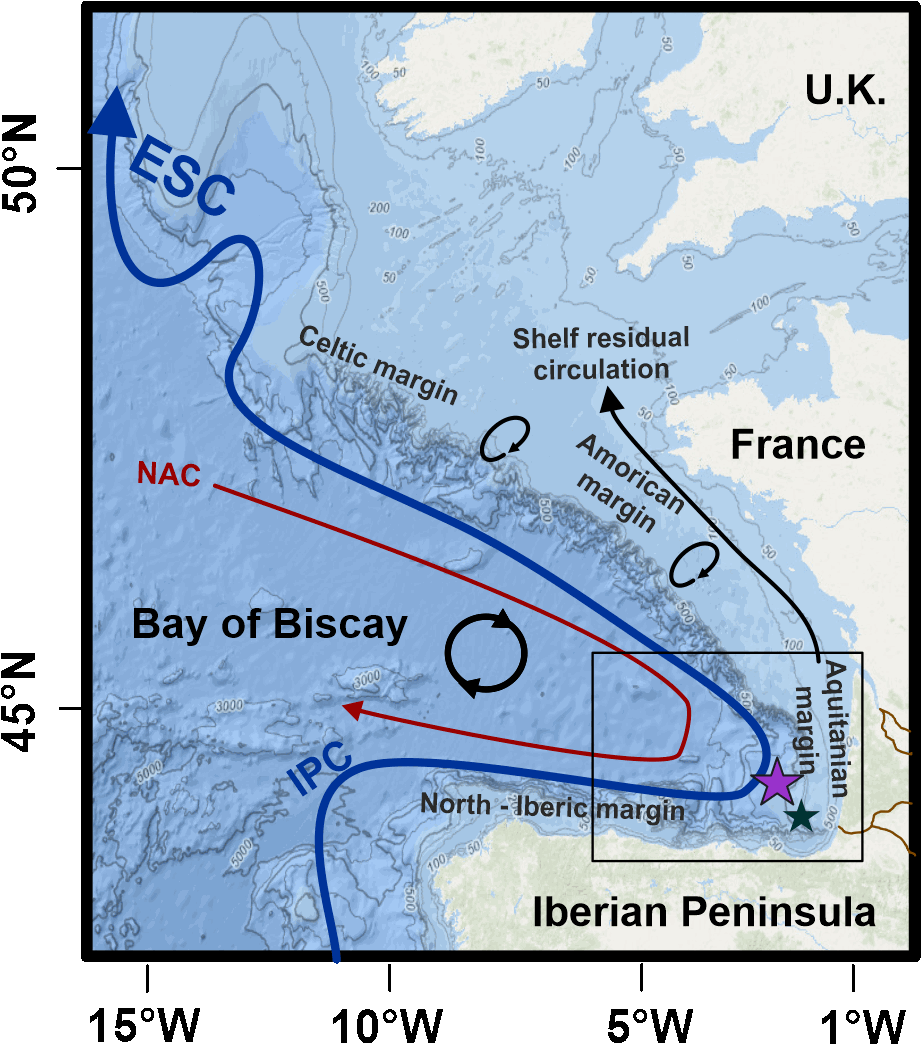
In the mid-latitudes of the northeast Atlantic, the study of the upper branch of the AMOC is poorly documented. This study provides a complete record of the glacial, deglacial and Holocene dynamics of the easternmost portion of the upper branch of the AMOC, namely the European Slope Current and its glacial equivalent know as the Glacial Eastern Boundary Current (GEBC). To do so, we use core SU81-44 (~1000 m water depth) from the of southern Bay of Biscay (BoB) upper slope, .The aim of this study is to reconstruct paleoenvironmental and hydrodynamic changes using a multiproxy approach (i.e. benthic foraminiferal assemblage, grain size proxies, oxygen and carbon stable isotopes, and foraminiferal εNd). During the glacial period and the onset of the deglaciation, our results show that the grain size proxies together with the relative densities of the high-energy indicator species Trifarina angulosa and the low oxygen tolerant Globobulimina spp. showed significant fluctuations. These were concomitant with the main climate changes recognized over this period and with the glacial slope paleoflow reconstruction from the northern BoB. This highlights a strong climatic/oceanographic forcing on the sedimentary characteristics of the region and a prominent forcing by changes in near-bottom flow speed. Our data also provide a new constraint on the strength of the slope current in the region during the late deglaciation and Holocene periods. We observe a reinvigoration of the upper branch of the AMOC during the Bølling-Allerød warming, preceding the abrupt resumption of the deeper branch of the AMOC in the western North Atlantic. This seems to confirm the crucial role of the European Slope Current in deep water formation, as it is the case today. Finally, our data show a progressive weakening of the ESC during the Holocene and we hypothesize a link with the long-term dynamics of the subpolar gyre.
-
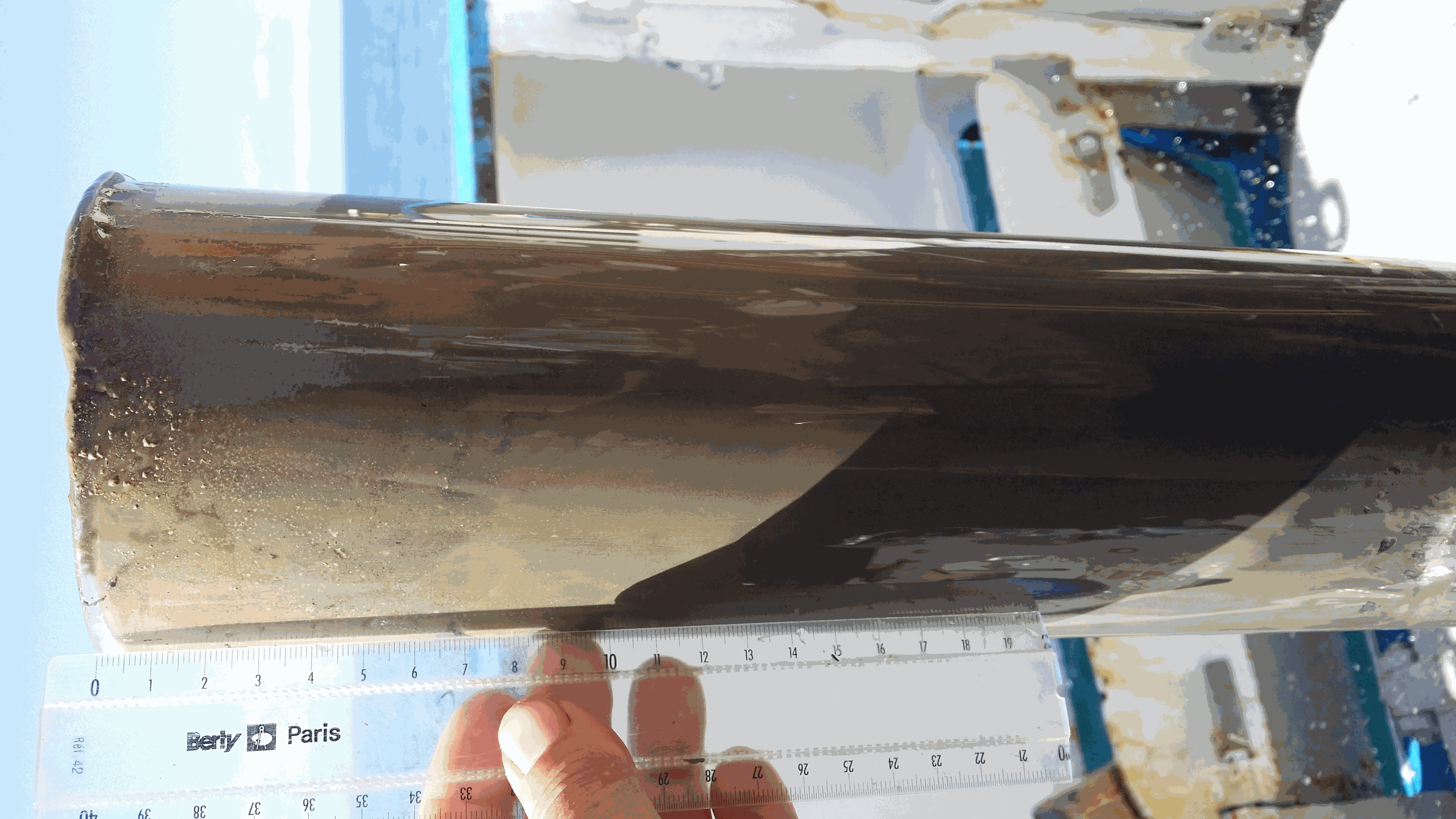
The West Gironde Mud Patch (WGMP) is a 420-km2 mud belt in the Bay of Biscay, located 25 km off the mouth of the Gironde estuary. This clay-silt feature of 4 m in thickness extends between 30 and 75m water depth, surrounded by the sands and gravels that cover the North Aquitaine continental shelf. Interface cores were collected during JERICOBent-1 cruise (October 2016; Deflandre (2016) doi.org/10.17600/16010400) along two cross-shelf transects for a total of 9 sites. Each sediment core was carefully extruded every 0.5 cm from the top core to 4 cm and every 1 cm below until the core bottom. The sediment layers were used to determine dry bulk density, grain size and selected radioisotope activities (210Pb, 226Ra, 137Cs, 228Th, K).
-
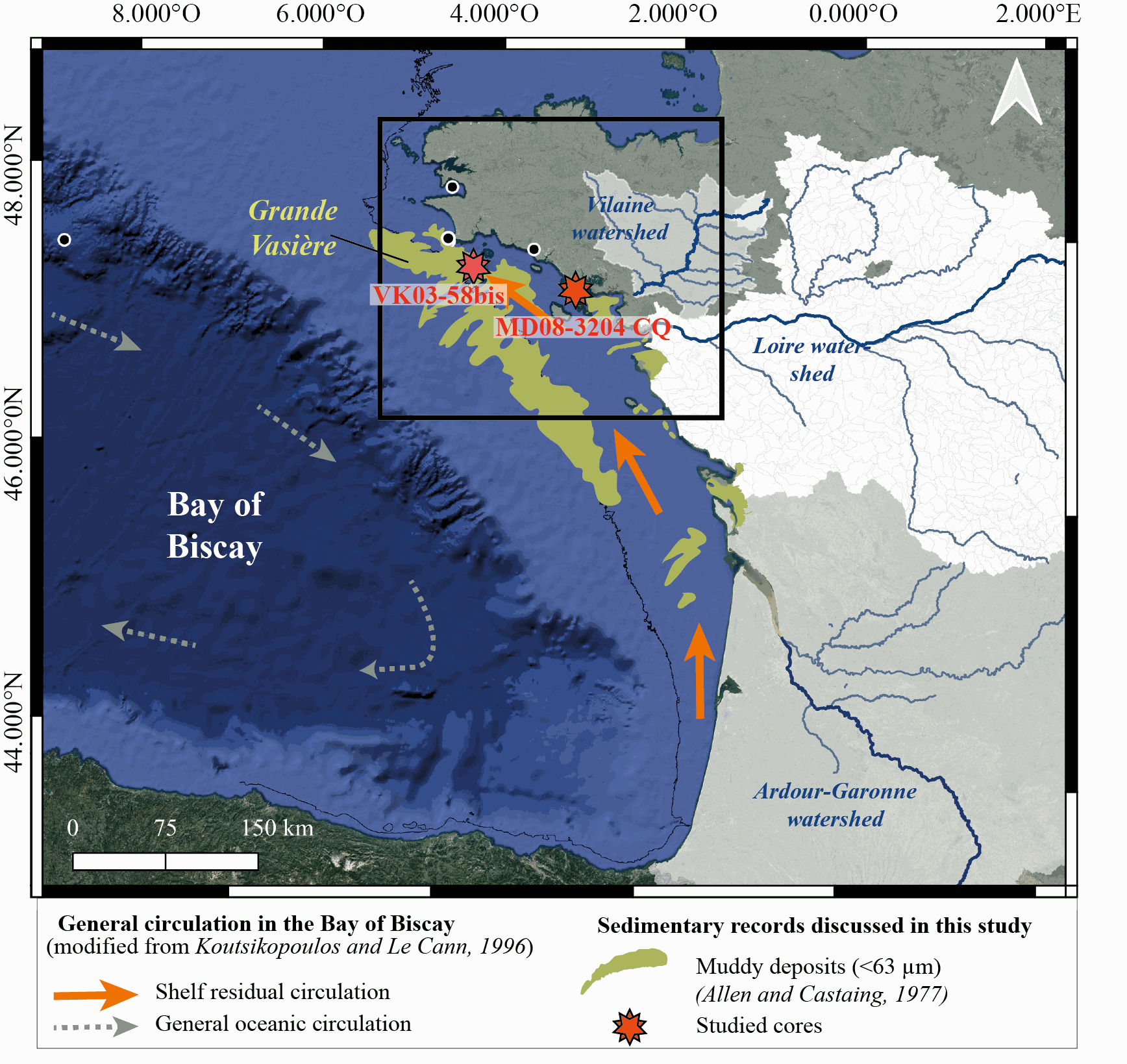
New results acquired in south-Brittany (MD08-3204 CQ core: Bay of Quiberon and VK03-58bis core: south Glénan islands) allow depicting Holocene paleoenvironmental changes from 8.5 ka BP to present through a multi-proxy dataset including sedimentological and palynological data. First, grain-size analyses and AMS-14C dates highlight a common sedimentary history for both study cores. The relative sea level (RSL) slowdown was accompanied by a significant drop of the sedimentation rates between ca. 8.3 and 5.7 ka BP, after being relatively higher at the onset of the Holocene. This interval led to the establishment of a shell-condensed level, identified in core VK03-58bis by the “Turritella layer” and interpreted as a marker for the maximum flooding surface. Palynological data (pollen grains and dinoflagellate cyst assemblages) acquired in core MD08-3204 CQ argue for an amplification of the fluvial influence since 5.7 ka BP; the establishment of the highstand system tract (i.e., mixed marine and fluviatile influences on the platform) then accompanying the slowdown of the RSL rise-rates. On the shelf, the amplification of Anthropogenic Pollen Indicators (API) is then better detected since 4.2 ka BP, not only due to human impact increase but also due to a stronger fluvial influence on the shelf during the Late Holocene. Palynological data, recorded on the 8.5–8.3 ka BP interval along an inshore-offshore gradient, also demonstrate the complexity of the palynological signal such as i) the fluvial influence that promotes some pollinic taxa (i.e., Corylus, Alnus) from proximal areas and ii) the macro-regionalization of palynomorph sources in distal cores. In addition, the comparison of palynological tracers, including API, over the last 7 kyrs, with south-Brittany coastal and mid-shelf sites subjected to northern vs. southern Loire catchment areas, allowed discussing a major hydro-climatic effect on the reconstructed palynological signals. Strengthened subpolar gyre dynamics (SPG), combined with recurrent positive North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO) configurations, appear responsible for increased winter precipitations and fluvial discharges over northern Europe, such as in Brittany. Conversely, weakened SPG intervals, associated with negative NAO-like modes, are characterized by intensified winter fluvial discharges over southern Europe. Interestingly, we record, at an infra-orbital timescale, major peaks of API during periods of strengthened (/weakened) SPG dynamics in sites subjects to Brittany watersheds (/Loire watersheds) inputs.
-

As part of the European Horizon Europe FOCCUS project (https://foccus-project.eu/), the metadata inventory of European coastal platforms has been extracted. The inventory was based on the following History and Latest products, downloaded from the CMEMS website (https://marine.copernicus.eu/fr/acces-donnees) at: 1) Global Ocean-In-Situ Near-Real-Time Observation, 2) Atlantic Iberian Biscay Irish Ocean-In-Situ Near Real Time Observations, 3) Mediterranean Sea-In-Situ Near Real Time Observations, 4) Atlantic-European North West Shelf-Ocean In-Situ Near Real Time Observations. To carry out this inventory, it was decided to target only coastal platforms, located less than 200km from the coast and at a depth of less than 400m. For mobile platforms, it was also decided to focus only on the first position in the file. This data must be located within 200 km of the coast and at a depth of less than 400 m. In this inventory, FerryBox platforms have all been considered as coastal platforms. The following platforms were extracted from the products: BO (Bottles), CT (CTD), DB (Drifting Buoys), FB (Ferry Box), GL (Gliders), HF (High Frequency Radar), MO (Mooring), PF (Profiling Float), TG (Tide Gauge) and XB (XBT). Once the metadata had been extracted from the files, duplicates were removed (files with the same names). Duplicate platforms of type _TS_ and _WS_ were merged (date and parameters). Latest‘ files have been merged with ’History" files. Missing metadata have been replaced in the Excel file by ‘Missing Data’. Some old dates were also revised by hand because they had been badly extracted, as well as some institution names that included special characters. Platforms located on estuaries/rivers/lakes/ponds have also been removed by hand. This inventory identified a total of 10,479 coastal platforms.
-
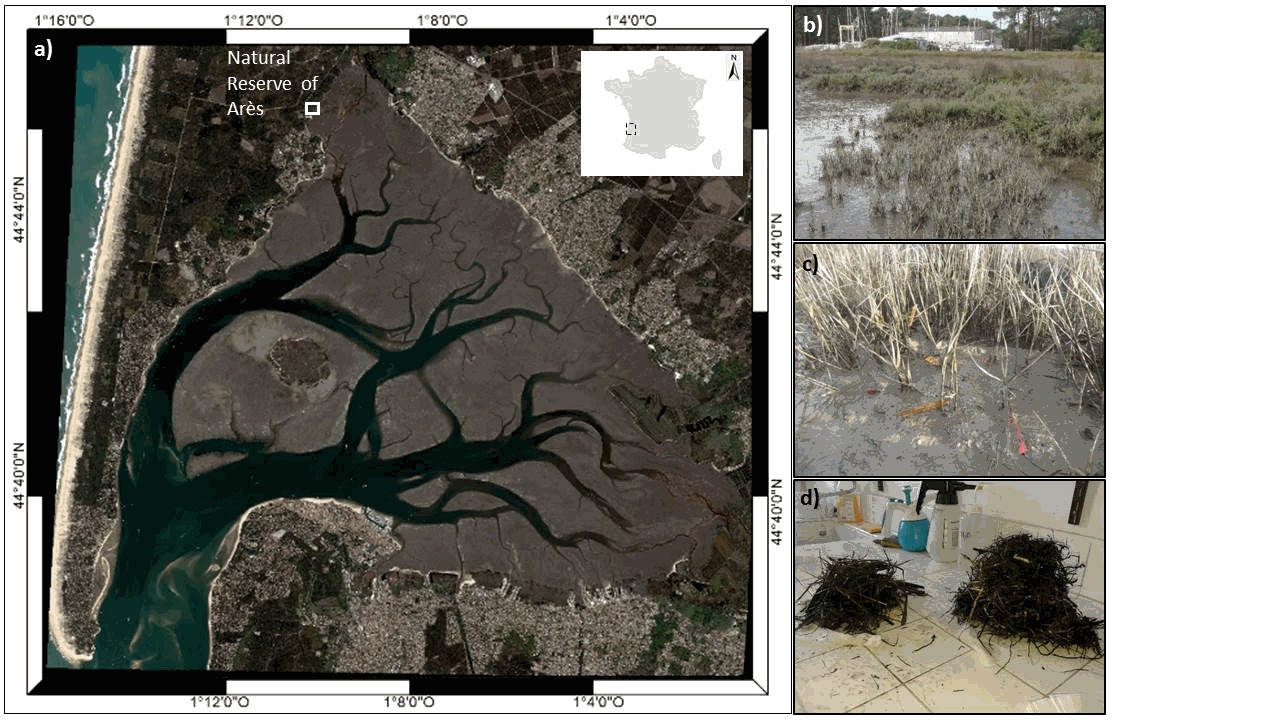
Questions: Invasiveness depends in part on the ability of exotic species to either exclude native dominants or to fill an empty niche. Comparisons of niches and effects of closely related native and invasive species enable the investigation of this topic. Does Spartina anglica invade European salt marshes through competitive exclusion of the native Spartina maritima or due to the occurrence of an empty ecological niche in highly anoxic conditions? Location: The Arcachon Bay (France). Methods: At three intertidal levels, we quantified competitive response and effect abilities of the two species through a cross-transplantation removal experiment. We also compared at three intertidal levels the biomass, root/shoot ratio, productivity and environmental conditions (elevation, salinity, potential redox and soil moisture) of salt marsh communities dominated by the exotic Spartina anglica or the native Spartina maritima. Results: Both established species showed similar biotic resistance to the invasion of the other species, but the exotic showed important intraspecific facilitation for growth. Species had similar niches and total biomass along a gradient of anoxic conditions, but the exotic had a much higher root/shoot ratio and productivity than the native. Owing to its rhizome density, the exotic showed a high ability to increase sediment oxygenation, likely to explain its important intraspecific facilitation. Conclusions: Our results showed that the invasion success of S. anglica cannot be explained by the competitive exclusion of the native or by its ability to fill an empty niche along a gradient of anoxia. Its behaviour as a self-facilitator invasive engineer is very likely to explain its rapid spread in the Bay and biotic resistance to the colonization of other congeneric species when established in dense patches. Additionally, we suggest that physical disturbance in the marsh communities dominated by the native S. maritima may disrupt its biotic resistance against the invasion of S. anglica.
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA