CSV
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
Resolution
-
The dataset includes age- and length-based catch per unit effort data for commercial fish species collected by the French trawl survey EVHOE.
-

This is the FAO Fishery and Aquaculture Reference Data repository: Codes and reference data for fishing gear, species, currencies, commodities, countries and others.
-
Data collected by the Spindrift 2 Sails of Change vessel during its attempt at the round-the-world sailing record, the Jules Verne Trophy. More information at https://spindrift-racing.com/fr/.
-
The general objective of the PEACETIME cruise is to study the fundamental processes and their interactions at the ocean-atmosphere interface, occurring after atmospheric deposition (especially Saharan dust) in the Mediterranean Sea, and how these processes impact the functioning of the pelagic ecosystem. During the proposed 33 days cruise in the western and central Mediterranean Sea in May 2017, we will study the impact of atmospheric deposition on the cycles of chemical elements, on marine biogeochemical processes and fluxes, on marine aerosols emission and how ongoing changes will impact the functioning of Mediterranean Sea communities in the future. The cruise is designed to explore a variety of oligotrophic regimes. Combining in situ observations both in the atmosphere and the ocean, and in situ and minicosm-based on-board process studies, the 40 embarking scientists from atmosphere and ocean sciences will characterize the chemical, biological and physical/optical properties of both the atmosphere and the sea-surface microlayer, mixed layer and deeper waters. The PEACETIME strategy (season and cruise track) associated to a combination of dust transport forecasting tools and near real-time satellite remote sensing is designed to maximize the probability to catch a Saharan dust deposition event in a stratified water column in order to follow the associated processes in-situ. This coordinated multidisciplinary effort will allow us to fill the current weaknesses/lacks in our knowledge of atmospheric deposition impact in the ocean and feedbacks to the atmosphere in such oligotrophic systems. As a key joint-project between MERMEX and CHARMEX : The PEACETIME project comes in the scope of the regional multidisciplinaryprogramme MISTRALS (Mediterranean Integrated STudies at Regional And Local Scales ), which aims at predicting the evolution of this region following strong expected changes in climate and human pressures. In this framework, the PEACETIME project constitutes a key joint project between the ChArMEx (the Chemistry-Aerosol Mediterranean Experiment) and MERMEx (Marine Ecosystems Response in the Mediterranean Experiment) initiatives, enabling to gather communities of atmospheric chemists and marine biogeochemists around the common question of assessing the impact of atmospheric deposition on the marine biogeochemical processes and air-sea exchanges.
-

-
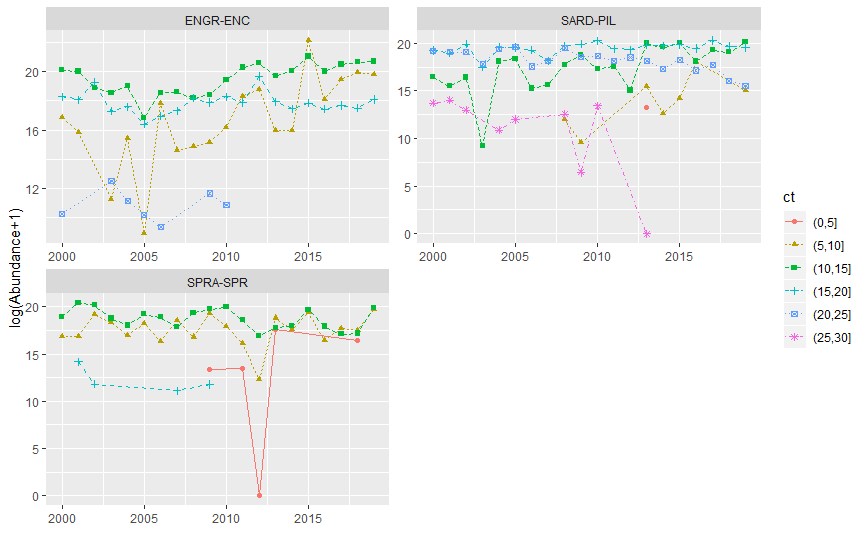
The Pélagiques Gascogne (PELGAS, Doray et al., 2000) integrated survey aims at assessing the biomass of small pelagic fish and monitoring and studying the dynamics and diversity of the Bay of Biscay pelagic ecosystem in springtime. PELGAS has been conducted within the EU Common Fisheries Policy Data Collection Framework and Ifremer’s Fisheries Information System. Details on survey protocols and data processing methodologies can be found in Doray et al., (2018a, 2021). This dataset comprises the mean length-at-age (cm) and weight-at-age (g) estimated annualy since 2000 for anchovy and sardine, based on PELGAS survey data. Both indices were weighted by fish abundance per length class, and are provided with an estimation error (coefficient of variation in %). Indices were produced following a standard methodology implemented in the EchoR R package (Doray et al. 2013). Those estimates have been validated by the ICES WGACEGG group and provided to the ICES WGHANSA group for stock assessment purposes. Data have been used in Doray et al., 2018b.
-
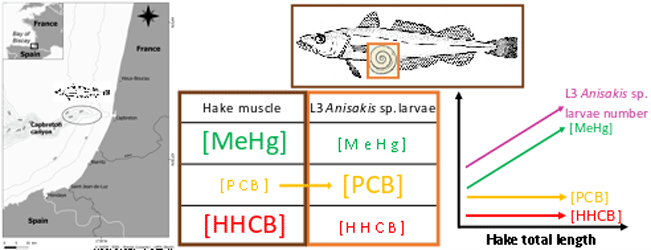
This dataset gathers isotopic ratios (carbon and nitrogen) and concentrations of both priority (mercury species and polychlorinated biphenyls congeners) and emerging (musks and sunscreens) micropollutants measured in a host-parasite couple (hake Merluccius merluccius muscle and in its parasite Anisakis sp) from the south of Bay of Biscay in 2018. In addition, the hake infection degree measured as the number of Anisakis sp. larvae was added for each hake collected.
-

Long-term time series of coliform bacteria concentration (fecal coliform or Escherichia coli) in shellfish in four submarine areas (North Sea/Channel, Britany, Atlantic, Mediterranean).
-
Global Fishing Watch is working across the globe to provide governments and authorities with actionable reports and capacity building to help strengthen fisheries monitoring and compliance. Our global team of experts produce analyses to inform monitoring, control and surveillance of fisheries in five key areas: - Illegal, unreported and unregulated fishing - Transshipment - Port controls - Marine protected areas - Operation support Collaboration and information sharing are integral to achieving well-managed fisheries. By working with stakeholders and making analyses available to national, regional and intergovernmental partners, Global Fishing Watch is enabling fisheries agencies to make more informed and cost-efficient decisions. Topics: - Commercial fishing, Global Fishing Watch is harnessing innovative technology to turn transparent data into actionable information and drive tangible change in the way that fisheries are governed. - Transshipment, Through publicly sharing map visualisations and creating data and analysis tools, we seek to inform management and policy efforts and provide a more complete picture of transshipment at sea. - Marine protected areas, Global Fishing Watch is harnessing the data and technology revolution to support the effective design, management and monitoring of marine protected areas.
-

The Commission for the Conservation Southern Bluefin Tuna collects a variety of data types from its Members and Cooperating Non-Members, including total catch, catch and effort data, and catch at size data. Catch, size and trade information is also collected through the Commission's Catch Documentation Scheme, Japanese import statistics, and other monitoring programs. Annual catches provided on this page are reported on a calendar year basis. CCSBT Members use quota years (not calendar years) for managing catching limits, but quota years differ between Members, so calendar years are used to provide catches on a common timescale. Relevant subsets and summaries of these data are provided below. All figures are subject to change as improved data or estimates become available. In particular, reviews of SBT data in 2006 indicated that southern bluefin tuna catches may have been substantially under-reported over the previous 10-20 years and the data presented here do not include estimates for this unreported catch. Also, data for the last reported year of catch (2020) are preliminary and are subject to revision. Any latitudes and longitudes presented in these summaries represent the north western corner of the relevant grid, which is a 5*5 grid unless otherwise specified. Other information on Members and Cooperating Non-Members fishing activities appears in the reports of the Extended Scientific Committee, Compliance Committee and Extended Commission.
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA