environment
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
Resolution
-

Ce document se décompose en deux parties: La première énonce les valeurs et fonctions du massif forestier communes à tous les acteurs concernés par son avenir. La seconde présente les pressions et les enjeux qui pèsent sur le massif forestier des Landes de Gascogne.
-
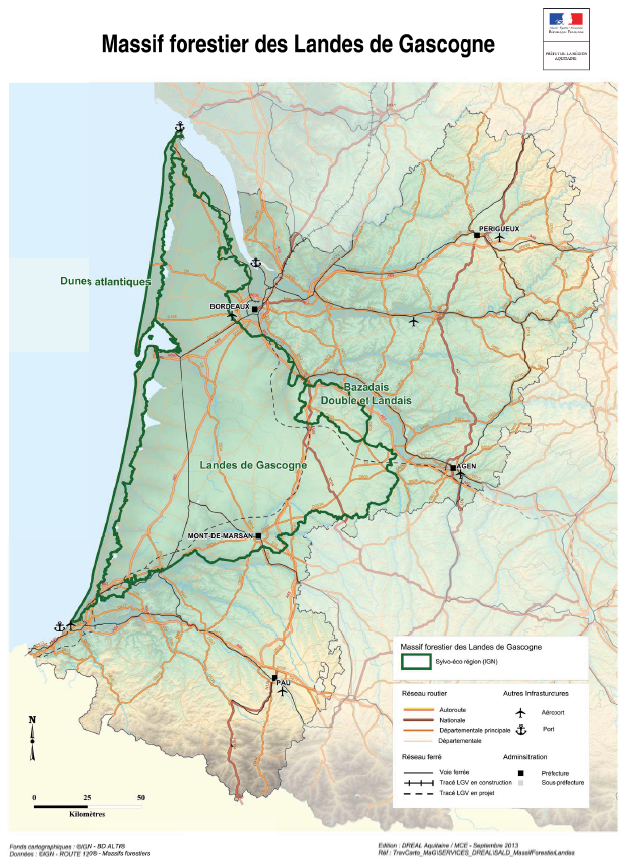
Ces travaux ont été réalisés dans le cadre de la Directive Territoriale d'Aménagement et de Développement Durable (DTADD) portée par la Préfecture de la région ex-Aquitaine. La partie I de ces travaux porte sur les valeurs du massif forestier des Landes de Gascogne. Le massif est dépositaire d’importantes valeurs et fonctions non marchandes d’intérêt général notamment : paysagères, naturalistes, hydrologiques et climatiques. Ce rapport explique également que les modes de valorisation du territoire, autres que ceux liés à la production de bois d’œuvre et d’industrie, interfèrent étroitement avec la présence même de la forêt de production : l'activité touristique, l'arrivée de nouveaux habitants et l'économie induite, ainsi que le foncier forestier.
-
Rapport final ONF
-

Extrait de l'Atlas Aquitaine, Limousin et Poitou-Charentes sur la filière forêt-bois
-

This dataset presents the resulting assessment grid (based on the EEA reference grid) with the classification of chemical status of the transitional, coastal and marine waters in the context of the Water Framework Directive (WFD) and the Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD). This classification has been performed using the CHASE+ tool, with classifications of the matrices ‘water’, ‘sediment’ and ‘biota’ and indicators of ‘biological effects’, as well as an integrated classification of chemical status, combining results of all matrices. The chemical status is evaluated in five classes, where NPAhigh and NPAgood are recognised as ‘non-problem areas’ and PAmoderate, PApoor and PAbad are recognised as ‘problem areas’. This is the assessment made excluding concentrations of metals. The overall area of interest used is based on the marine regions and subregions under the Marine Strategy Framework Directive. Additionally, Norwegian (Barent Sea and Norwegian Sea) and Icelandic waters (’Iceland Sea’) have been added (see Surrounding seas of Europe). Note that within the North East Atlantic region only the subregions within EEZ boundaries (~200 nm) have been included. This dataset underpins the findings and cartographic representations published in the report "Contaminants in Europe's Seas" (EEA, 2019).
-
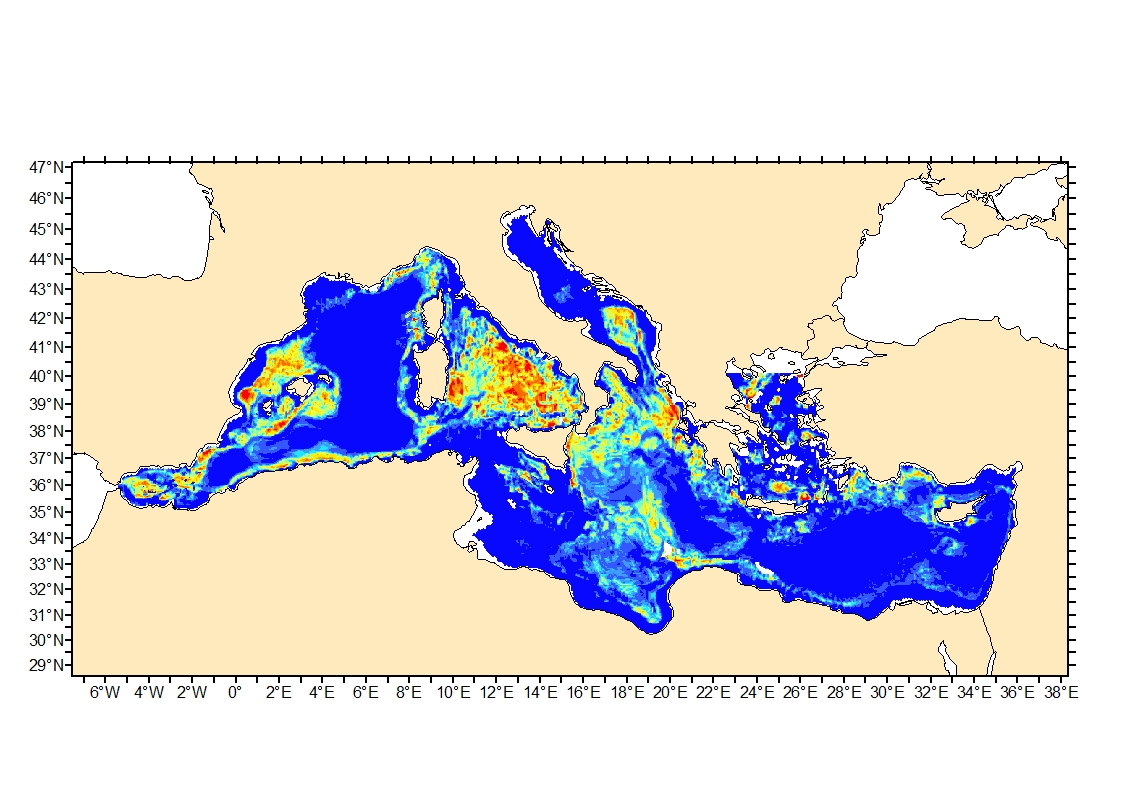
Process-driven seafloor habitat sensitivity (PDS) has been defined from the method developed by Kostylev and Hannah (2007), which takes into account physical disturbances and food availability as structuring factors for benthic communities. It is a conceptual model, relating species’ life history traits to environmental properties. Physical environment maps have been converted into a map of benthic habitat types, each supporting species communities with specific sensitivity to human pressures. It is based on two axes of selected environmental forces. The "Disturbance" (Dist) axis reflects the magnitude of change (destruction) of habitats (i.e. the stability through time of habitats), only due to natural processes influencing the seabed and which are responsible for the selection of life history traits. The "Scope for Growth" (SfG) axis takes into account environmental stresses inducing a physiological cost to organisms and limiting their growth and reproduction potential. This axis estimates the remaining energy available for growth and reproduction of a species (the energy spent on adapting itself to the environment being already taken into account). It can be related to the metabolic theory of the ecology. The process-driven sensitivity (PDS) can be seen as a risk map that combines the two previous axes and reflects the main ecological characteristics of the benthic habitats regarding natural processes. Areas with low disturbance are areas with a naturally low reworking of the sediment, allowing the establishment of a rich sessile epifauna community, with K-strategy species. Areas with low SfG means that the environmental factors, even though there are not limiting, are in lower values, i.e. that it imposes a cost for species to live. In areas combining low disturbance and low SfG, big suspension-feeder species with long life and slow growth can often be found: these species are more vulnerable in case of added disturbance.
-

This dataset is the coastal zone land surface region from Europe, derived from the coastline towards inland, as a series of 10 consecutive buffers of 1km width each. The coastline is defined by the extent of the Corine Land Cover 2018 (raster 100m) version 20 accounting layer. In this version all Corine Land Cover pixels with a value of 523, corresponding to sea and oceans, were considered as non-land surface and thus were excluded from the buffer zone.
-

This dataset presents the resulting assessment grid (based on the EEA reference grid) with the classification of chemical status of the transitional, coastal and marine waters in the context of the Water Framework Directive (WFD) and the Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD). This classification has been performed using the CHASE+ tool, with classifications of the matrices ‘water’, ‘sediment’ and ‘biota’ and indicators of ‘biological effects’, as well as an integrated classification of chemical status, combining results of all matrices. The chemical status is evaluated in five classes, where NPAhigh and NPAgood are recognised as ‘non-problem areas’ and PAmoderate, PApoor and PAbad are recognised as ‘problem areas’. This is the assessment made excluding concentrations of mercury (Hg) and polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) The overall area of interest used is based on the marine regions and subregions under the Marine Strategy Framework Directive. Additionally, Norwegian (Barent Sea and Norwegian Sea) and Icelandic waters (’Iceland Sea’) have been added (see Surrounding seas of Europe). Note that within the North East Atlantic region only the subregions within EEZ boundaries (~200 nm) have been included. This dataset underpins the findings and cartographic representations published in the report "Contaminants in Europe's Seas" (EEA, 2019): https://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/contaminants-in-europes-seas.
-

Here, our study aimed to first assess the influence of plastic on the bacterial community belonging to water, plastic and the microbiome of the giant clam and on the organism's physiology of this putative sentinel species. Our second objective was to identify bacteria whose abundance varies significantly with plastic concentration. Overall, this study will fill the gap towards a better understanding of the impact of plastic pollution on bacterial community assemblages in both inert and living environments.
-

The eleven collected wild strains of T. lutea were compared phenotypically, in particular with regard to their pigment and lipid profiles. The genome of each T. lutea strain was also sequenced to investigate the genetic structure and genome organisation of this species. Collected data were summarized in a genome browser to provide easy-to-use support for the scientific community (https://genomes-catalog.ifremer.fr). This provides an important resource- to understand, exploit and predict the biodiversity of this species.
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA