/Environmental Status/Habitats
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Resolution
-
The shapefile corresponds to areas where predicted bioregions were extrapolated for lack of benthic in-situ observations.
-
The raster corresponds to the predicted Mediterranean bioregions of megabenthic communities.
-
The rasters correspond to the prediction uncertainties associted with the production of Mediterranean bioregions of megabenthic communities
-
These rasters correspond to the environmental predictors used in the production of Mediterranean bioregions of megabenthic communities
-
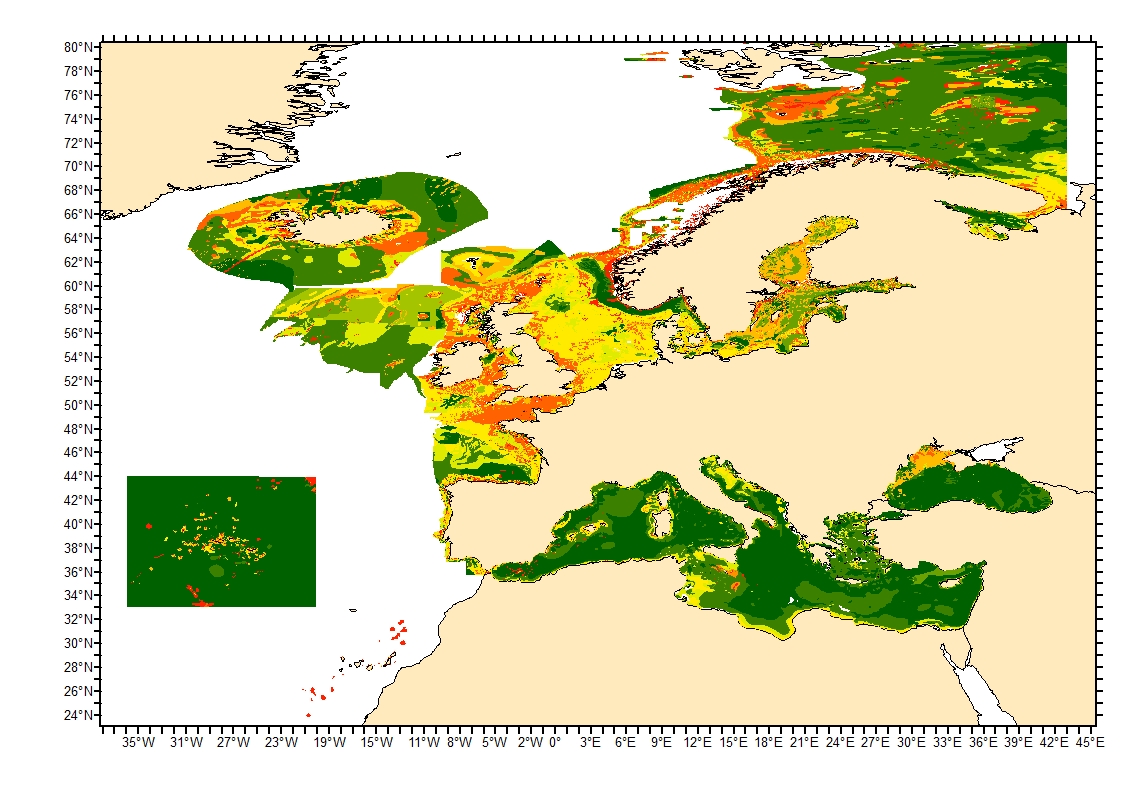
Sediment average grain size in the European North-East Atlantic and Mediterranean waters was generated from Euseamap 2023 sediment categories. This rough granulometry estimate may be used for habitat models at meso- and large scale.
-
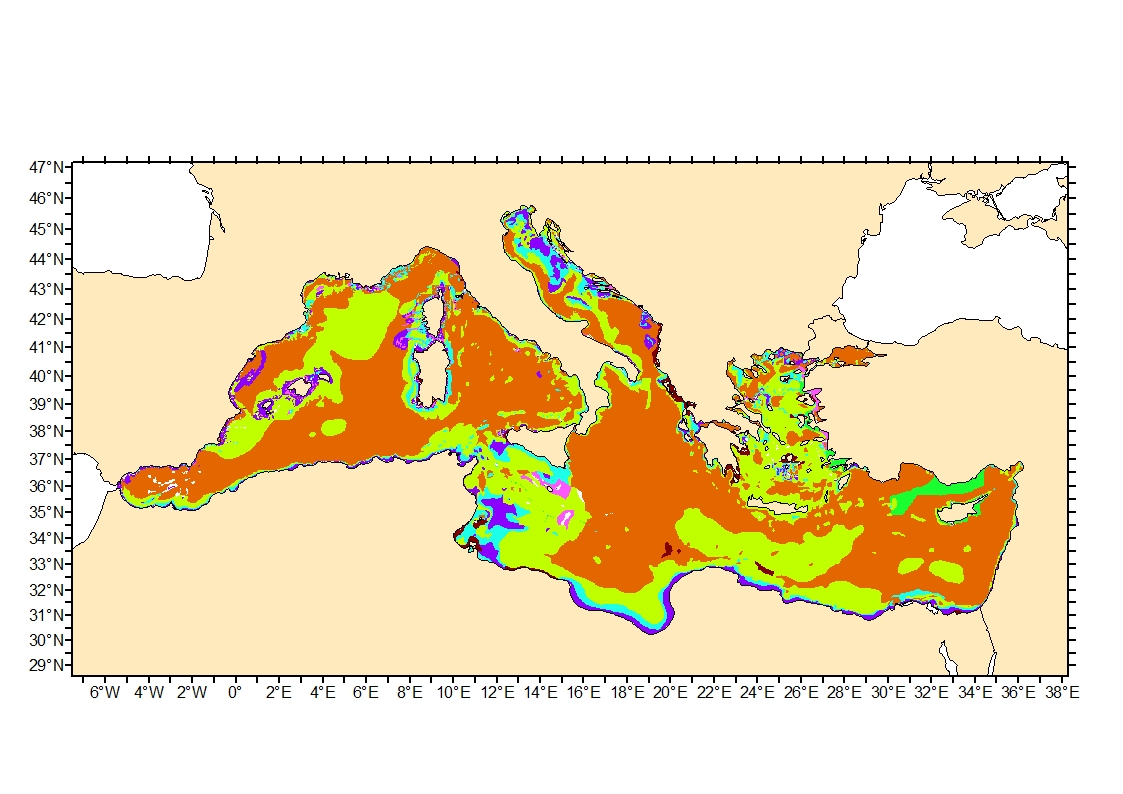
Sediment average grain size in the Mediterranean was generated from sediment categories. This rough granulometry estimate may be used for habitat models at meso- and large scale.
-
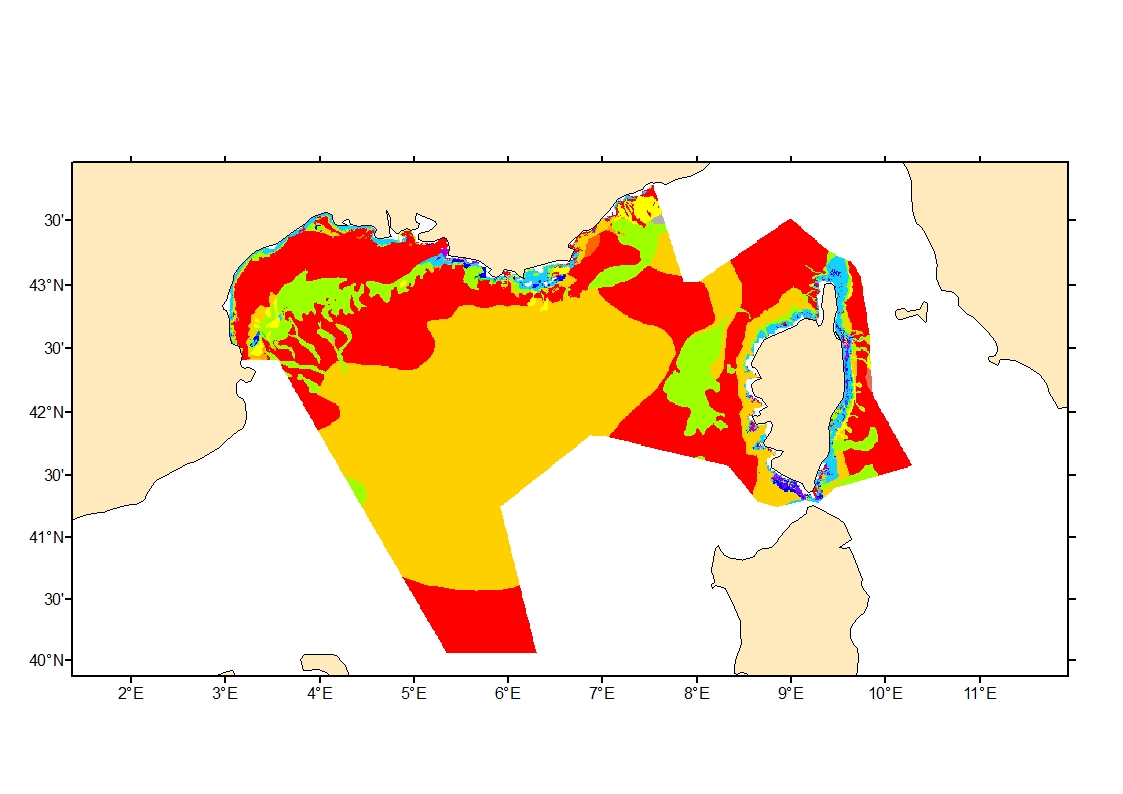
Sediment average grain size in French Mediterranean waters was generated from sediment categories. This rough granulometry estimate may be used for habitat models at meso- and large scale.
-
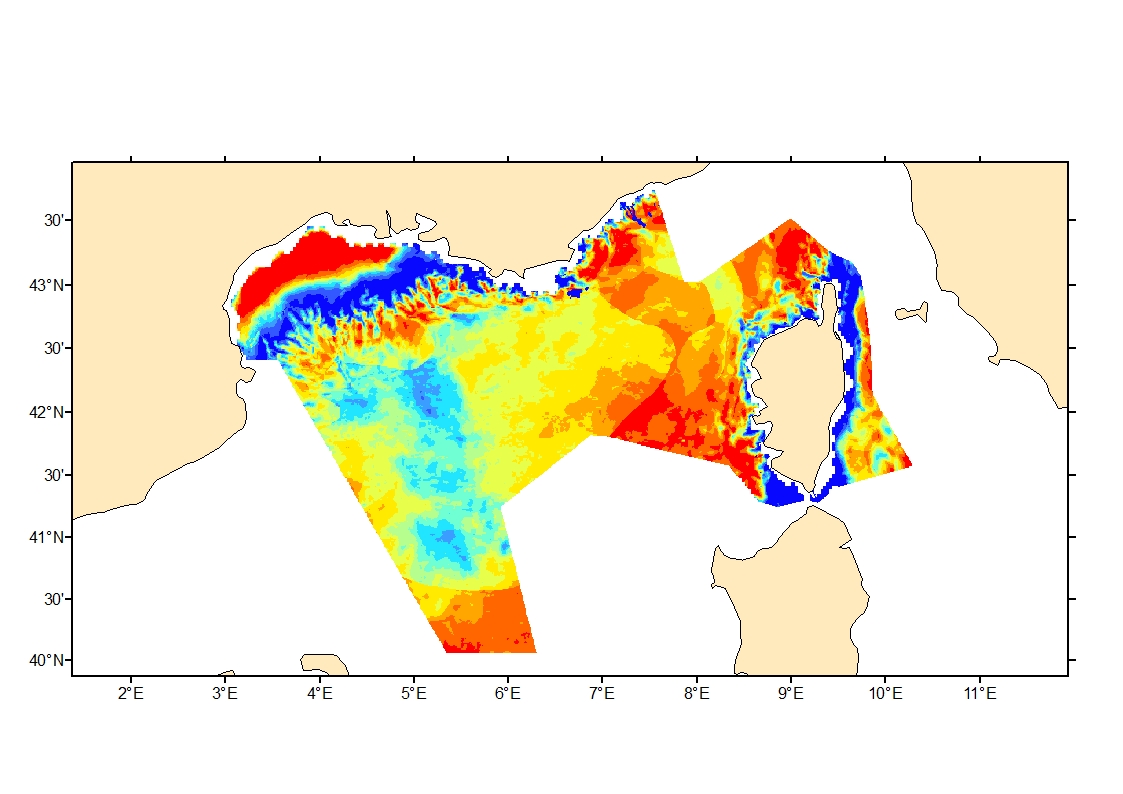
Process-driven seafloor habitat sensitivity (PDS) has been defined from the method developed by Kostylev and Hannah (2007), which takes into account physical disturbances and food availability as structuring factors for benthic communities. It is a conceptual model, relating species’ life history traits to environmental properties. Physical environment maps have been converted into a map of benthic habitat types, each supporting species communities with specific sensitivity to human pressures. It is based on two axes of selected environmental forces. The "Disturbance" (Dist) axis reflects the magnitude of change (destruction) of habitats (i.e. the stability through time of habitats), only due to natural processes influencing the seabed and which are responsible for the selection of life history traits. The "Scope for Growth" (SfG) axis takes into account environmental stresses inducing a physiological cost to organisms and limiting their growth and reproduction potential. This axis estimates the remaining energy available for growth and reproduction of a species (the energy spent on adapting itself to the environment being already taken into account). It can be related to the metabolic theory of the ecology. The process-driven sensitivity (PDS) can be seen as a risk map that combines the two previous axes and reflects the main ecological characteristics of the benthic habitats regarding natural processes. Areas with low disturbance are areas with a naturally low reworking of the sediment, allowing the establishment of a rich sessile epifauna community, with K-strategy species. Areas with low SfG means that the environmental factors, even though there are not limiting, are in lower values, i.e. that it imposes a cost for species to live. In areas combining low disturbance and low SfG, big suspension-feeder species with long life and slow growth can often be found: these species are more vulnerable in case of added disturbance.
-
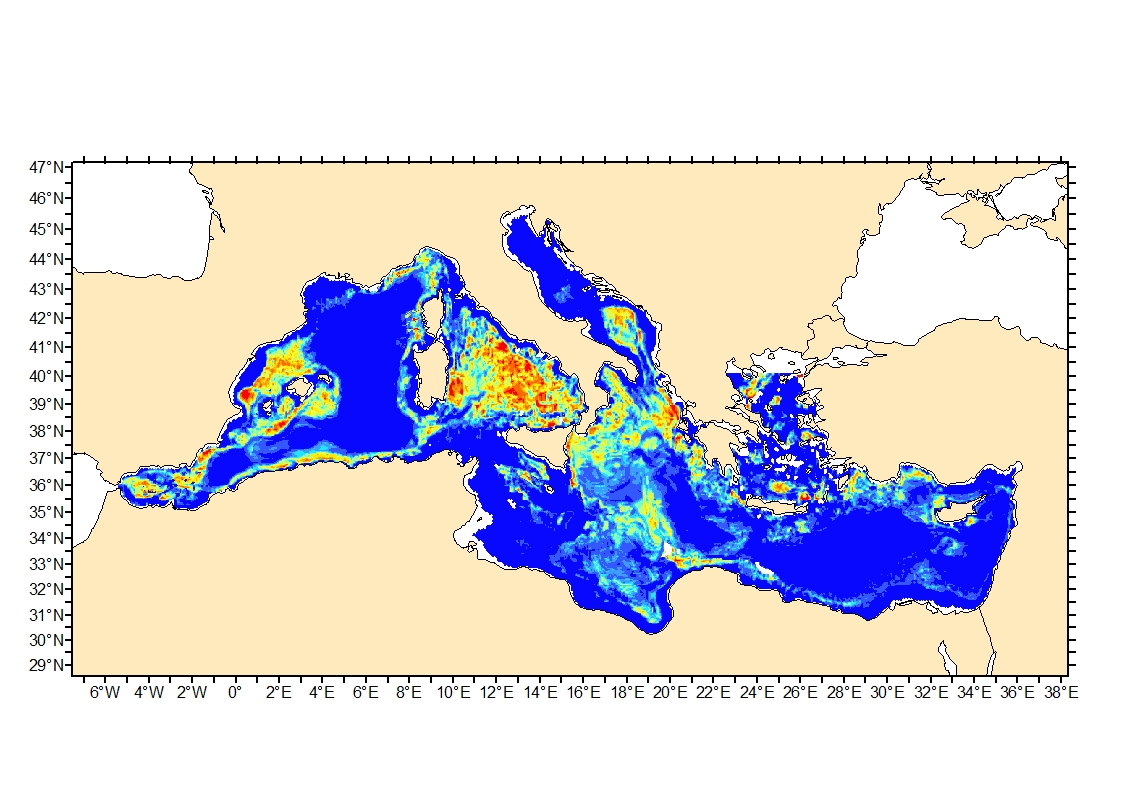
Process-driven seafloor habitat sensitivity (PDS) has been defined from the method developed by Kostylev and Hannah (2007), which takes into account physical disturbances and food availability as structuring factors for benthic communities. It is a conceptual model, relating species’ life history traits to environmental properties. Physical environment maps have been converted into a map of benthic habitat types, each supporting species communities with specific sensitivity to human pressures. It is based on two axes of selected environmental forces. The "Disturbance" (Dist) axis reflects the magnitude of change (destruction) of habitats (i.e. the stability through time of habitats), only due to natural processes influencing the seabed and which are responsible for the selection of life history traits. The "Scope for Growth" (SfG) axis takes into account environmental stresses inducing a physiological cost to organisms and limiting their growth and reproduction potential. This axis estimates the remaining energy available for growth and reproduction of a species (the energy spent on adapting itself to the environment being already taken into account). It can be related to the metabolic theory of the ecology. The process-driven sensitivity (PDS) can be seen as a risk map that combines the two previous axes and reflects the main ecological characteristics of the benthic habitats regarding natural processes. Areas with low disturbance are areas with a naturally low reworking of the sediment, allowing the establishment of a rich sessile epifauna community, with K-strategy species. Areas with low SfG means that the environmental factors, even though there are not limiting, are in lower values, i.e. that it imposes a cost for species to live. In areas combining low disturbance and low SfG, big suspension-feeder species with long life and slow growth can often be found: these species are more vulnerable in case of added disturbance.
-
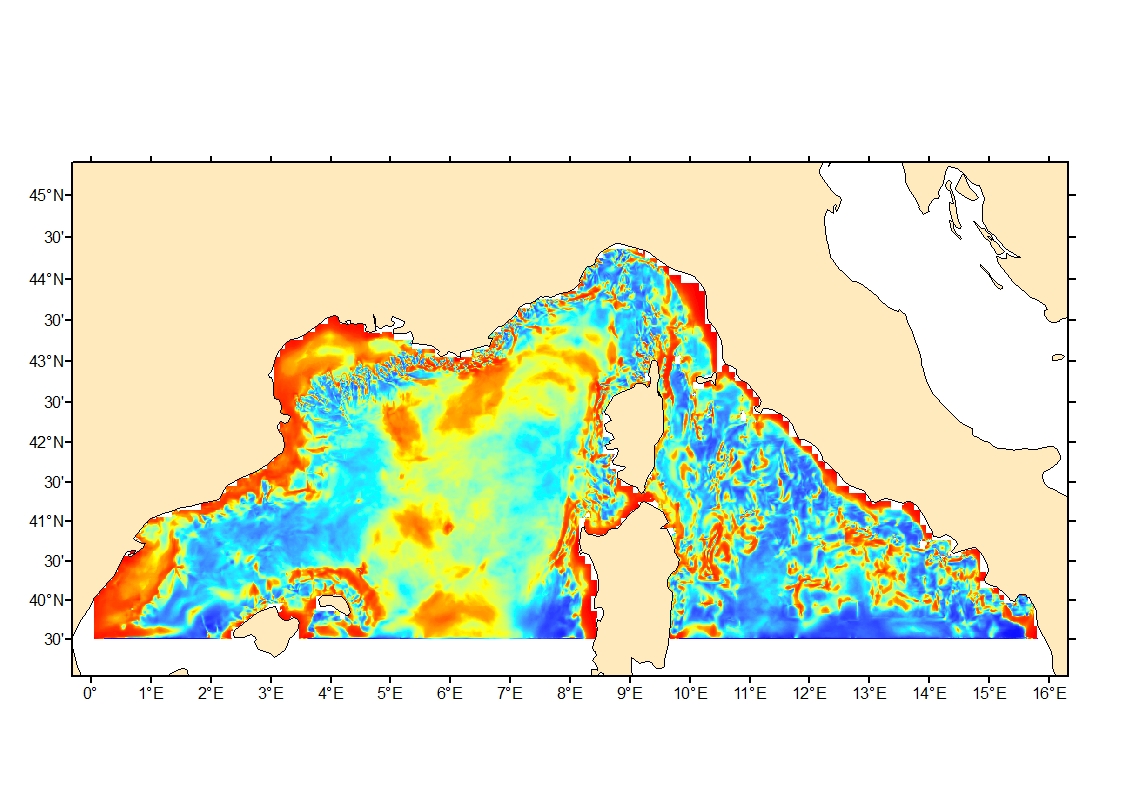
Seabed shear stress (in N.m-2) is a measure of the friction of water on the seabed due to waves and currents. The 90th percentile over the available period is used as layer for habitat models prediction.
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA