/Metropolitan France
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Representation types
Update frequencies
Scale
-
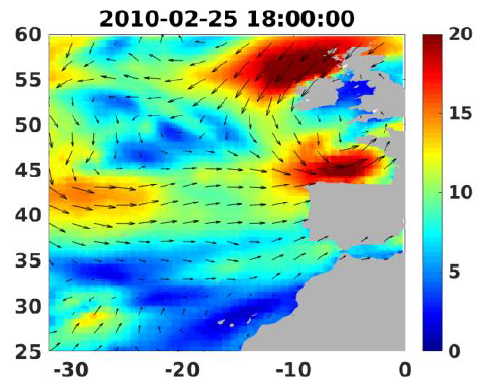
Wind analyses, estimated over the North Atlantic Ocean with a focus on some specific regions, are one the main ARCWIND (http://www.arcwind.eu/) project deliverables. They are estimated from various remotely sensed wind observations in combination with numerical model (WRF), with regular space (0.25deg in latitude and longitude), and time (00h:00, 06h:00, 12h:00, 18h:00 UTC), and based the method described in (Bentamy A., A. Mouche, A. Grouazel, A. Moujane, M. A. Ahmed. (2019): Using sentinel-1A SAR wind retrievals for enhancing scatterometer and radiometer regional wind analyses . International Journal Of Remote Sensing , 40(3), 1120-1147 . https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2018.1524174).
-
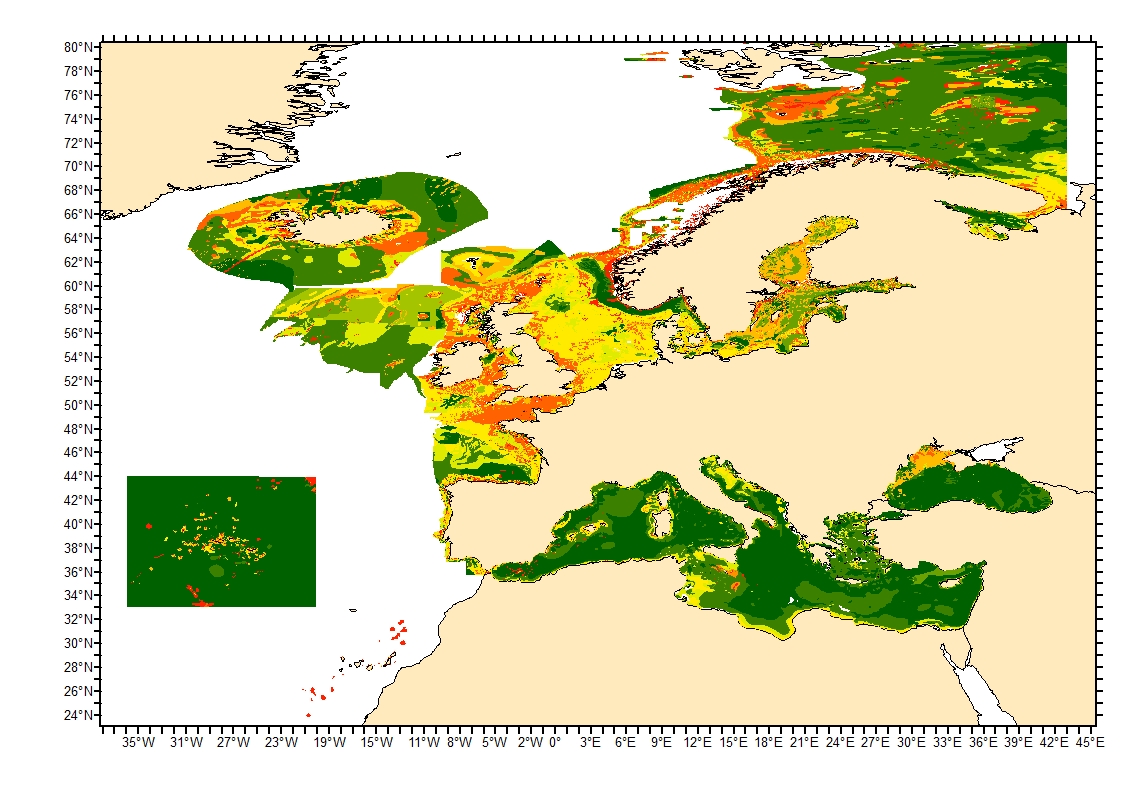
Sediment average grain size in the European North-East Atlantic and Mediterranean waters was generated from Euseamap 2023 sediment categories. This rough granulometry estimate may be used for habitat models at meso- and large scale.
-
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA