Species distribution
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
Resolution
-
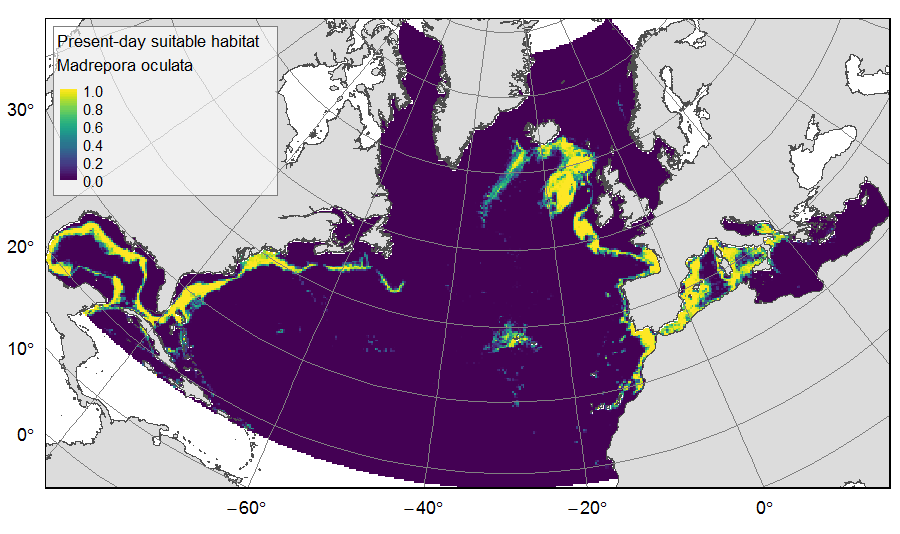
Distribution of predicted suitable habitat for six cold-water-coral, six deep-water fish and one sponge species, on the North Atlantic (18°N to 76°N and 36°E to 98°W). For each species, predicted habitat distribution was obtained for present-day conditions (1951-2000) and for the future climate refugias, i.e. the areas that were predicted as suitable both for present-day and forecasted future (2081-2010) conditions. The dataset gathers 26 raster layers created on the same grid of 25km * 25km resolution, downgraded from source layers (3km *3km resolution) that were created within the work package 3 of EU ATLAS project. The presence (value=1) of climate refugia and the relative cover (value ranging from 0 to 1) of present-day suitable habitat was extracted in gridsquares. This dataset was built to feed a basin-wide spatial conservation planning exercise, targeting the deep sea of the North Atlantic. The goal of this approach was to identify conservation priority areas for Vulnerable Marine Ecosystems (VMEs) and deep fish species, based on the distribution of species and habitats, human activities and current spatial management.
-
Phyto plankton Abundance: Identify the 3 most abundant phytoplankton species in the North Atlantic and calculate a timeseries of their abundance within the basin.
-
The development of the ecosystem approach and models for the management of ocean marine resources requires easy access to standard validated datasets of historical catch data for the main exploited species. They are used to measure the impact of biomass removal by fisheries and to evaluate the models skills, while the use of standard dataset facilitates models inter-comparison. North Atlantic albacore tuna is exploited all year round by longline and in summer and autumn by surface fisheries and fishery statistics compiled by the International Commission for the Conservation of Atlantic Tunas (ICCAT). Catch and effort with geographical coordinates at monthly spatial resolution of 1° or 5° squares were extracted for this species with a careful definition of fisheries and data screening. In total, thirteen fisheries were defined for the period 1956-2010, with fishing gears longline, troll, mid-water trawl and bait fishing. However, the spatialized catch effort data available in ICCAT database represent a fraction of the entire total catch. Length frequencies of catch were also extracted according to the definition of fisheries above for the period 1956-2010 with a quarterly temporal resolution and spatial resolutions varying from 1°x 1° to 10°x 20°. The resolution used to measure the fish also varies with size-bins of 1, 2 or 5 cm (Fork Length). The screening of data allowed detecting inconsistencies with a relatively large number of samples larger than 150 cm while all studies on the growth of albacore suggest that fish rarely grow up over 130 cm. Therefore, a threshold value of 130 cm has been arbitrarily fixed and all length frequency data above this value removed from the original data set.
-
Excel file containing CPR data from Standard Areas B4,C3,C4,D3,D4,D5,E4,F4 for the plankton Calanus finmarchicus and helgolandicus, total traverse (small) copepods, total large copepods, Phytoplankton Colour Index and Cnidaria (presence denoted by a 1, absence by a zero). All taxa are from 1980, except Cnidaria which are from 2011. Dataset is in the format of sample level data, with each row being a discrete sample, with a sample being 3m3 filtered seawater, and 10nm of tow. For each row, a sample has the following information, starting at column a: Standard area of sample, sample id, latitude (decimal degrees) of sample mid point, longitude (decimal degrees) of sample midpoint, sample midpoint date and local time, year of sample, month of sample, then plankton abundance values (or PCI index or cnidaria presence/absence). All taxa have been looked for during the period this dataset spans, so zero values represent true absence.
-
Annual time series of eel recruitement, (2005-2014) • Time series of glass and yellow eel for those rivers used in the annual ICES advice to the EU • Location, data availability and long term annual (LTA) eel recruiment per river mouth
-
Phyto plankton Abundance: Identify the 3 most abundant phytoplankton species in the North Atlantic and calculate a timeseries of their abundance within the basin.
-
Annual time series of eel recruitement, (2005-2014) • Time series of glass and yellow eel for those rivers used in the annual ICES advice to the EU • Location, data availability and long term annual (LTA) eel recruiment per river mouth
-

-

-
List of fish stocks referenced for the year 2018. The repository includes 477 stocks. Each stock is identified by a unique key in accordance with the ICES codification in use. Each record contains a stock identifier, a species or group of species identifier according to the ASFIS/FAO classification, the English stock name, the Latin name of the species, the assessment area according to the FAO codification of fishing sectors. When the stock assessment area groups a series of sectors, the first and last sectors in the series are separated by a dash.
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA