Ifremer, France
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
-
The data-set is composed of three tables, Environmental variables, Phytoplankton ( in log+1 abundance) and the coordinates of the station used in the study. They are the processed data.
-
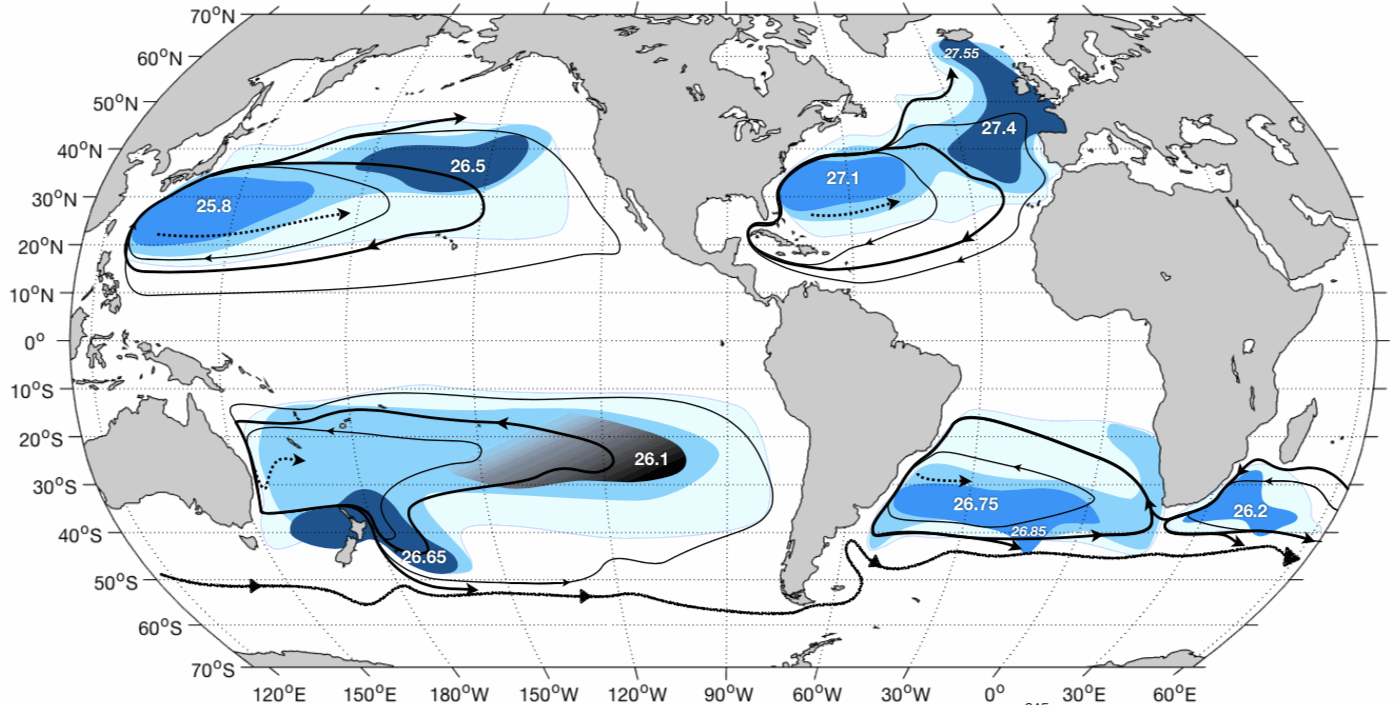
This dataset contains OAC-P results from application to Argo data in the World Ocean : - the 2000-2015 climatology of OAC-P results mapped onto a 0.5x0.5 grid with mapping error estimates; - the 2000-2015 probability density function of the permanent pycnocline potential density referenced to the sea surface vs Brunt-Väisälä frequency squared.OAC-P is an "Objective Algorithm for the Characterization of the permanent Pycnocline" developed to characterize subtropical gyre stratification features with both observed and modeled potential density profiles. OAC-P estimates the following properties: - for the permanent pycnocline: depth, upper and lower thicknesses, Brunt-Väisälä frequency squared, potential density, temperature and salinity; - for the surface mode water overlying the permanent pycnocline: depth, Brunt-Väisälä frequency squared, potential density, temperature and salinity. Argo data were download from Coriolis Argo GDAC on February, 8th 2016. Only Argo data with QC=1, 2, 5 or 8 were used.
-
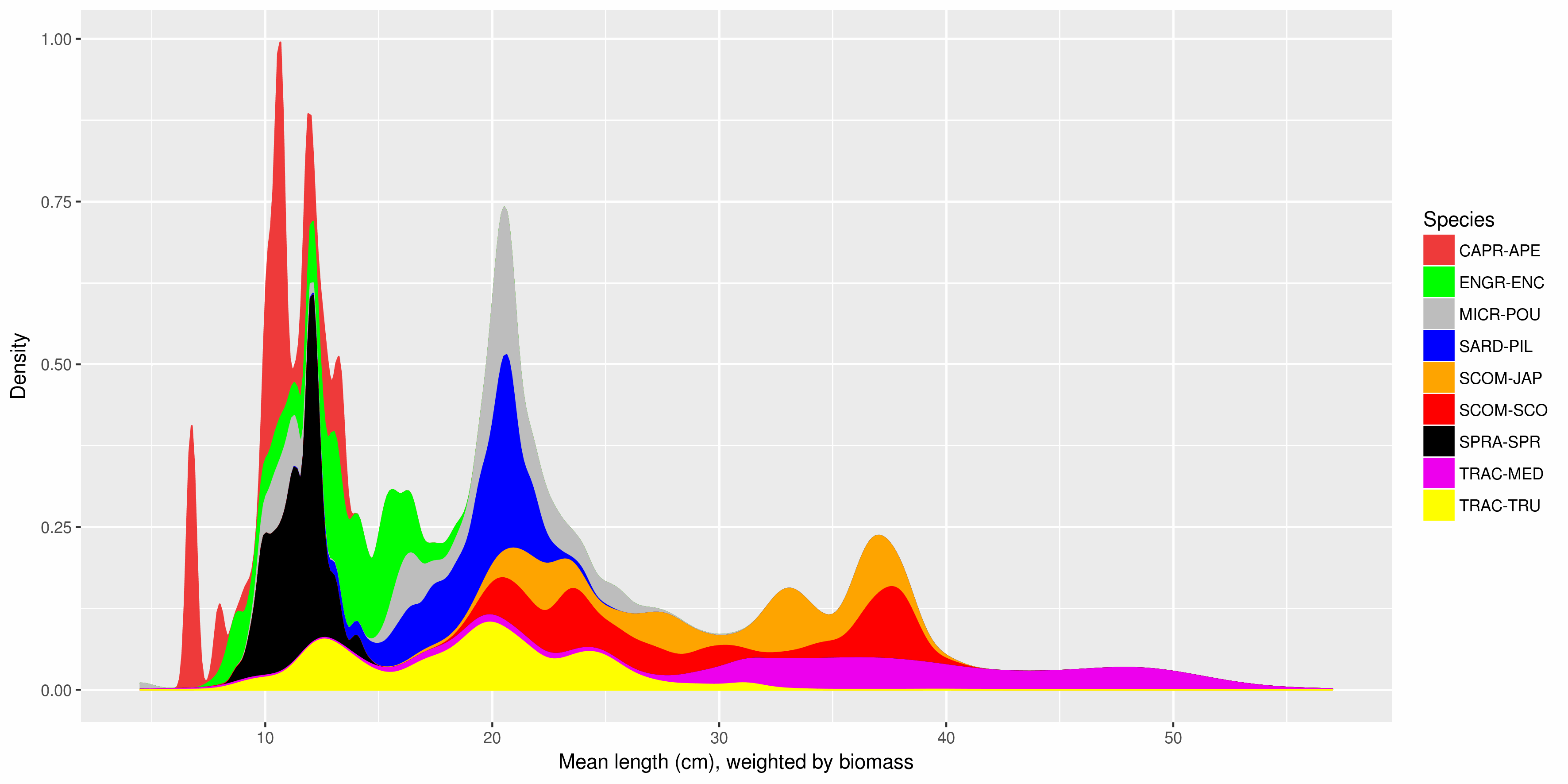
The Pélagiques Gascogne (PELGAS, Doray et al., 2000) integrated survey aims at assessing the biomass of small pelagic fish and monitoring and studying the dynamics and diversity of the Bay of Biscay pelagic ecosystem in springtime. PELGAS has been conducted within the EU Common Fisheries Policy Data Collection Framework and Ifremer’s Fisheries Information System. Details on survey protocols and data processing methodologies can be found in Doray et al., (2014, 2017a). This dataset comprises the biomass (in metric tons) and abundance (in thousands of individuals) at length (in cm) of small pelagic fish estimated during the PELGAS survey in the Bay of Biscay in springtime. Total biomass and abundance per species on one hand, and frequencies-at-lenght per species and acoustic Elementary Distance Sampling Units (EDSUs) on the other hand, have been derived from fisheries acoustic and midwater trawl data based on the methodology described in Doray et al. (2010). Frequencies-at-lenght per species and EDSUs have been averaged over the survey area for each species and multiplied by the total biomass and abundance per species, to derive global biomass and abundance at length estimates. This dataset was used in Doray et al., 2017b.
-
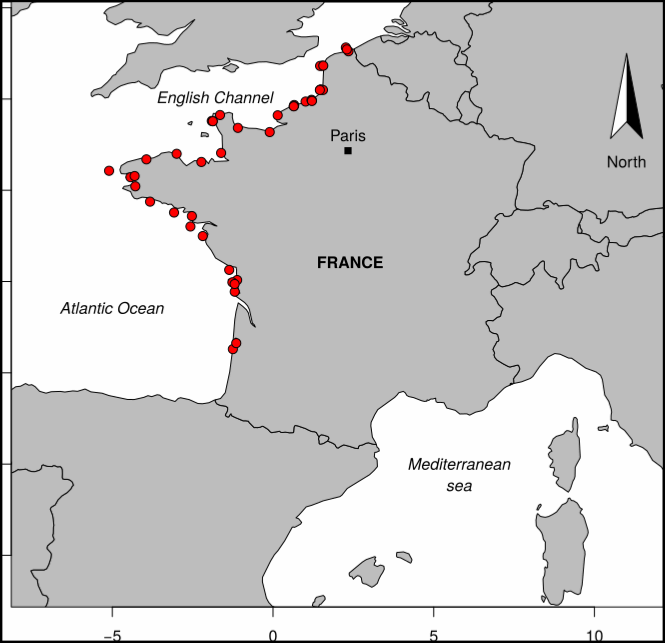
Data were collected by the Laboratoire de Ressources Halieutiques d'Aquitaine (Ifremer). The observations were carried out between April 1992 and July 2006. Observations and measures were made on board commercial vessels, practicing on Adour River generally in springtime and in summer. Sampling of catches took place on the river between March and July; The researchers took scales, a blood sample, took measurements of length and weight on the fish caught by the fishermen during the observed fishing trips. Sampling was of sampling-by-opportunity type. The driftnet is an emblematic and very old métier in this area, targeting different species as atlantic salmon (Salmo salar), sea trout (Salmo trutta), sea Lamprey (Pétromyzon marinus) and also allis shad (Alosa alosa). This activity is framed by particular regulation as quota of fishing days and licenses. Between 15 and 20 costal boats practice this métier during the year and the fleet characteristics are homogenous. The boats put the net in the water (around 100 m long) and let it drift with the surface current (downstream) while the tide is rising; the fish swimming upstream the river are then trapped in the water column. Different meshes can be used.
-

Particularly suited to the purpose of measuring the sensitivity of benthic communities to trawling, a trawl disturbance indicator (de Juan and Demestre, 2012, de Juan et al. 2009) was proposed based on benthic species biological traits to evaluate the sensibility of mega- and epifaunal community to fishing pressure known to have a physical impact on the seafloor (such as dredging and bottom trawling). The selected biological traits were chosen as they determine vulnerability to trawling: mobility, fragility, position on substrata, average size and feeding mode that can easily be related to the fragility, recoverability and vulnerability ecological concepts. The five categories retained are functional traits that were selected based on the knowledge of the response of benthic taxa to trawling disturbance (de Juan et al., 2009). They reflect respectively the possibility to avoid direct gear impact, to benefit from trawling for feeding, to escape gear, to get caught by the net and to resist trawling/dredging action, each of these characteristics being either advantageous or sensitive to trawling. To expand this approach to that proposed by Certain et al. (2015), the protection status of certain species was also indicated. To enable quantitative analysis, a score was assigned to each category: from low sensitivity (0) to high sensitivity (3). Biological traits of species have been defined, from the BIOTIC database (MARLIN, 2014) and from information given by Garcia (2010), Le Pape et al. (2007) and Brind’Amour et al. (2009). For missing traits, additional information from literature has been considered. The protection status of each taxa was also scored: Atlantic species listed in OSPAR List of Threatened and/or Declining Species and Habitats (https://www.ospar.org/work-areas/bdc/species-habitats/list-of-threatened-declining-species-habitats) and Mediterranean species listed in Vulnerable Marine Ecosystems (FAO, 2018 and Oceana, 2017) were scored 3 and other species were scored 1. The scores of 1085 taxa commonly found in bottom trawl by-catch in the southern North Sea, English Channel and north-western Mediterranean were described.
-

The Pélagiques Gascogne (PELGAS, Doray et al., 2000) integrated survey aims at assessing the biomass of small pelagic fish and monitoring and studying the dynamics and diversity of the Bay of Biscay pelagic ecosystem in springtime. PELGAS has been conducted within the EU Common Fisheries Policy Data Collection Framework and Ifremer’s Fisheries Information System. Details on survey protocols and data processing methodologies can be found in Doray et al., (2014, 2018). This dataset comprises the abundance (no. of individuals), biomass (metric tons), mean length (cm), mean weight (g) of marine organisms collected by midwater trawling to identify fish echoes detected during PELGAS surveys (2000-2018). All parameters have been raised to the trawl haul level. Trawl haul metadata and species reference list are also provided.
-
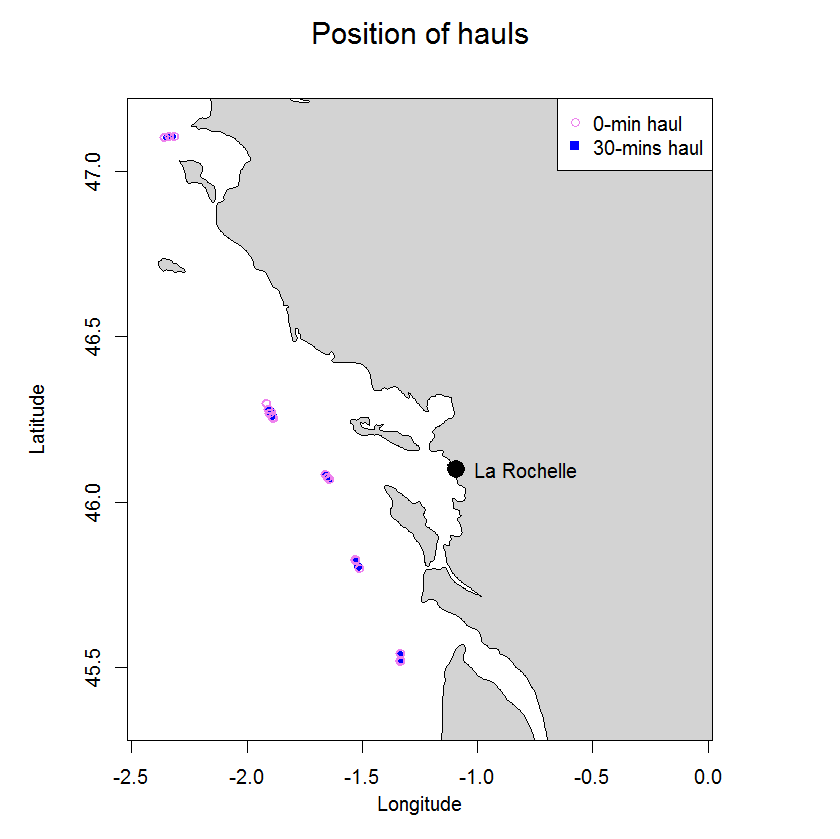
In 2003 two experiments were carried out in the Bay of Biscay to compare catch numbers obtained in standard research 30-min hauls with those from 0-min hauls to determine the so called end effect. The end effect in trawl catches is defined as the proportion of the fish catch taken during shooting and hauling of the net, a period excluded from what is nominally referred to as haul duration. In 0-hauls the trawl was hauled as soon as the trawl geometry stabilized on the seabed. The trawl used was a beam trawl rigged as twin trawl. Overall 24 hauls were carried out, six 30-min and 18 0-min hauls. Average catch ratios (0-min/30-min hauls) ranged from 0.05 (s.d. 0.06) for sole to 0.34 (s.d. 0.64) for hake.
-
The Pélagiques Gascogne (PELGAS, Doray et al., 2000) integrated survey aims at assessing the biomass of small pelagic fish and monitoring and studying the dynamics and diversity of the Bay of Biscay pelagic ecosystem in springtime. PELGAS has been conducted within the EU Common Fisheries Policy Data Collection Framework and Ifremer’s Fisheries Information System. Details on survey protocols and data processing methodologies can be found in Doray et al., (2014, 2018a). This dataset comprises the biomass (in metric tons) and abundance (in thousands of individuals) of small pelagic fish estimated during the PELGAS survey in the Bay of Biscay in springtime. The dataset also includes the estimation coefficient of variation, derived based on the hydroacoustic methodology described in Doray et al. (2010), and the survey area. Those estimates have been validated by the ICES WGACEGG group and provided to the ICES WGHANSA group for stock assessment purposes. Data have been used in Doray et al., 2018b.
-

Particularly suited to the purpose of measuring the sensitivity of benthic communities to trawling, a trawl disturbance indicator (de Juan and Demestre, 2012, de Juan et al. 2009) was proposed based on benthic species life history traits to evaluate the sensibility of mega- and epifaunal community to fishing pressure known to have a physical impact on the seafloor (such as dredging and bottom trawling). The selected biological traits were chosen as they determine vulnerability to trawling: mobility, fragility, position on substrata, average size and feeding mode that can easily be related to the fragility, recoverability and vulnerability ecological concepts. Life history traits of species have been defined from the BIOTIC database (MARLIN, 2014) and from information given by Le Pape et al. (2007), Brindamour et al. (2009) and Garcia (2010). For missing life history traits, additional information from literature has been considered. The five categories retained are life history functional traits that were selected based on the knowledge of the response of benthic taxa to trawling disturbance (de Juan and Demestre, 2012). They reflect respectively the possibility to avoid direct gear impact, to benefit from trawling for feeding, to escape gear, to get caught by the net and to resist trawling/dredging action, each of these characteristics being either advantageous or sensitive to trawling. Then, to allow quantitative analysis, a score was assigned to each category: from low vulnerability (0) to high vulnerability (3). The five categories scores were then summed for each taxon (the highly vulnerable taxon could reach the maximum score is 15) and this value may be considered as a species index of sensitivity to trawling disturbance. The scores of 812 taxa commonly found in bottom trawl by-catch in the southern North Sea, English Channel and north-western Mediterranean were described.
-
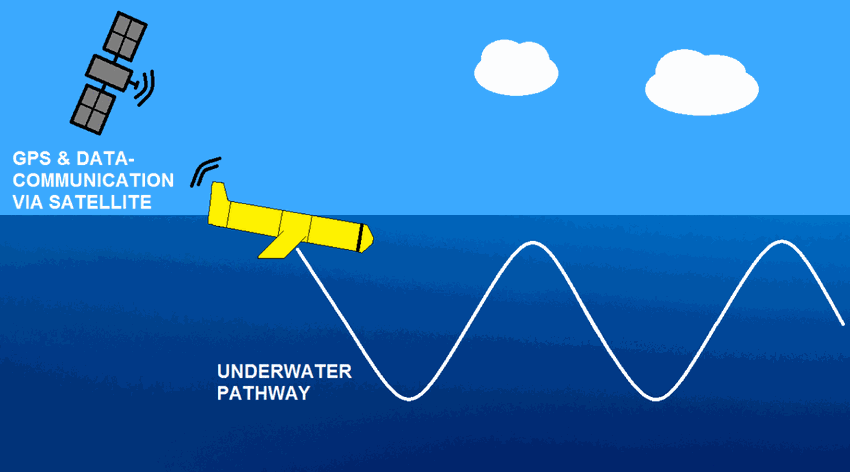
The observations of campe glider on imedia deployment (Mediterranean Sea - Western basin) are distributed in 4 files: - EGO NetCDF time-series (data, metadata, derived sea water current) - NetCDF profiles extracted from the above time-series - Raw data - JSON metadata used by the decoder The following parameters are provided : - Practical salinity - Sea temperature in-situ ITS-90 scale - Electrical conductivity - Sea water pressure, equals 0 at sea-level
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA