Sea surface height
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Resolution
-
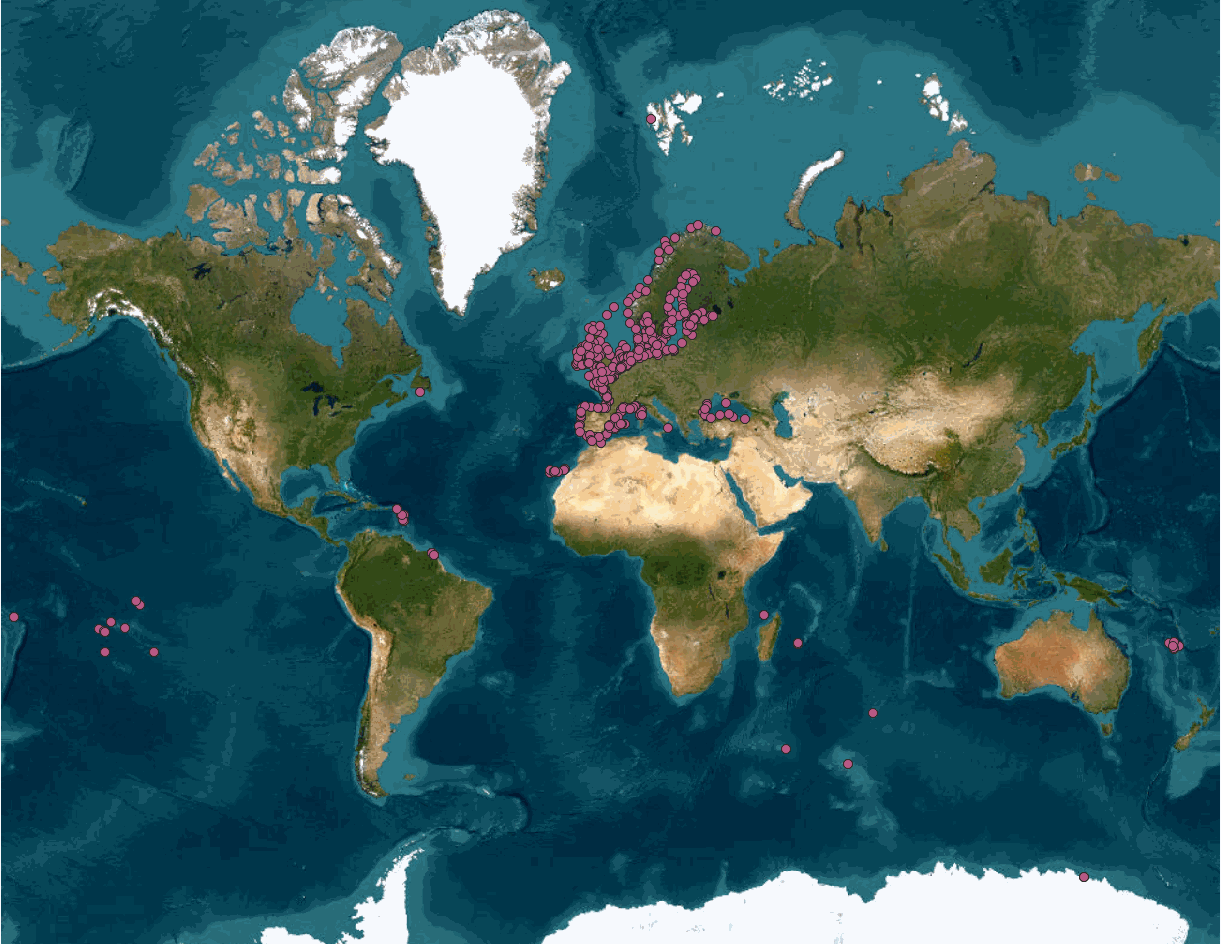
This product integrates sea level observations aggregated and validated from the Regional EuroGOOS consortium (Arctic-ROOS, BOOS, NOOS, IBI-ROOS, MONGOOS) and Black Sea GOOS as well as from the Global telecommunication system (GTS) used by the Met Offices. The latest version of Copernicus delayed-mode Sea level product is also distributed from Copernicus Marine catalogue.
-
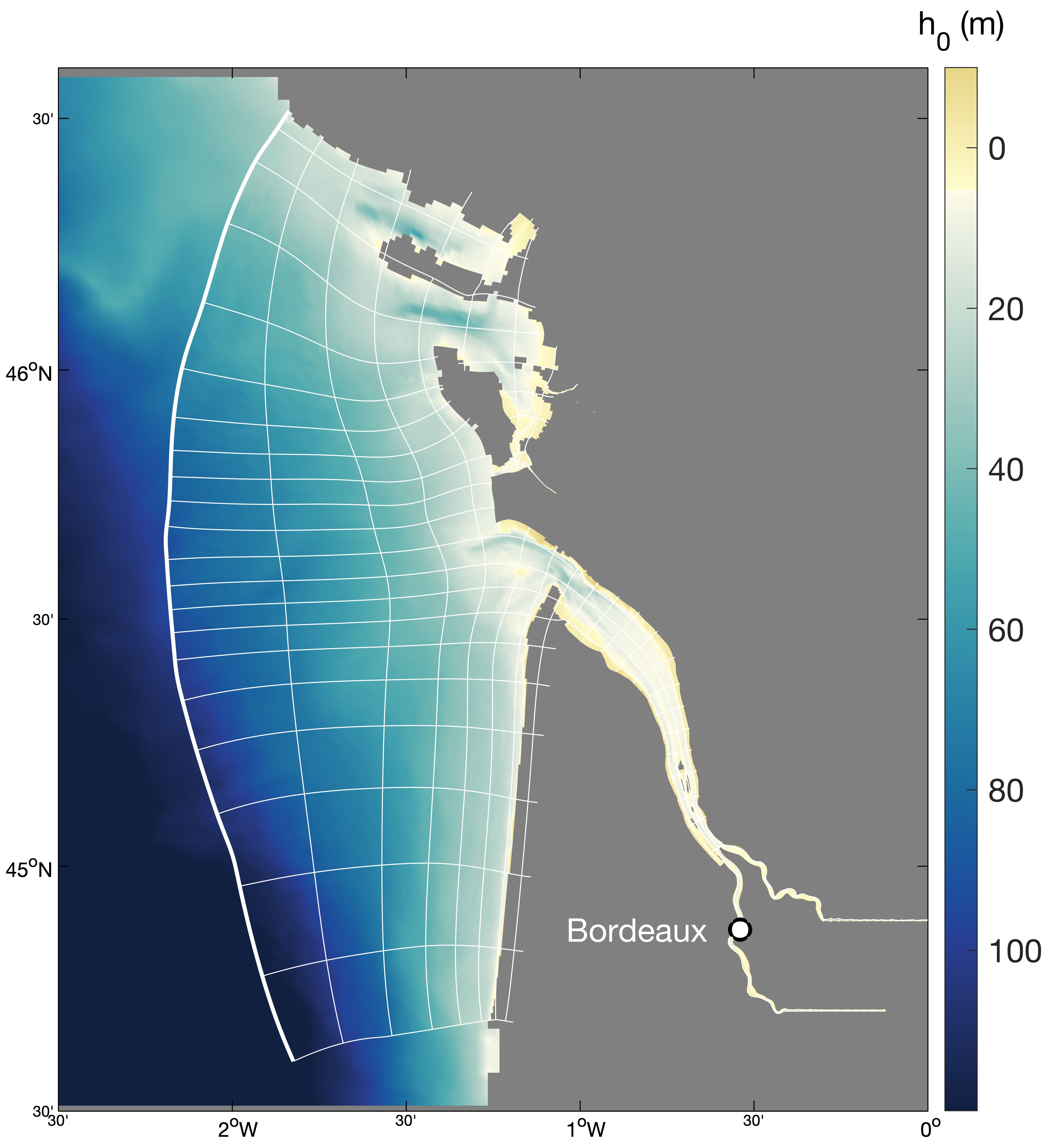
Hydrodynamics and sediment dynamics hindcast in the Gironde Estuary (France), produced by coupling the hydrodynamics model MARS3D (with sediment dynamics module MUSTANG) and wave spectral model WAVEWATCH III®.
-

These gridded products are produced from the following upstream data: - for satellites SARAL/AltiKa, Cryosat-2, HaiYang-2B, Jason-3, Copernicus Sentinel-3A&B, Sentinel 6A, SWOT Nadir => NRT (Near-Real-Time) Nadir along-track (or Level-3) SEA LEVEL products (DOI: https://doi.org/10.48670/moi-00147) delivered by the Copernicus Marine Service (CMEMS, http://marine.copernicus.eu/ ). The gridded product is based on NRT L3 Nadir datasets for the period from July 1, 2024, to December 31, 2024. => MY (Multi-Year) Nadir along-track (or Level-3) SEA LEVEL products (DOI: https://doi.org/10.48670/moi-00146 ) delivered by the Copernicus Marine Service (CMEMS, http://marine.copernicus.eu/ ). The gridded product is based on MY L3 Nadir datasets for the period from March 28, 2023, to June 30, 2024. - for SWOT KaRIn : the SEA LEVEL products L3_LR_SSH (V2.0.1) delivered by AVISO for Expert SWOT L3 SSH KaRin (DOI: https://doi.org/10.24400/527896/A01-2023.018) for the period from March 28, 2023 to December 31, 2024. One mapping algorithm is proposed: the MIOST approach which give the global SSH solutions: the MIOST method is able of accounting for various modes of variability of the ocean surface topography (e.g., geostrophic, barotrope, equatorial waves dynamic …) by constructing several independent components within an assumed covariance model.
-
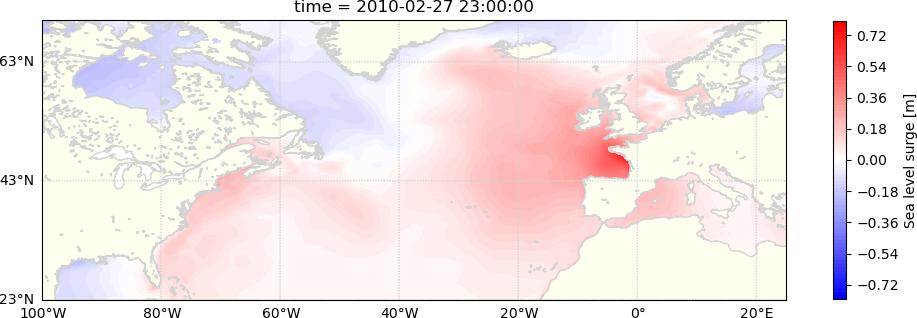
The dataset consists of hourly sea levels and surges over 1900-2015 in the North Atlantic, on a 0.1° grid (directory "HINDCAST" ) and extracted at 34 stations (directory “STATIONS”).
-
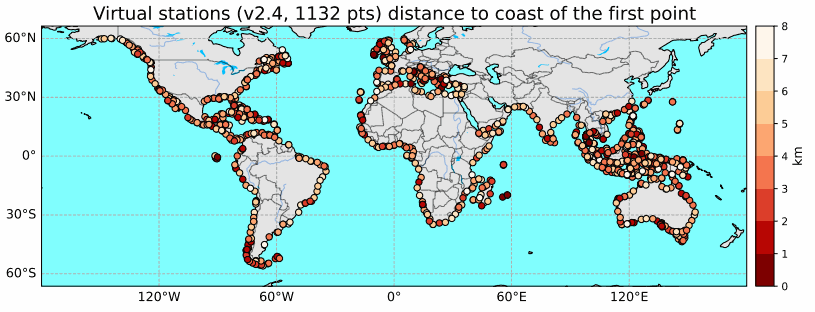
Until recently, classical radar altimetry could not provide reliable sea level data within 10 km to the coast. However dedicated reprocessing of radar waveform together with geophysical corrections adapted for the coastal regions now allows to fill this gap at a large number of coastal sites. In the context of the Climate Change Initiative Sea Level project of the European Space Agency, we have recently performed a complete reprocessing of high resolution (20 Hz, i.e., 350m) along-track altimetry data of the Jason-1, Jason-2 and Jason-3 missions over January 2002 to June 2021 along the coastal zones of Northeast Atlantic, Mediterranean Sea, whole African continent, North Indian Ocean, Southeast Asia, Australia and North and South America. This reprocessing has provided valid sea level data in the 0-20 km band from the coast. More than 1000 altimetry-based virtual coastal stations have been selected and sea level anomalies time series together with associated coastal sea level trends have been computed over the study time span. In the coastal regions devoid from tide gauges (e.g., African coastlines), these virtual stations offer a unique tool for estimating sea level change close to the coast (typically up to 3 km to the coast but in many instances up to 1 km or even closer). Results show that at most of the virtual stations, the rate of sea level rise at the coast is similar to the rate offshore (15 km away from the coast). However, at some stations, the sea level rate in the last 3-4 km to the coast is either faster or slower than offshore.
-

The CDR-derived Wet Tropospheric Correction (WTC) Product V2 is generated from the Level-2+ along-track altimetry products version 2024 (L2P 2024) distributed by AVISO+ (www.aviso.altimetry.fr). It provides a long-term, homogenized estimation of the wet tropospheric correction based on Climate Data Records (CDRs) of atmospheric water vapour combined with high frequencies MWR data. Two independent CDRs datasets are used: - REMSS V7R2 (coverage until 2022) https://www.remss.com/measurements/atmospheric-water-vapor/tpw-1-deg-product/ - HOAPS V5 precursor CDR from EUMETSAT CM SAF (coverage until 2020) HOAPS V4/V5 data available via https://wui.cmsaf.eu Note: the HOAPS V5 precursor is not yet an official CM SAF product; full validation and public release are pending. The MWR/CDR WTC V2 estimates is derived using spatially varying but temporally constant polynomial coefficients (ai). 1. WTC V2 – Along-track L2P Product Data format: The WTC V2 product is delivered in Level-2+ (L2P) format, along the satellite ground track. Each mission is distributed as a compressed archive (.tar.gz) containing one NetCDF4 CF-1.8 file per mission cycle. Archive naming convention: <mission>_WTC_from_WV_CDR_<version>.tar.gz mission: TP (TOPEX/Poseidon), J1, J2, J3 version: product version (currently V2) File naming convention inside archives: <mission>_C<cycle>.nc cycle: 4-digit cycle index (e.g., C0001) Each NetCDF file contains: 1/ Along-track WTC estimate; 2/ Ancillary information; 3/ Space–time coordinates 2. WTC CDR Uncertainties – Gridded Product: A complementary product is provided, delivering regional trend estimates and associated uncertainties from the WTC Climate Data Record. The uncertainty product is distributed as a single NetCDF4 file: wtc_trend_uncertainties.nc . This file contains global gridded fields of WTC CDR trend and uncertainty parameters. Product content: This is the first dedicated version providing both: WTC CDR (HOAPS) linear trends, and Uncertainty estimates on these trends. Uncertainties are expressed as 1-sigma confidence intervals, and propagated using the methodology described in Section 2.3 of the Product User Manual. The product includes: - Total uncertainty on the WTC trend, propagated from all identified uncertainty sources in the WTC–TCWV regression. - Individual contributions of uncertainty sources (Uncertainties on regression coefficients: a0, a1 and their standard deviations; Uncertainties inherited from the HOAPS TCWV CDR) These fields enable users to assess the relative importance of each uncertainty component and recompute uncertainty propagation with alternative methods. Included regression input variables: To ensure transparency and reproducibility, the product provides: 1/ regression coefficients a0, a1; 2/ their associated uncertainties (std of a0, std of a1); 3/additional diagnostic fields required to recompute uncertainties if needed.
-

These gridded products are produced from the following upstream data: - for satellites SARAL/AltiKa, Cryosat-2, HaiYang-2B, Jason-3, Copernicus Sentinel-3A/B, Sentinel-6 MF, SWOT Nadir => NRT (Near-Real-Time) Nadir along-track (or Level-3) SEA LEVEL products (DOI: https://doi.org/10.48670/moi-00147) delivered by the Copernicus Marine Service (http://marine.copernicus.eu/ ). The gridded product is based on near-real-time (NRT) Level-3 Nadir datasets for the period from July 1, 2024, to December 31, 2024. => MY (Multi-Year) Nadir along-track (or Level-3) SEA LEVEL products (DOI: https://doi.org/10.48670/moi-00146 ) delivered by the Copernicus Marine Service (CMEMS, http://marine.copernicus.eu/ ). The gridded product is based on MY Level-3 Nadir datasets for the period from March 28, 2023, to June 30, 2024. - for SWOT KaRIn : the L3_LR_SSH Expert v2.0.1 product distributed by AVISO (DOI: https://doi.org/10.24400/527896/A01-2023.018) from March 28, 2023 to December 31, 2024. One mapping algorithm is proposed: the MIOST approach which give the global SSH solutions: the MIOST method is able of accounting for various modes of variability of the ocean surface topography (e.g., geostrophic, barotrope, equatorial waves dynamic, etc.) by constructing several independent components within an assumed covariance model.
-

This dataset contains the dynamical outputs of a global ocean simulation coupling dynamics and biogeochemistry at ¼° over the year 2019. The simulation has been performed using the coupled circulation/ecosystem model NEMO/PISCES (https://www.nemo-ocean.eu/), which is here enhanced to perform an ensemble simulation with explicit simulation of modeling uncertainties in the physics and in the biogeochemistry. This dataset is one of the 40 members of the ensemble simulation. This study was part of the Horizon Europe project SEAMLESS (https://seamlessproject.org/Home.html), with the general objective of improving the analysis and forecast of ecosystem indicators. See Popov et al. (https://os.copernicus.org/articles/20/155/2024/) for more details on the study.
-

These gridded products are produced from the along-track (or Level-3) SEA LEVEL products (DOI: doi.org/10.48670/moi-00147) delivered by the Copernicus Marine Service (CMEMS, marine.copernicus.eu) for satellites SARAL/AltiKa, Cryosat-2, HaiYang-2B, Jason-3, Copernicus Sentinel-3A/B, Sentinel-6 MF, SWOT nadir, and SWOT Level-3 KaRIn sea level products (DOI: https://doi.org/10.24400/527896/A01-2023.018). Three mapping algorithms are proposed: MIOST, 4DvarNET, 4DvarQG: - the MIOST approach which give the global SSH solutions: the MIOST method is able of accounting for various modes of variability of the ocean surface topography (e.g., geostrophic, barotrope, equatorial waves dynamic …) by constructing several independent components within an assumed covariance model. - the 4DvarNET approach for the regional SSH solutions: the 4DvarNET mapping algorithm is a data-driven approach combining a data assimilation scheme associated with a deep learning framework. - the 4DvarQG approach for the regional SSH solutions: the 4DvarQG mapping technique integrates a 4-Dimensional variational (4DVAR) scheme with a Quasi-Geostrophic (QG) model.
-
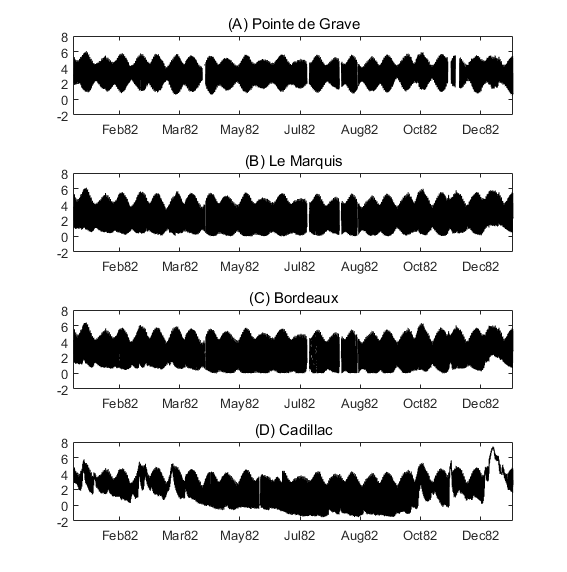
Times series of water level at four stations of the Gironde Estuary (Pointe de Grave, Le Marquis, Bordeaux and Cadillac) for the the years 1953, 1971, 1982, 1994, 2005 and 2014. The dataset includes all of the time seris used in the publication: To what extent multidecadal changes in morphology and fluvial discharge impact tide in a convergent (turbid) tidal river (2018), Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans.
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA