2025
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Service types
Scale
Resolution
-

Particularly suited to the purpose of measuring the sensitivity of benthic communities to trawling, a trawl disturbance indicator (de Juan and Demestre, 2012, de Juan et al. 2009) was proposed based on benthic species life history traits to evaluate the sensibility of mega- and epifaunal community to fishing pressure known to have a physical impact on the seafloor (such as dredging and bottom trawling). The selected biological traits were chosen as they determine vulnerability to trawling: mobility, fragility, position on substrata, average size and feeding mode that can easily be related to the fragility, recoverability and vulnerability ecological concepts. Life history traits of species have been defined from the BIOTIC database (MARLIN, 2014) and from information given by Le Pape et al. (2007), Brindamour et al. (2009) and Garcia (2010). For missing life history traits, additional information from literature has been considered. The five categories retained are life history functional traits that were selected based on the knowledge of the response of benthic taxa to trawling disturbance (de Juan and Demestre, 2012). They reflect respectively the possibility to avoid direct gear impact, to benefit from trawling for feeding, to escape gear, to get caught by the net and to resist trawling/dredging action, each of these characteristics being either advantageous or sensitive to trawling. Then, to allow quantitative analysis, a score was assigned to each category: from low vulnerability (0) to high vulnerability (3). The five categories scores were then summed for each taxon (the highly vulnerable taxon could reach the maximum score is 15) and this value may be considered as a species index of sensitivity to trawling disturbance. The scores of 812 taxa commonly found in bottom trawl by-catch in the southern North Sea, English Channel and north-western Mediterranean were described.
-
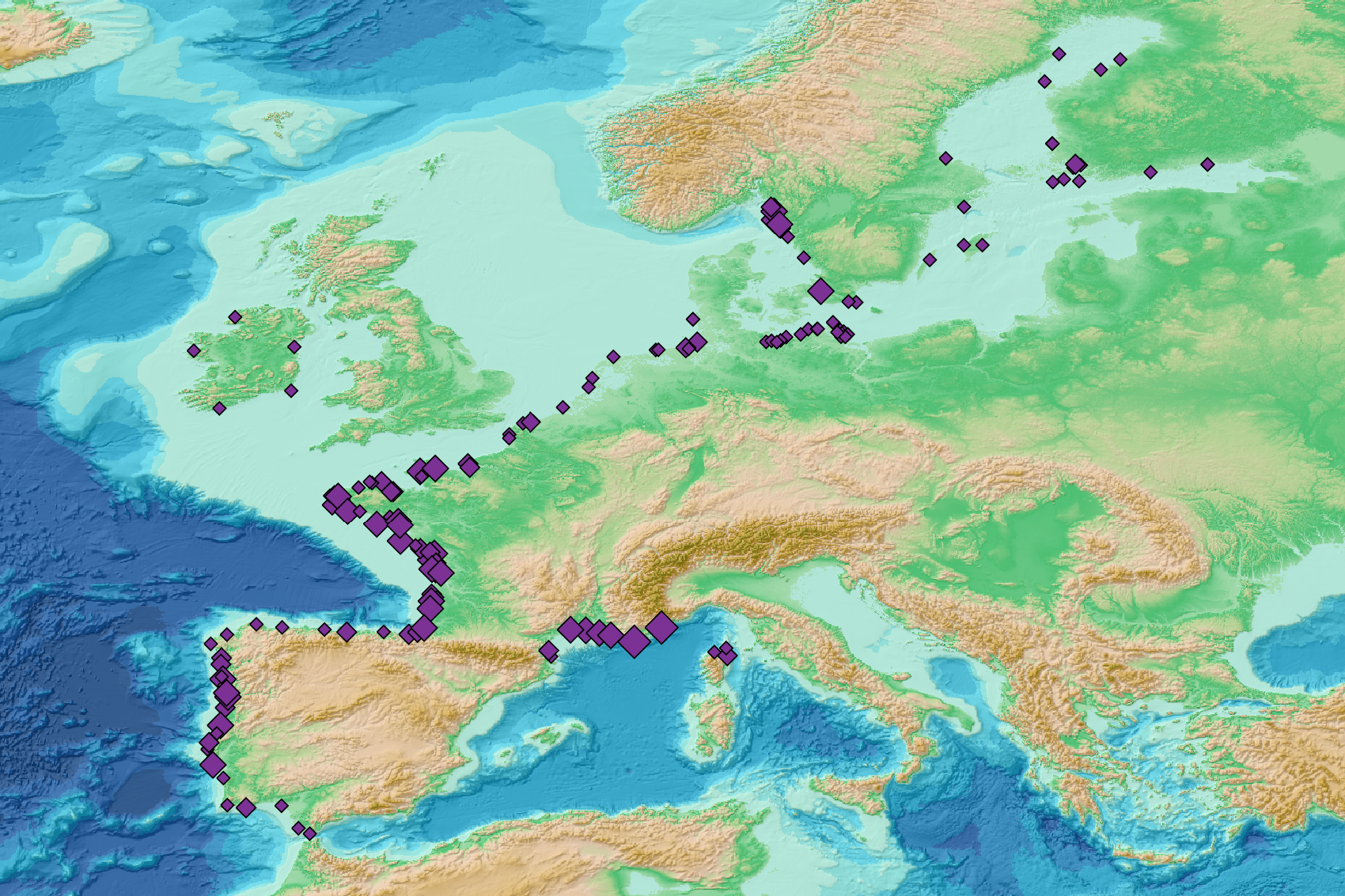
This visualization product displays the total abundance of marine macro-litter (> 2.5cm) per beach per year from Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD) monitoring surveys. EMODnet Chemistry included the collection of marine litter in its 3rd phase. Since the beginning of 2018, data of beach litter have been gathered and processed in the EMODnet Chemistry Marine Litter Database (MLDB). The harmonization of all the data has been the most challenging task considering the heterogeneity of the data sources, sampling protocols and reference lists used on a European scale. Preliminary processings were necessary to harmonize all the data: - Exclusion of OSPAR 1000 protocol: in order to follow the approach of OSPAR that it is not including these data anymore in the monitoring; - Selection of MSFD surveys only (exclusion of other monitoring, cleaning and research operations); - Exclusion of beaches without coordinates; - Some categories & some litter types like organic litter, small fragments (paraffin and wax; items > 2.5cm) and pollutants have been removed. The list of selected items is attached to this metadata. This list was created using EU Marine Beach Litter Baselines, the European Threshold Value for Macro Litter on Coastlines and the Joint list of litter categories for marine macro-litter monitoring from JRC (these three documents are attached to this metadata); - Normalization of survey lengths to 100m & 1 survey / year: in some cases, the survey length was not exactly 100m, so in order to be able to compare the abundance of litter from different beaches a normalization is applied using this formula: Number of items (normalized by 100 m) = Number of litter per items x (100 / survey length) Then, this normalized number of items is summed to obtain the total normalized number of litter for each survey. Finally, the median abundance for each beach and year is calculated from these normalized abundances per survey. Sometimes the survey length was null or equal to 0. Assuming that the MSFD protocol has been applied, the length has been set at 100m in these cases. Percentiles 50, 75, 95 & 99 have been calculated taking into account MSFD data for all years. More information is available in the attached documents. Warning: the absence of data on the map does not necessarily mean that it does not exist, but that no information has been entered in the Marine Litter Database for this area.
-

Rapid changes in ocean circulation and climate have been observed in marine-sediment and ice cores over the last glacial period and deglaciation, highlighting the non-linear character of the climate system and underlining the possibility of rapid climate shifts in response to anthropogenic greenhouse gas forcing. To date, these rapid changes in climate and ocean circulation are still not fully explained. One obstacle hindering progress in our understanding of the interactions between past ocean circulation and climate changes is the difficulty of accurately dating marine cores. Here, we present a set of 92 marine sediment cores from the Atlantic Ocean for which we have established age-depth models that are consistent with the Greenland GICC05 ice core chronology, and computed the associated dating uncertainties, using a new deposition modeling technique. This is the first set of consistently dated marine sediment cores enabling paleoclimate scientists to evaluate leads/lags between circulation and climate changes over vast regions of the Atlantic Ocean. Moreover, this data set is of direct use in paleoclimate modeling studies.
-

EMODnet Chemistry aims to provide access to marine chemistry datasets and derived data products concerning eutrophication, acidity and contaminants. The importance of the selected substances and other parameters relates to the Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD). This aggregated dataset contains all unrestricted EMODnet Chemistry data on potential hazardous substances, despite the fact that some data might not be related to pollution (e.g. collected by deep corer). Temperature, salinity and additional parameters are included when available. It covers the Northeast Atlantic Ocean (40W). Data were harmonised and validated by '‘IFREMER / IDM / SISMER - Scientific Information Systems for the SEA’ in France. The dataset contains water (profiles), sediment (profiles and timeseries) and biota (timeseries). The temporal coverage is 1974–2018 for water measurements, 1966–2022 for sediment measurements and 1979–2023 for biota measurements. Regional datasets concerning contaminants are automatically harvested and the resulting collections are harmonised and validated using ODV Software and following a common methodology for all sea regions ( https://doi.org/10.6092/8b52e8d7-dc92-4305-9337-7634a5cae3f4 ). Parameter names are based on P01 vocabulary, which relates to BODC Parameter Usage Vocabulary and is available at: https://vocab.nerc.ac.uk/search_nvs/P01/ . The harmonised dataset can be downloaded as as an ODV spreadsheet, which is composed of a metadata header followed by tab separated values. This spreadsheet can be imported into ODV Software for visualisation (more information can be found at: https://www.seadatanet.org/Software/ODV ). In addition, the same dataset is offered also as a txt file in a long/vertical format, in which each P01 measurement is a record line. Additionally, there are a series of columns that split P01 terms into subcomponents (substance, CAS number, matrix...).This transposed format is more adapted to worksheet applications (e.g. LibreOffice Calc).
-

'''Short description:''' The NWSHELF_ANALYSISFORECAST_PHY_LR_004_001 is produced by a coupled hydrodynamic-biogeochemical model system with tides, implemented over the North East Atlantic and Shelf Seas at 7 km of horizontal resolution and 24 vertical levels. The product is updated daily, providing 7-day forecast for temperature, salinity, currents, sea level and mixed layer depth. Products are provided at quarter-hourly, hourly, daily de-tided (with Doodson filter), and monthly frequency. '''DOI (product) :''' https://doi.org/10.48670/mds-00367
-

This visualization product displays the cigarette related items abundance of marine macro-litter (> 2.5cm) per beach per year from Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD) monitoring surveys without UNEP-MARLIN data. EMODnet Chemistry included the collection of marine litter in its 3rd phase. Since the beginning of 2018, data of beach litter have been gathered and processed in the EMODnet Chemistry Marine Litter Database (MLDB). The harmonization of all the data has been the most challenging task considering the heterogeneity of the data sources, sampling protocols and reference lists used on a European scale. Preliminary processings were necessary to harmonize all the data: - Exclusion of OSPAR 1000 protocol: in order to follow the approach of OSPAR that it is not including these data anymore in the monitoring; - Selection of MSFD surveys only (exclusion of other monitoring, cleaning and research operations); - Exclusion of beaches without coordinates; - Selection of cigarette related items only. The list of selected items is attached to this metadata. This list was created using EU Marine Beach Litter Baselines, the European Threshold Value for Macro Litter on Coastlines and the Joint list of litter categories for marine macro-litter monitoring from JRC (these three documents are attached to this metadata); - Exclusion of surveys referring to the UNEP-MARLIN list: the UNEP-MARLIN protocol differs from the other types of monitoring in that cigarette butts are surveyed in a 10m square. To avoid comparing abundances from very different protocols, the choice has been made to distinguish in two maps the cigarette related items results associated with the UNEP-MARLIN list from the others; - Normalization of survey lengths to 100m & 1 survey / year: in some case, the survey length was not exactly 100m, so in order to be able to compare the abundance of litter from different beaches a normalization is applied using this formula: Number of cigarette related items of the survey (normalized by 100 m) = Number of cigarette related items of the survey x (100 / survey length) Then, this normalized number of cigarette related items is summed to obtain the total normalized number of cigarette related items for each survey. Finally, the median abundance of cigarette related items for each beach and year is calculated from these normalized abundances of cigarette related items per survey. Sometimes the survey length was null or equal to 0. Assuming that the MSFD protocol has been applied, the length has been set at 100m in these cases. Percentiles 50, 75, 95 & 99 have been calculated taking into account cigarette related items from MSFD monitoring data (excluding UNEP-MARLIN protocol) for all years. More information is available in the attached documents. Warning: the absence of data on the map does not necessarily mean that they do not exist, but that no information has been entered in the Marine Litter Database for this area.
-
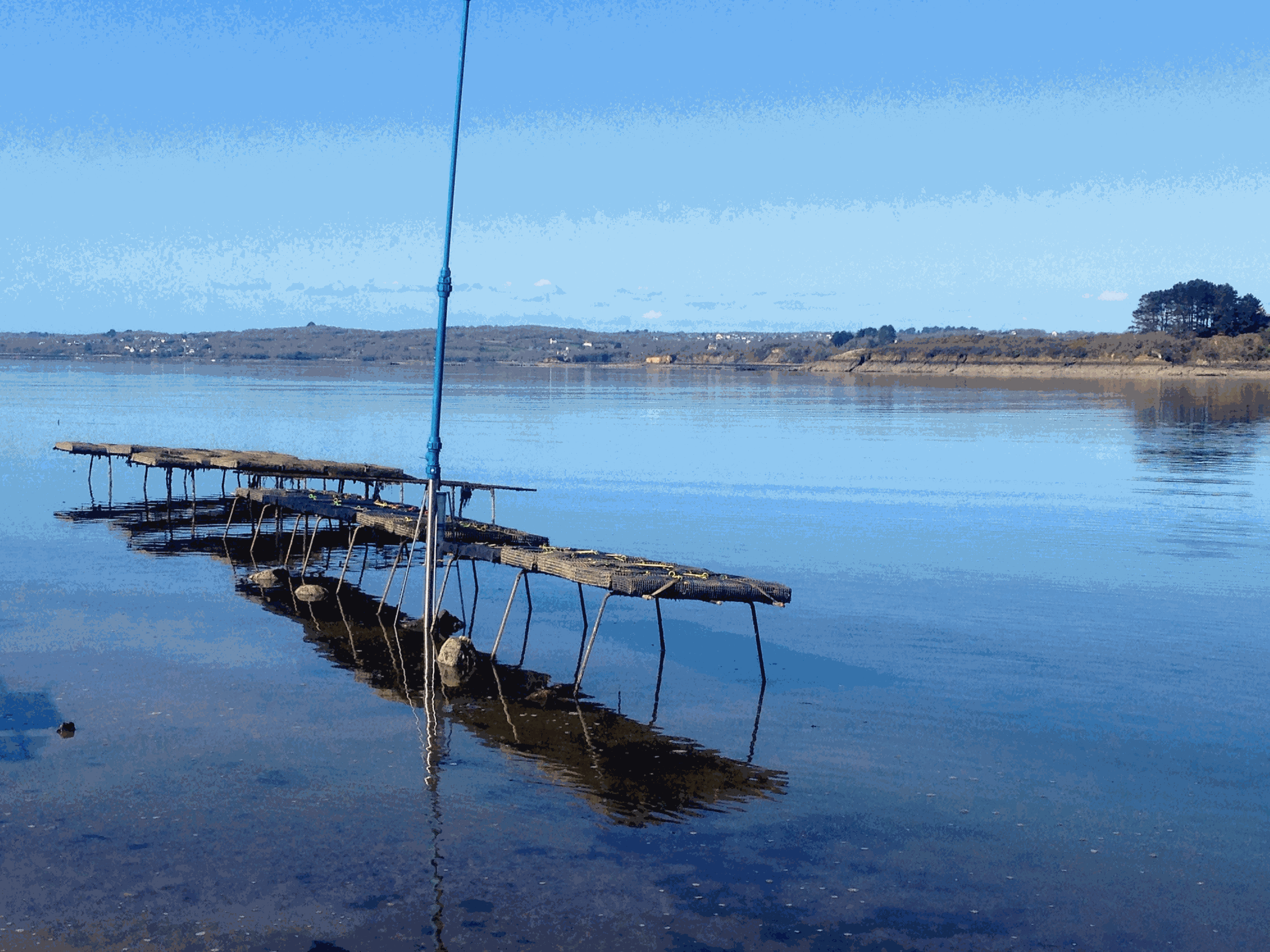
Based on the consolidation of the Ifremer networks RESCO (https://doi.org/10.17882/53007) and VELYGER (https://doi.org/10.17882/41888), the general objective of the ECOSCOPA project is to analyze the causes of spatio-temporal variability of the main life traits (Larval stage - Recruitment - Reproduction - Growth – Survival – Cytogenetic anomalies) of the Pacific oyster in France and follow their evolution over the long term in the context of climate change. The high frequency environmental data are monitored since 2010 at several stations next to oyster farm areas in eight bays of the French coast (from south to north): Thau Lagoon and bays of Arcachon, Marennes Oléron, Bourgneuf, Vilaine, Brest, Mont Saint-Michel and Veys (see map below). Sea temperature and practical salinity are recorded at 15-mins frequency. For several sites, fluorescence and turbidity data are also available. Data are acquired with automatic probes directly put in oyster bags or fixed on metallic structure at 50 cm over the sediment bottom, except for Thau Lagoon whose probes are deployed at 2m below sea surface. Since 2010, several types of probes were used: STP2, STPS, SMATCH or WiSens CTD from NKE (www.nke-instrumentation.fr) and recently ECO FLNTU (www.seabird.com). The probes are regularly qualified by calibrations in the Ifremer coastal laboratories. Precision estimated of the complete data collection process is: temperature (±0.1°C), salinity (±0.5psu), in vivo fluorescence (±10%), turbidity (±10%). The data are qualified into several levels: 0-No Quality Check performed, 1-Good data, 2-Probably good data, 3-Probably bad data, 4-Bad data, 5-Value changed, 7-Nominal value, 8-Interpolated value, 9-Missing value.
-
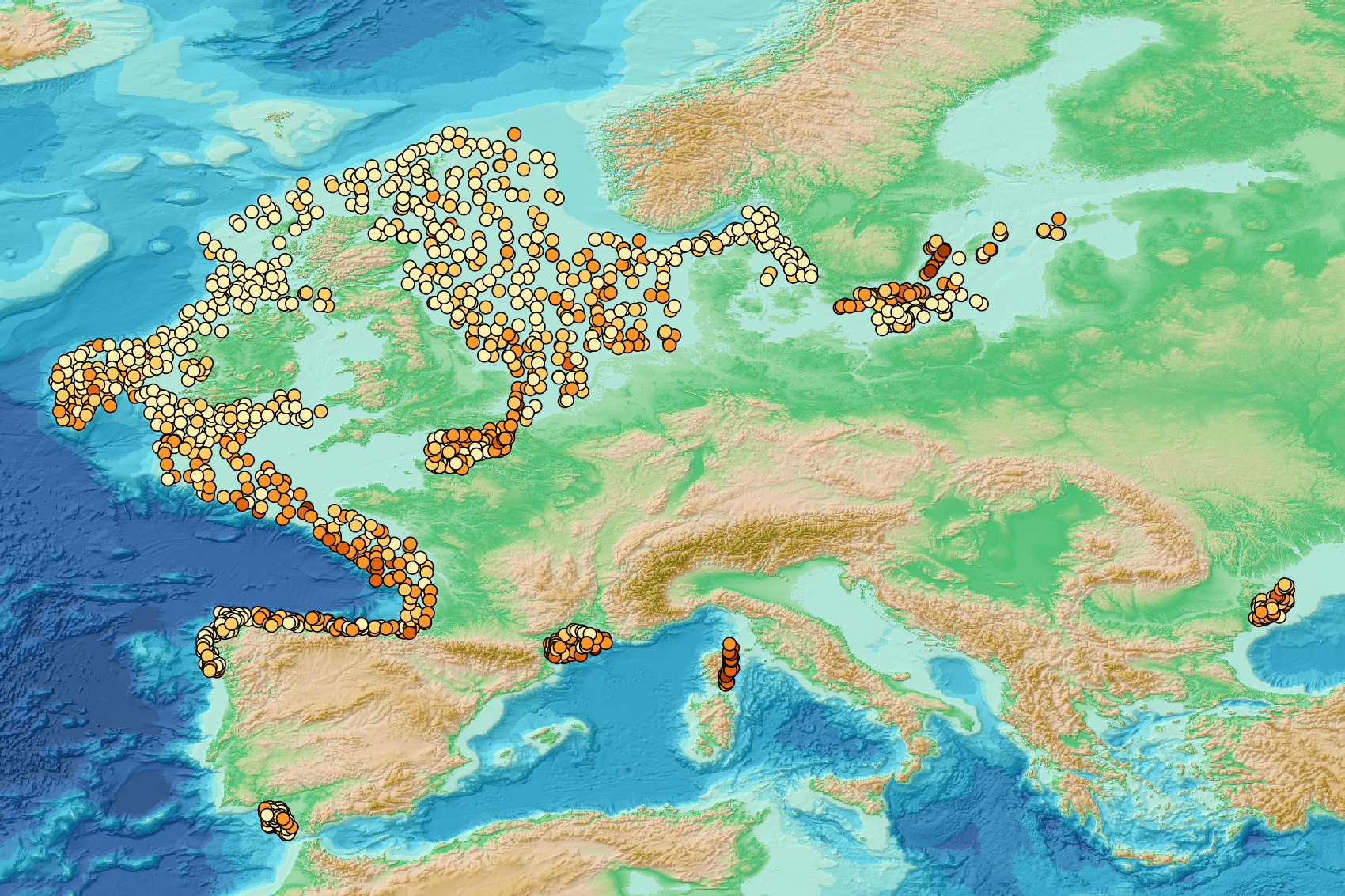
This visualization product displays the density of seafloor litter per trawl. EMODnet Chemistry included the collection of marine litter in its 3rd phase. Since the beginning of 2018, data of seafloor litter collected by international fish-trawl surveys have been gathered and processed in the EMODnet Chemistry Marine Litter Database (MLDB). The harmonization of all the data has been the most challenging task considering the heterogeneity of the data sources, sampling protocols (OSPAR and MEDITS protocols) and reference lists used on a European scale. Moreover, within the same protocol, different gear types are deployed during bottom trawl surveys. In cases where the wingspread and/or the number of items were/was unknown, it was not possible to use the data because these fields are needed to calculate the density. Data collected before 2011 are concerned by this filter. When the distance reported in the data was null, it was calculated from: - the ground speed and the haul duration using the following formula: Distance (km) = Haul duration (h) * Ground speed (km/h); - the trawl coordinates if the ground speed and the haul duration were not filled in. The swept area was calculated from the wingspread (which depends on the fishing gear type) and the distance trawled: Swept area (km²) = Distance (km) * Wingspread (km) Densities were calculated on each trawl and year using the following computation: Density (number of items per km²) = ∑Number of items / Swept area (km²) Percentiles 50, 75, 95 & 99 were calculated taking into account data for all years. More information on data processing and calculation are detailed in the attached document. Warning: the absence of data on the map does not necessarily mean that they do not exist, but that no information has been entered in the Marine Litter Database for this area.
-
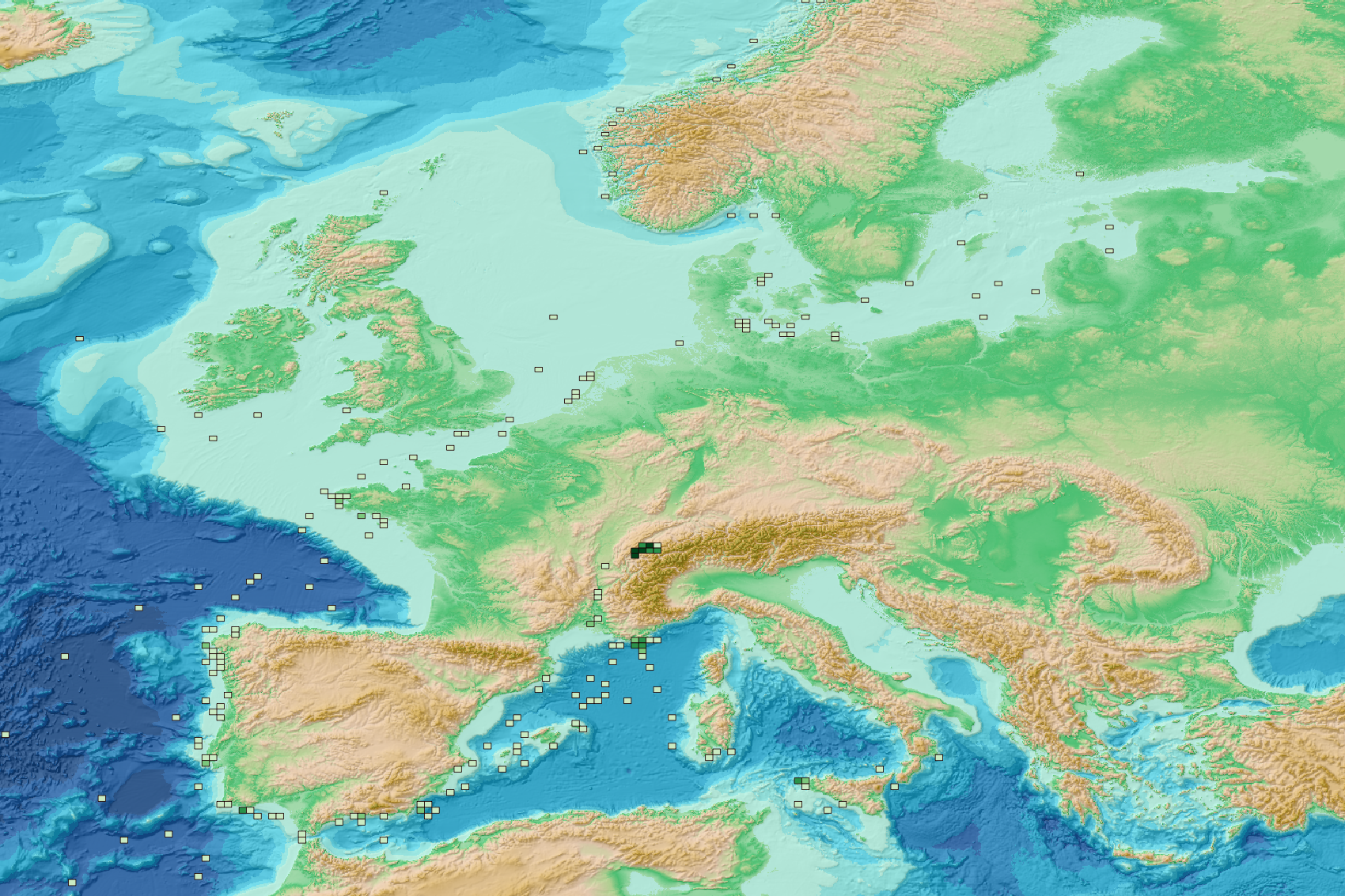
This visualization product displays the spatial distribution of the sampling effort (based on the start position of the sampling tow) over the six-years' period 2017-2022 from other specific protocols. EMODnet Chemistry included the collection of marine litter in its 3rd phase. Before 2021, there was no coordinated effort at the regional or European scale for micro-litter. Given this situation, EMODnet Chemistry proposed to adopt the data gathering and data management approach as generally applied for marine data, i.e., populating metadata and data in the CDI Data Discovery and Access service using dedicated SeaDataNet data transport formats. EMODnet Chemistry is currently the official EU collector of micro-litter data from Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD) National Monitoring activities (descriptor 10). A series of specific standard vocabularies or standard terms related to micro-litter have been added to SeaDataNet NVS (NERC Vocabulary Server) Common Vocabularies to describe the micro-litter. European micro-litter data are collected by the National Oceanographic Data Centres (NODCs). Micro-litter map products are generated from NODCs data after a test of the aggregated collection including data and data format checks and data harmonization. A filter is applied to represent only micro-litter samplings carried out according to a very specific protocol such as the Volvo Ocean Race (VOR) or Oceaneye. The spatial distribution was then determined by calculating the number of times each cell was sampled during the period 2017-2022, only taking into account the start position of the tows. The corresponding total distance (kms) sampled in each cell is also provided in the attribute table. Information on data processing and calculation are detailed in the attached methodology document. Warning: the absence of data on the map does not necessarily mean that they do not exist, but that no information has been entered in the National Oceanographic Data Centre (NODC) for this area. This work is based on the work presented in the following scientific article: O. Gerigny, M. Brun, M.C. Fabri, C. Tomasino, M. Le Moigne, A. Jadaud, F. Galgani, Seafloor litter from the continental shelf and canyons in French Mediterranean Water: Distribution, typologies and trends, Marine Pollution Bulletin, Volume 146, 2019, Pages 653-666, ISSN 0025-326X, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.07.030.
-
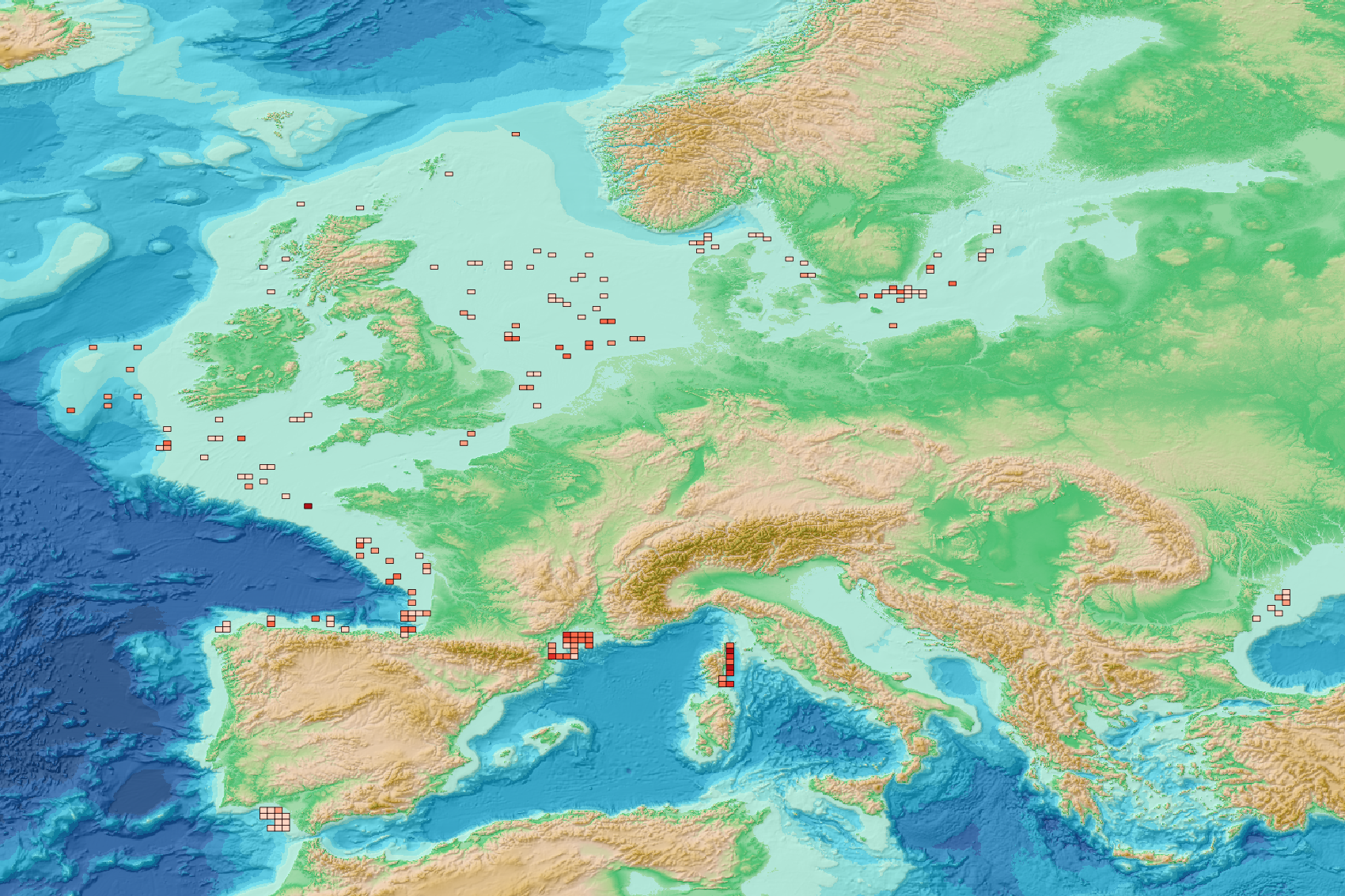
This visualization product displays the spatial distribution of plastic bags density per trawl. EMODnet Chemistry included the collection of marine litter in its 3rd phase. Since the beginning of 2018, data of seafloor litter collected by international fish-trawl surveys have been gathered and processed in the EMODnet Chemistry Marine Litter Database (MLDB). The harmonization of all the data has been the most challenging task considering the heterogeneity of the data sources, sampling protocols (OSPAR and MEDITS protocols) and reference lists used on a European scale. Moreover, within the same protocol, different gear types are deployed during bottom trawl surveys. In cases where the wingspread and/or number of items were/was unknown, it was not possible to use the data because these fields are needed to calculate the density. Data collected before 2011 are concerned by this filter. When the distance reported in the data was null, it was calculated from: - the ground speed and the haul duration using the following formula: Distance (km) = Haul duration (h) * Ground speed (km/h); - the trawl coordinates if the ground speed and the haul duration were not filled in. The swept area was calculated from the wingspread (which depends on the fishing gear type) and the distance trawled: Swept area (km²) = Distance (km) * Wingspread (km) Densities were calculated on each trawl and year using the following computation: Density of plastic bags (number of items per km²) = ∑Number of plastic bags related items / Swept area (km²) Then a grid with 30km x 30km cells was used to calculate the weighted mean of densities in each cell from the formula : Weighted mean (number of items per km²) = ∑ (Distance (km) * Density (number of items per km²)) / ∑ Distance (km) Percentiles 50, 75, 95 & 99 were calculated taking into account data for all years. More information on data processing and calculation are detailed in the attached methodological document. Warning: the absence of data on the map does not necessarily mean that they do not exist, but that no information has been entered in the Marine Litter Database for this area. This work is based on the work presented in the following scientific article: O. Gerigny, M. Brun, M.C. Fabri, C. Tomasino, M. Le Moigne, A. Jadaud, F. Galgani, Seafloor litter from the continental shelf and canyons in French Mediterranean Water: Distribution, typologies and trends, Marine Pollution Bulletin, Volume 146, 2019, Pages 653-666, ISSN 0025-326X, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.07.030.
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA