environment
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
Resolution
-

In European sea bass like in other animals, the tongue plays a fundamental role in the mechanics of food ingestion. It is composed from the surface in depth of mucosa, submucosa, musculature and fibro cartilaginous skeleton. The tunica mucosa exhibits a stratified epithelium interrupted by numerous teeth differently distributed that erupt more or less completely from the layers below. The European sea bass tongue is composed of canine-like teeth, surrounded by taste buds and numerous fungiform and conical papillae. The tongue beeing directly in contact with external environment, the success of the adaptation of fishes to different environments in the context of global change, depends oamong other on the modifications occurring on the tongue structures. The present study investigates the potential effect of ocean acidification on the lingual transcriptome.
-

La Région Nouvelle-Aquitaine accompagne les acteurs publics et privés dans leur transition énergétique et écologique à l'horizon 2030. Avec ses 11 ambitions, la feuille de route Néo Terra guide l'action régionale et celle de ses partenaires pour la mise en œuvre d'actions concrètes. Un engagement collectif pour la Nouvelle-Aquitaine de demain.
-

The dataset presents the potential combined effects of human activities and pressures on marine species and habitats estimated using the method for assessment of cumulative effects, for the entire suite of pressures and a selected set of marine species groups and habitats by an index (Halpern et al. 2008). The spatial assessment of combined effects of multiple pressures informs of the risks of human activities on the marine ecosystem health. The methodology builds on the spatial layers of pressures and ecosystem components and on an estimate of ecosystem sensitivity through an expert questionnaire. The raster dataset consists of a division of the Europe's seas in 10km and 100 km grid cells, which values represents the combined effects index values for pressures caused by human activities. The relative values indicate areas where the pressures potentially affect the marine ecosystem. This dataset underpins the findings and cartographic representations published in the report "Marine Messages" (EEA, 2020).
-

The ABYSS project aims at describing deep-sea benthic biodiversity spanning several branches of the tree of life with eDNA metabarcoding tools. To accommodate both micro- and macro biologists, we designed a bioinformatic pipeline based on Illumina read correction with Dada2 allowing analysing metabarcodes from prokaryotic and eukaryotic life compartments.
-

This dataset presents the resulting assessment grid (based on the EEA reference grid) with the classification of chemical status of the transitional, coastal and marine waters in the context of the Water Framework Directive (WFD) and the Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD). This classification has been performed using the CHASE+ tool, with classifications of the matrices ‘water’, ‘sediment’ and ‘biota’ and indicators of ‘biological effects’, as well as an integrated classification of chemical status, combining results of all matrices. The chemical status is evaluated in five classes, where NPAhigh and NPAgood are recognised as ‘non-problem areas’ and PAmoderate, PApoor and PAbad are recognised as ‘problem areas’. The overall area of interest used is based on the marine regions and subregions under the Marine Strategy Framework Directive. Additionally, Norwegian (Barent Sea and Norwegian Sea) and Icelandic waters (’Iceland Sea’) have been added (see Surrounding seas of Europe). Note that within the North East Atlantic region only the subregions within EEZ boundaries (~200 nm) have been included. This dataset underpins the findings and cartographic representations published in the report "Contaminants in Europe's Seas" (EEA, 2019): https://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/contaminants-in-europes-seas.
-
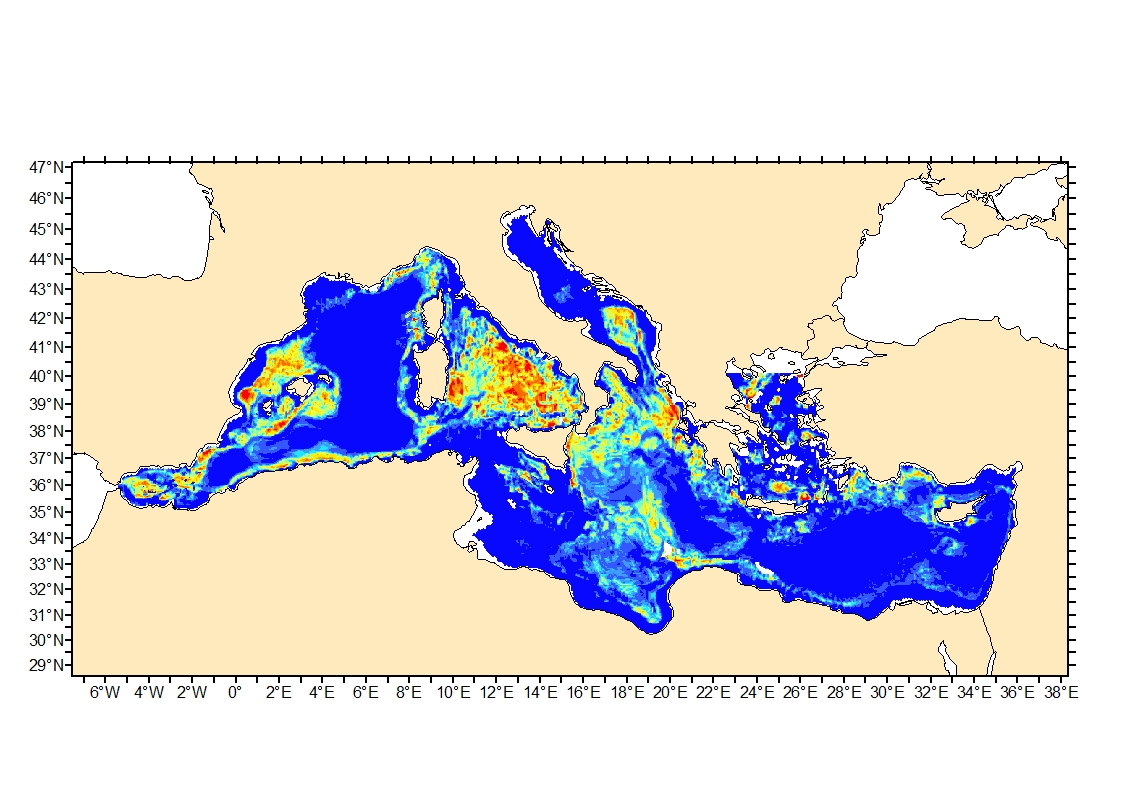
Process-driven seafloor habitat sensitivity (PDS) has been defined from the method developed by Kostylev and Hannah (2007), which takes into account physical disturbances and food availability as structuring factors for benthic communities. It is a conceptual model, relating species’ life history traits to environmental properties. Physical environment maps have been converted into a map of benthic habitat types, each supporting species communities with specific sensitivity to human pressures. It is based on two axes of selected environmental forces. The "Disturbance" (Dist) axis reflects the magnitude of change (destruction) of habitats (i.e. the stability through time of habitats), only due to natural processes influencing the seabed and which are responsible for the selection of life history traits. The "Scope for Growth" (SfG) axis takes into account environmental stresses inducing a physiological cost to organisms and limiting their growth and reproduction potential. This axis estimates the remaining energy available for growth and reproduction of a species (the energy spent on adapting itself to the environment being already taken into account). It can be related to the metabolic theory of the ecology. The process-driven sensitivity (PDS) can be seen as a risk map that combines the two previous axes and reflects the main ecological characteristics of the benthic habitats regarding natural processes. Areas with low disturbance are areas with a naturally low reworking of the sediment, allowing the establishment of a rich sessile epifauna community, with K-strategy species. Areas with low SfG means that the environmental factors, even though there are not limiting, are in lower values, i.e. that it imposes a cost for species to live. In areas combining low disturbance and low SfG, big suspension-feeder species with long life and slow growth can often be found: these species are more vulnerable in case of added disturbance.
-

UWWTD Discharge Points, Jan. 2022 is one of the datasets produced within the frame of the reporting under 11th UWWTD Art.15 reporting period (UWWTD data call 2019). The Urban Waste Water Treatment Directive (UWWTD) (91/271/EEC) obliges Member States to report data on the implementation of the Directive upon request from the European Commission bi-annually. Reported data include receiving areas as designated under UWWTD, agglomerations, urban waste water treatment plants serving the agglomerations and points of discharges. Dataset UWWTD_DischargePoints contains information on individual points of discharge from urban waste water treatment plants or collecting systems, including their coordinates of discharge, link to specific treatment plant, type of receiving area into which the effluent / wastewater is discharged, related waterbody (or river basin), information on the discharge on land and potential reuse of the treated waste water. This dataset includes the reported discharge points which are displayed on the UWWTD maps (https://www.eea.europa.eu/themes/water/european-waters/water-use-and-environmental-pressures/uwwtd/interactive-maps/urban-waste-water-treatment-maps-3). The active discharge points with correct coordinates in the reported data were selected from the source European UWWTD tabular dataset, which is available on the download link https://www.eea.europa.eu/data-and-maps/data/waterbase-uwwtd-urban-waste-water-treatment-directive-7. The definition of the UWWTD Discharge Points dataset attributes (fields) is available on the link https://dd.eionet.europa.eu/datasets/latest/UWWTDArt15/tables/DischargePoints The full (internal) dataset including inactive discharge points is available under "Urban Waste Water Treatment Directive, Discharge points reported under UWWTD data call 2019 - INTERNAL VERSION, Jan. 2022". In comparison to the previous version (Nov. 2020), late redeliveries and corrections provided by several countries during 2021 are included in current revision. Next, the dataset is provided in GeoPackage and ESRI File geodatabase formats instead of shapefile used up to now, to avoid truncation of attribute names.
-
Massif forestier des Landes de Gascogne : Guide pour la prise en compte du risque incendie de forêt.

Ce guide a pour vocation d'informer sur les caractéristiques du risque incendie de forêt propres au massif des Landes de Gascogne, de définir les modalités de prise en compte du risque dans les documents d'urbanisme et de regrouper l'ensemble des réglementations et recommandations ayant trait à la protection contre les incendies. Il a été élaboré par l'Etat en partenariat avec l'Association des Maires des Landes et les organismes concernés par cette problématique.
-

Here, our study aimed to first assess the influence of plastic on the bacterial community belonging to water, plastic and the microbiome of the giant clam and on the organism's physiology of this putative sentinel species. Our second objective was to identify bacteria whose abundance varies significantly with plastic concentration. Overall, this study will fill the gap towards a better understanding of the impact of plastic pollution on bacterial community assemblages in both inert and living environments.
-
PPRIF
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA