environment
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
Resolution
-

Ce document se décompose en deux parties: La première énonce les valeurs et fonctions du massif forestier communes à tous les acteurs concernés par son avenir. La seconde présente les pressions et les enjeux qui pèsent sur le massif forestier des Landes de Gascogne.
-
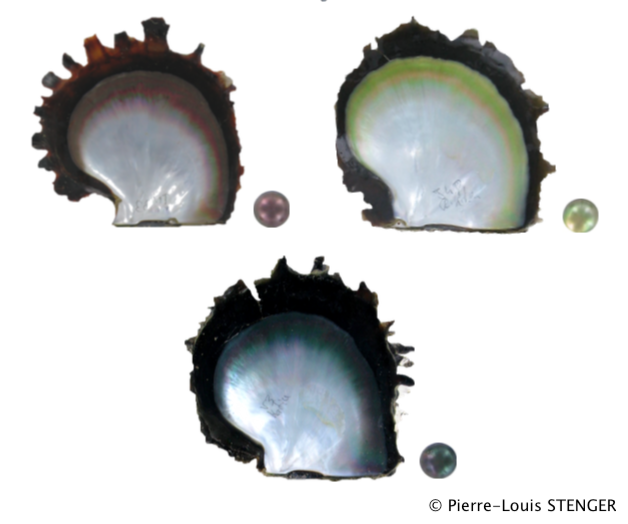

Whole genome pooled sequencing of individuals from 4 populations and 3 different color phenotype in order to uncover the genetic variants linked to color expression in the pearl oyster P. margaritifera.
-

The ABYSS project aims at describing deep-sea benthic biodiversity spanning several branches of the tree of life with eDNA metabarcoding tools. To accommodate both micro- and macro biologists, we designed a bioinformatic pipeline based on Illumina read correction with Dada2 allowing analysing metabarcodes from prokaryotic and eukaryotic life compartments.
-
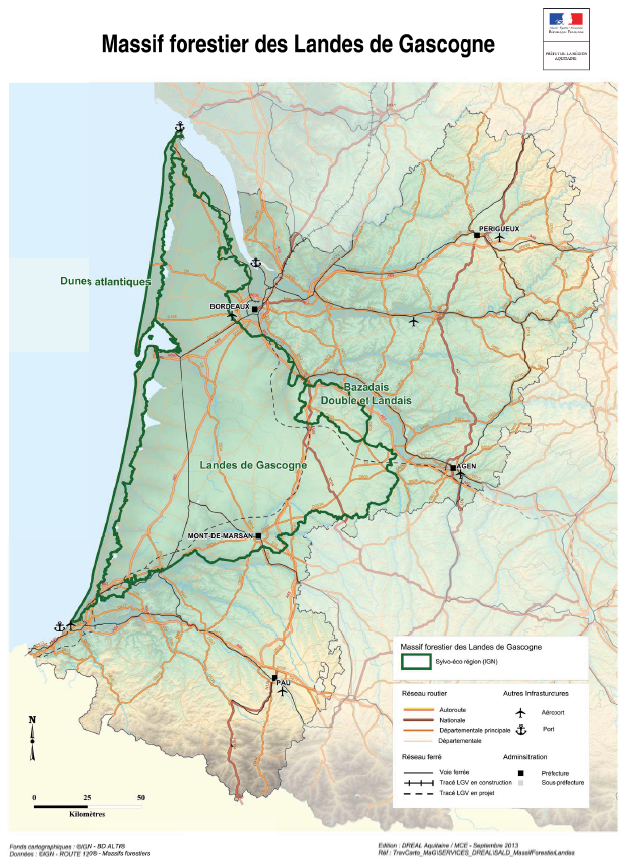
Ces travaux ont été réalisés dans le cadre de la Directive Territoriale d'Aménagement et de Développement Durable (DTADD) portée par la Préfecture de la région ex-Aquitaine. La partie I de ces travaux porte sur les valeurs du massif forestier des Landes de Gascogne. Le massif est dépositaire d’importantes valeurs et fonctions non marchandes d’intérêt général notamment : paysagères, naturalistes, hydrologiques et climatiques. Ce rapport explique également que les modes de valorisation du territoire, autres que ceux liés à la production de bois d’œuvre et d’industrie, interfèrent étroitement avec la présence même de la forêt de production : l'activité touristique, l'arrivée de nouveaux habitants et l'économie induite, ainsi que le foncier forestier.
-

Les ministères chargés de l'écologie (Meeddm) et de l'agriculture (Maap) ont confié au Gip Ecofor une mission d'expertise collective scientifique et technique à visée prospective sur « l'avenir du massif forestier des Landes de Gascogne ». Son objectif est de mobiliser la connaissance autour d'options envisageables pour assurer l'avenir du massif forestier landais et de la partager avec l'ensemble des parties intéressées. Les document disponibles sont les rapports finaux des groupes de travail et d'experts.
-

L’objectif général de ce projet de thèse est d’analyser et d’évaluer les données sources (actuelles et potentielles) des matrices de changements d’occupation du sol afin d’améliorer la robustesse de l’inventaire. Il s’agit d’expertiser par une démarche scientifique la pertinence des travaux réalisés annuellement pour l’inventaire UTCATF. En particulier, il s’agit de comprendre les causes des incertitudes des données sources ; compiler les données disponibles et leurs métadonnées ; étudier qualitativement les dynamiques paysagères décrites ; et redéfinir un cadre méthodologique permettant d’estimer des taux de changements plus pertinent.
-

Ce jeu de données représente sous forme de polygones, les espaces situés à moins de 200m de terrains en nature de bois et forêt, appelés "zones exposées au risque feu de forêt", dont les paramètres sont précisés par l'article R133-5 du Code forestier. Ces zones sensibles au risque d'incendie de forêt comprennent les formations forestières ainsi que la zone périphérique de 200m de large les entourant. Sur cet ensemble s'applique une règlementation particulière afin d'y réduire le risque. Notamment concernant l'obligation légale de débroussaillement qui s'applique dans ces espaces, cette cartographie est annexée aux plan locaux d'urbanisme ou aux documents d'urbanisme en tenant lieu (article L134-15 du Code forestier).
-
Rapport final ONF
-

Larvae from Pacific oyster, Manila clam, European abalone and great scallop were subjected to two temperatures and two pH over the course of early development. RNAseq data was collected in order to evaluate which genes are modulated in response to stress.
-

Individuals from 5 populations were kept in common garden conditions in order to examine acclimation and adaptation to temperature in the honeycomb worm. Worms were exposed to 5 temperature treatments, and collected for RNAseq analysis. Gene expression patterns were then examined.
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA