TEXTE
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
-
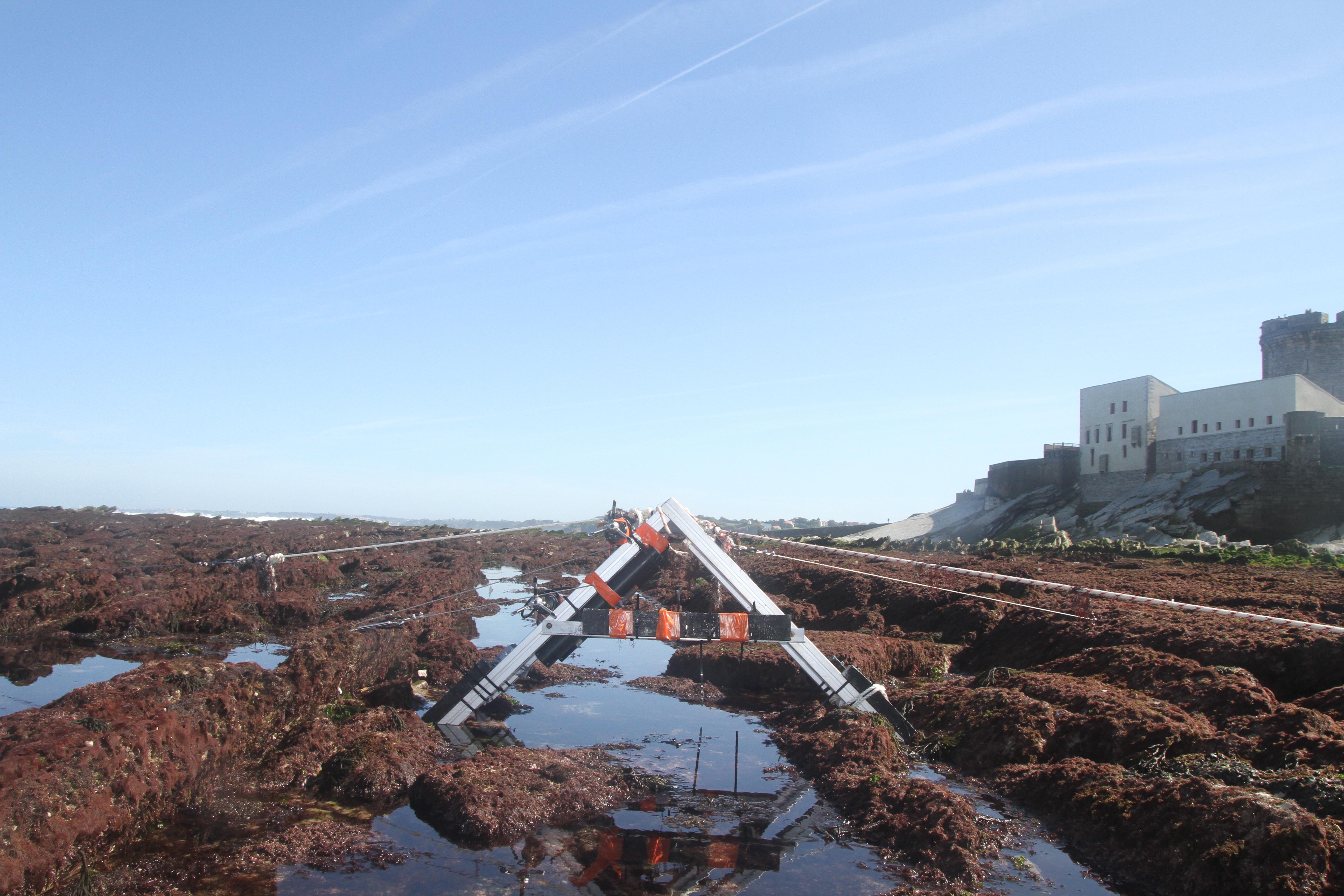

The database displays the field measurements recover during a one-week experiment in October 2021 on the Socoa's rocky platform, France. The general objective of the study was to evaluate the momentum balance over the rocky platform, in particular to quantifiy the combined effect of high seabed roughness and waves on the coupling between circulation, wave force and mean water level. The analysis is performed along a single cross-shore transect. The data include: - the cross-shore bathymetric profile - the time-series of integrated wave parameters, local mean water depth and wave-averaged currents over successive 30-min bursts - the depth- and wave-averaged momentum fluxes following the formulation proposed by Smith 2006 and Bruneau et al. 2011. The fluxes are median values obtained over significant wave height to depth ratio bins
-
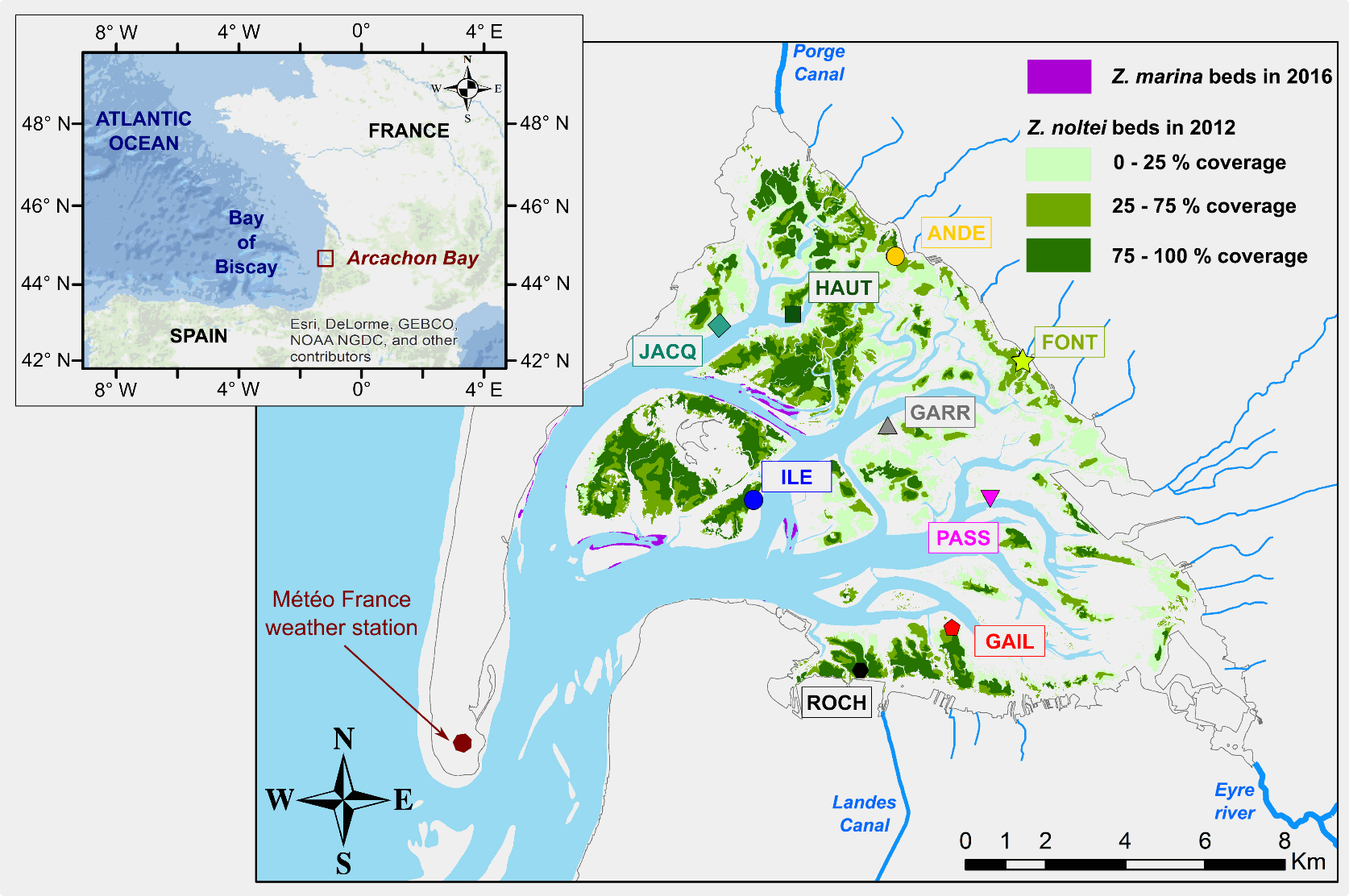
The ReZoEnv field campaign was conducted at 9 sites distributed within contrasted seagrass (Zostera notlei) meadows in the Arcachon Bay. This multi-parameter survey was conducted during one year (November 2015 – November 2016). Water levels, temperature and light were recorded every 10 minutes. While bed sediment characteristics (granulometry, water content, organic matter content), seagrass characteristics (coverage, biometry, chlorophyll and CNP content) were measured monthly. Additionally, wind-wave parameters were obtained from high frequency pressure sensor at 4 sites, every 20 minutes. List of sites : - ANDE : 44.745091 N, 1.121366 O - FONT : 44.722631 N, 1.080133 O - GAIL : 44.662573 N, 1.099575 O - GARR : 44.705132 N, 1.121562 O - HAUT : 44.729331 N, 1.15608 O - ILE : 44.683117 N, 1.162716 O - JACQ : 44.724563 N, 1.181109 O - PASS : 44.689927 N, 1.089491 O - ROCH : 44.648529 N, 1.127736 O
-
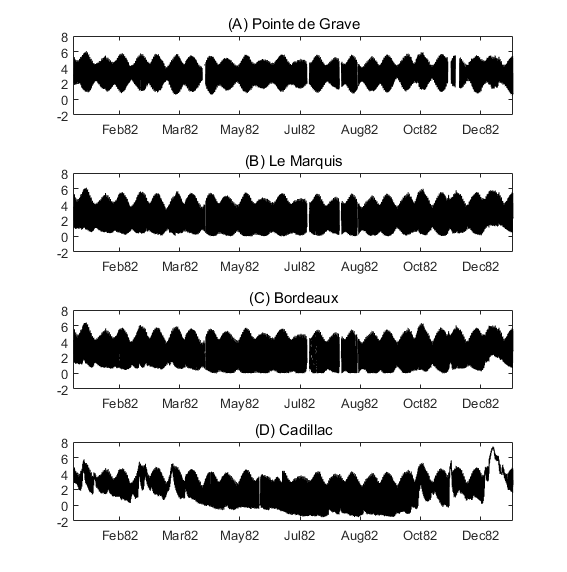
Times series of water level at four stations of the Gironde Estuary (Pointe de Grave, Le Marquis, Bordeaux and Cadillac) for the the years 1953, 1971, 1982, 1994, 2005 and 2014. The dataset includes all of the time seris used in the publication: To what extent multidecadal changes in morphology and fluvial discharge impact tide in a convergent (turbid) tidal river (2018), Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans.
-
Global mean sea level is an integral of changes occurring in the climate system in response to unforced climate variability as well as natural and anthropogenic forcing factors. Its temporal evolution allows detecting changes (e.g., acceleration) in one or more components. Study of the sea level budget provides constraints on missing or poorly known contributions, such as the unsurveyed deep ocean or the still uncertain land water component. In the context of the World Climate Research Programme Grand Challenge entitled “Regional Sea Level and Coastal Impacts”, an international effort involving the sea level community worldwide has been recently initiated with the objective of assessing the various data sets used to estimate components of the sea level budget during the altimetry era (1993 to present). These data sets are based on the combination of a broad range of space-based and in situ observations, model estimates and algorithms. Evaluating their quality, quantifying uncertainties and identifying sources of discrepancies between component estimates is extremely useful for various applications in climate research. This effort involves several tens of scientists from about sixty research teams/institutions worldwide (www.wcrp-climate.org/grand-challenges/gc-sea-level). The results presented in this paper are a synthesis of the first assessment performed during 2017-2018. We present estimates of the altimetry-based global mean sea level (average rate of 3.1 +/- 0.3 mm/yr and acceleration of 0.1 mm/yr2 over 1993-present), as well as of the different components of the sea level budget. We further examine closure of the sea level budget, comparing the observed global mean sea level with the sum of components. Ocean thermal expansion, glaciers, Greenland and Antarctica contribute by 42%, 21%, 15% and 8% to the global mean sea level over the 1993-present. We also study the sea level budget over 2005-present, using GRACE-based ocean mass estimates instead of sum of individual mass components. Results show closure of the sea level budget within 0.3 mm/yr. Substantial uncertainty remains for the land water storage component, as shown in examining individual mass contributions to sea level.
-

The ORHAGO campaigns (Observation of the benthic aquatic resources of the Golfe de Gascogne) are designed to collect data on the composition, distribution and change in relative abundance of benthic fish fauna on the continental shelf (depth <100m) in November to December on a yearly basis. The ORHAGO survey was initiated in 2007 with the objective of developing a fishery-independent abundance index for flatfish species, with a particular focus on the common sole (Solea solea) of the Bay of Biscay. In accordance with the ICES-agreed gear for flatfish abundance surveys, ORHAGO employs a 4-meter-beam trawl with a chain mat, 50-millimeter mesh in the net, and 40-millimeter mesh in the cod-end. The sampling plan was designed to ensure full coverage of the common sole habitat in the Bay of Biscay during a period (November-December) for which fish behavior and distribution was suitable for obtaining an unbiased abundance index (young fish move offshore when coastal waters become colder and before the concentrations of the spawning season). The sampling design is a systematic sampling with 49 reference stations. The sampling design was validated in 2013 by the ICES Working Group on Beam Trawl Surveys (WGBEAM). Since 2013, the ORHAGO survey has been used to assess the status of the Bay of Biscay common sole stock (WGBIE, Working Group for the Bay of Biscay and the Iberian Waters Ecoregion).
-
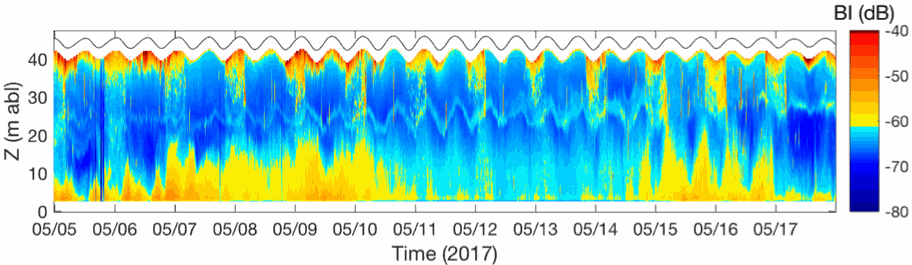
In the framework of the ANR AMORAD project, the METEOR cruises (Grasso, 2017) aimed at deploying the ‘Gironde Estuary Mouth MEasurement Stations’ (GEMMES) to measure hydrodynamics and sediment dynamics at the mouth of the Gironde Estuary and on the West Gironde Mud Patch (SW France, Bay of Biscay). Measurements were carried out between November 2016 and December 2017: i) from a buoy station around 20-m water depth (GEMMES-20), collecting sub-surface data of temperature, salinity and turbidity; and ii) a benthic station around 40-m water depth (GEMMES-40), collecting data of current velocity and turbidity. Bottom and surface water samples were regularly collected to calibrate turbidity measurements to SPM concentrations.
-
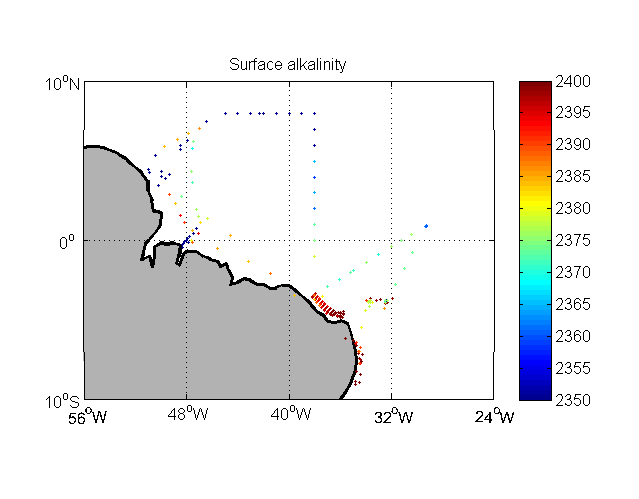
Inorganic carbon and alkalinity measurements (in micromoles/kg) from Brazilian cruises in the Western Tropical Atlantic.
-
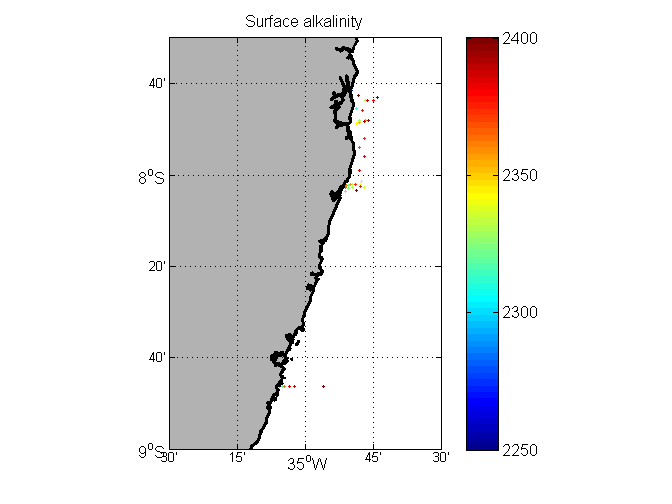
Inorganic carbon and alkalinity measurements (in micromoles/kg) along the coast of Brazil, 2013-2015.
-
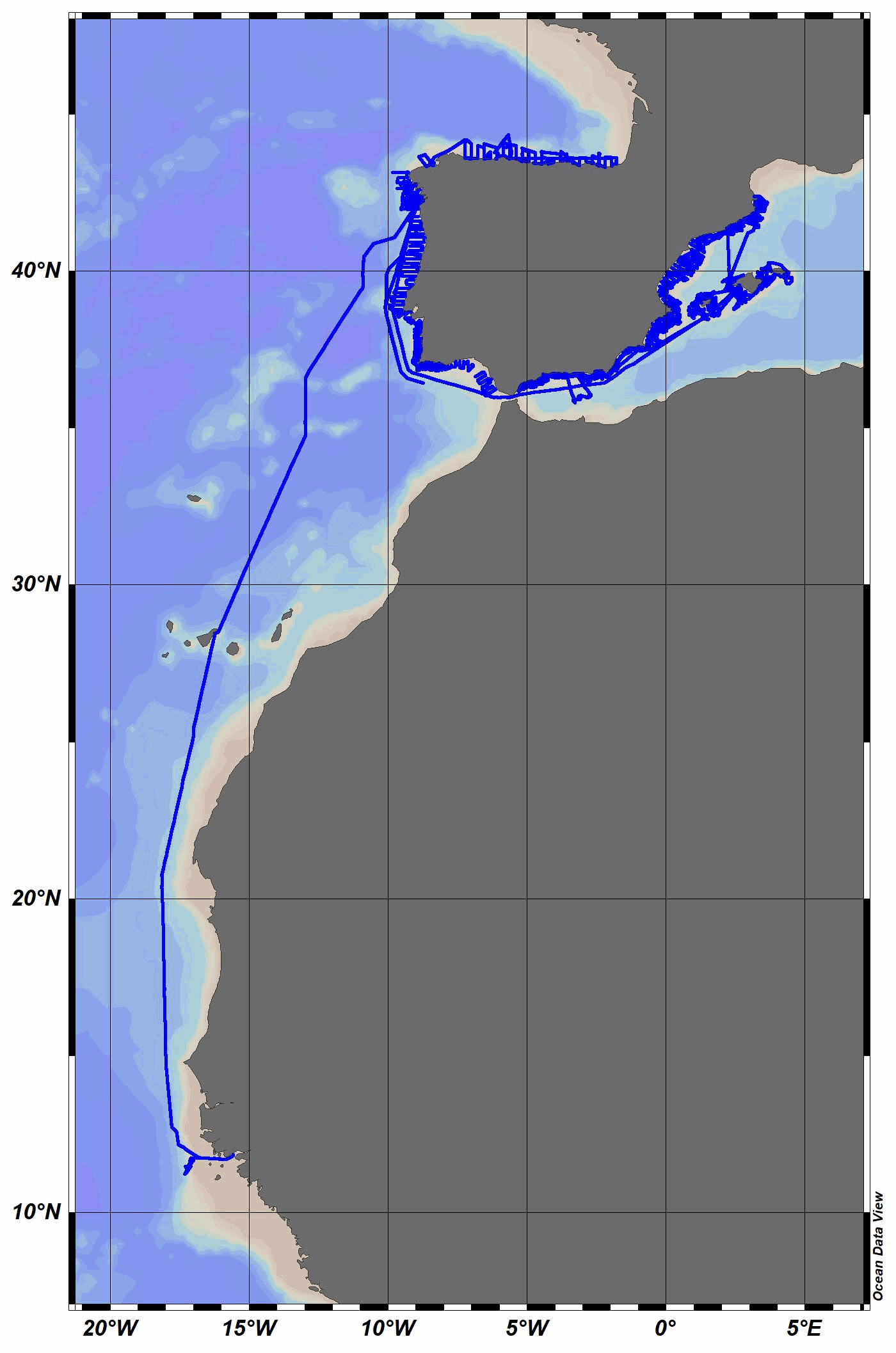
The R/V Miguel Oliver was built in 2007 for scientific fisheries assessment and oceanographic research purposes. Owned by the Spanish General Secretariat of Fisheries, it mainly operates around the Iberian Peninsula and Canary Islands waters. Equipped with an automatic weather station, collected data are daily sent to the Spanish Institute of Oceanography (IEO) Data Center / National Oceanographic Data Center (NODC) for delayed-mode quality control and long-term archive and dissemination. Recently, a semi-automatic process has been used to perform quality control and data assessment. The quality controlled data have been stored in MEDAR/MEDATLAS format, and the corresponding quality flag has been added to each individual measurement. This facilitates their reuse for different purposes, from climatology or academic studies to industrial sector needs, among others. In 2023, air temperature, relative humidity, wind speed and direction and solar radiation were collected.
-

The Mytilobs network, carried out by IFREMER (French Research Institute for Exploitation of the Sea), is a national network dedicated to building long-term physiological variations time series of blue mussels (Mytilus edulis), across a large spatial scale. This observation network, initially designed to survey production yields, also provides valuable data to track environmental variations of coastal ecosystems. Mussels exhibit high phenotypic plasticity in response to environmental variations. Collection of data describing phenotypic variations, over an extended period, reveals small-scale climate and habitat variations. With its broad deployment across time and space, the data produced under Mytilobs will be useful for the establishment of a baseline condition when studying the effect of a perturbation affecting an ecosystem’s functioning. Finally, the monitoring of mussel biometric traits and mortality was coupled with high-frequency measurements of salinity, temperature, and sea level, complementing this multi-layer observational framework.
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA