oceans
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
Resolution
-

'''Short description:''' The iceberg product contains 9 (6+3) datasets: Six gridded datasets in netCDF format: IW, EW and RCMNL modes and mosaic for the two modes) describing iceberg concentration as number of icebergs counted within 10x10 km grid cells. The iceberg concentration is derived by applying a Constant False Alarm Rate (CFAR) algorithm on data from Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) satellite sensors. Three datasets – individual iceberg positions – in shapefile format: The shapefile format allows the best representation of the icebergs. Each shapefile-dataset also includes a shapefile holding the polygonized satellite coverage Despite its precision (individual icebergs are proposed), this product is a generic and automated product and needs expertise to be correctly used. For all applications concerning marine navigation, please refer to the national Ice Service of the country concerned. '''DOI (product) :''' https://doi.org/10.48670/moi-00129
-

'''Short description:''' For the NWS/IBI Ocean- Sea Surface Temperature L3 Observations . This product provides daily foundation sea surface temperature from multiple satellite sources. The data are intercalibrated. This product consists in a fusion of sea surface temperature observations from multiple satellite sensors, daily, over a 0.05° resolution grid. It includes observations by polar orbiting from the ESA CCI / C3S archive . The L3S SST data are produced selecting only the highest quality input data from input L2P/L3P images within a strict temporal window (local nightime), to avoid diurnal cycle and cloud contamination. The observations of each sensor are intercalibrated prior to merging using a bias correction based on a multi-sensor median reference correcting the large-scale cross-sensor biases. '''DOI (product) :''' https://doi.org/10.48670/moi-00311
-
This product displays the stations present in EMODnet validated dataset where benzo[A]pyrene levels have been measured in sediment. EMODnet Chemistry has included the gathering of contaminants data since the beginning of the project in 2009. For the maps for EMODnet Chemistry Phase III, it was requested to plot data per matrix (water,sediment, biota), per biological entity and per chemical substance. The series of relevant map products have been developed according to the criteria D8C1 of the MSFD Directive, specifically focusing on the requirements under the new Commission Decision 2017/848 (17th May 2017). The Commission Decision points to relevant threshold values that are specified in the WFD, as well as relating how these contaminants should be expressed (units and matrix etc.) through the related Directives i.e. Priority substances for Water. EU EQS Directive does not fix any threshold values in sediments. On the contrary Regional Sea Conventions provide some of them, and these values have been taken into account for the development of the visualization products. To produce the maps the following process has been followed: 1. Data collection through SeaDataNet standards (CDI+ODV) 2. Harvesting, harmonization, validation and P01 code decomposition of data 3. SQL query on data sets from point 2 4. Production of map with each point representing at least one record that match the criteria The harmonization of all the data has been the most challenging task considering the heterogeneity of the data sources, sampling protocols. Preliminary processing were necessary to harmonize all the data : • For water: contaminants in the dissolved phase; • For sediment: data on total sediment (regardless of size class) or size class < 2000 μm • For biota: contaminant data will focus on molluscs, on fish (only in the muscle), and on crustaceans • Exclusion of data values equal to 0
-
'''This product has been archived''' For operationnal and online products, please visit https://marine.copernicus.eu '''Short description:''' Global Ocean- Gridded objective analysis fields of temperature and salinity using profiles from the reprocessed in-situ global product CORA (INSITU_GLO_TS_REP_OBSERVATIONS_013_001_b) using the ISAS software. Objective analysis is based on a statistical estimation method that allows presenting a synthesis and a validation of the dataset, providing a validation source for operational models, observing seasonal cycle and inter-annual variability. '''DOI (product) :''' https://doi.org/10.48670/moi-00038
-

'''DEFINITION''' The Strong Wave Incidence index is proposed to quantify the variability of strong wave conditions in the Iberia-Biscay-Ireland regional seas. The anomaly of exceeding a threshold of Significant Wave Height is used to characterize the wave behavior. A sensitivity test of the threshold has been performed evaluating the differences using several ones (percentiles 75, 80, 85, 90, and 95). From this indicator, it has been chosen the 90th percentile as the most representative, coinciding with the state-of-the-art. Two Copernicus Marine products are used to compute the Strong Wave Incidence index: * IBI-WAV-MYP: '''IBI_MULTIYEAR_WAV_005_006''' * IBI-WAV-NRT: '''IBI_ANALYSISFORECAST_WAV_005_005''' The Strong Wave Incidence index (SWI) is defined as the difference between the climatic frequency of exceedance (Fclim) and the observational frequency of exceedance (Fobs) of the threshold defined by the 90th percentile (ThP90) of Significant Wave Height (SWH) computed on a monthly basis from hourly data of IBI-WAV-MYP product: SWI = Fobs(SWH > ThP90) – Fclim(SWH > ThP90) Since the Strong Wave Incidence index is defined as a difference of a climatic mean and an observed value, it can be considered an anomaly. Such index represents the percentage that the stormy conditions have occurred above/below the climatic average. Thus, positive/negative values indicate the percentage of hourly data that exceed the threshold above/below the climatic average, respectively. '''CONTEXT''' Ocean waves have a high relevance over the coastal ecosystems and human activities. Extreme wave events can entail severe impacts over human infrastructures and coastal dynamics. However, the incidence of severe (90th percentile) wave events also have valuable relevance affecting the development of human activities and coastal environments. The Strong Wave Incidence index based on the Copernicus Marine regional analysis and reanalysis product provides information on the frequency of severe wave events. The IBI-MFC covers the Europe’s Atlantic coast in a region bounded by the 26ºN and 56ºN parallels, and the 19ºW and 5ºE meridians. The western European coast is located at the end of the long fetch of the subpolar North Atlantic (Mørk et al., 2010), one of the world’s greatest wave generating regions (Folley, 2017). Several studies have analyzed changes of the ocean wave variability in the North Atlantic Ocean (Bacon and Carter, 1991; Kushnir et al., 1997; WASA Group, 1998; Bauer, 2001; Wang and Swail, 2004; Dupuis et al., 2006; Wolf and Woolf, 2006; Dodet et al., 2010; Young et al., 2011; Young and Ribal, 2019). The observed variability is composed of fluctuations ranging from the weather scale to the seasonal scale, together with long-term fluctuations on interannual to decadal scales associated with large-scale climate oscillations. Since the ocean surface state is mainly driven by wind stresses, part of this variability in Iberia-Biscay-Ireland region is connected to the North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO) index (Bacon and Carter, 1991; Hurrell, 1995; Bouws et al., 1996, Bauer, 2001; Woolf et al., 2002; Tsimplis et al., 2005; Gleeson et al., 2017). However, later studies have quantified the relationships between the wave climate and other atmospheric climate modes such as the East Atlantic pattern, the Arctic Oscillation pattern, the East Atlantic Western Russian pattern and the Scandinavian pattern (Izaguirre et al., 2011, Martínez-Asensio et al., 2016). The Strong Wave Incidence index provides information on incidence of stormy events in four monitoring regions in the IBI domain. The selected monitoring regions (Figure 1.A) are aimed to provide a summarized view of the diverse climatic conditions in the IBI regional domain: Wav1 region monitors the influence of stormy conditions in the West coast of Iberian Peninsula, Wav2 region is devoted to monitor the variability of stormy conditions in the Bay of Biscay, Wav3 region is focused in the northern half of IBI domain, this region is strongly affected by the storms transported by the subpolar front, and Wav4 is focused in the influence of marine storms in the North-East African Coast, the Gulf of Cadiz and Canary Islands. More details and a full scientific evaluation can be found in the CMEMS Ocean State report (Pascual et al., 2020). '''CMEMS KEY FINDINGS''' The trend analysis of the SWI index for the period 1980–2024 shows statistically significant trends (at the 99% confidence level) in wave incidence, with an increase of at least 0.05 percentage points per year in regions WAV1, WAV3, and WAV4. The analysis of the historical period, based on reanalysis data, highlights the major wave events recorded in each monitoring region. In region WAV1 (panel B), the maximum wave event occurred in February 2014, resulting in a 28% increase in strong wave conditions. In region WAV2 (panel C), two notable wave events were identified in November 2009 and February 2014, with increases of 16–18% in strong wave conditions. Similarly, in region WAV3 (panel D), a major event occurred in February 2014, marking one of the most intense events in the region with a 20% increase in storm wave conditions. Additionally, a comparable storm affected the region two months earlier, in December 2013. In region WAV4 (panel E), the most extreme event took place in January 1996, producing a 25% increase in strong wave conditions. Although each monitoring region is generally affected by independent wave events, the analysis reveals several historical events with above-average wave activity that propagated across multiple regions: November–December 2010 (WAV3 and WAV2), February 2014 (WAV1, WAV2, and WAV3), and February–March 2018 (WAV1 and WAV4). The analysis of the near-real-time (NRT) period (from January 2024 onward) identifies a significant event in February 2024 that impacted regions WAV1 and WAV4, resulting in increases of 20% and 15% in strong wave conditions, respectively. For region WAV4, this event represents the second most intense event recorded in the region. '''DOI (product):''' https://doi.org/10.48670/moi-00251
-
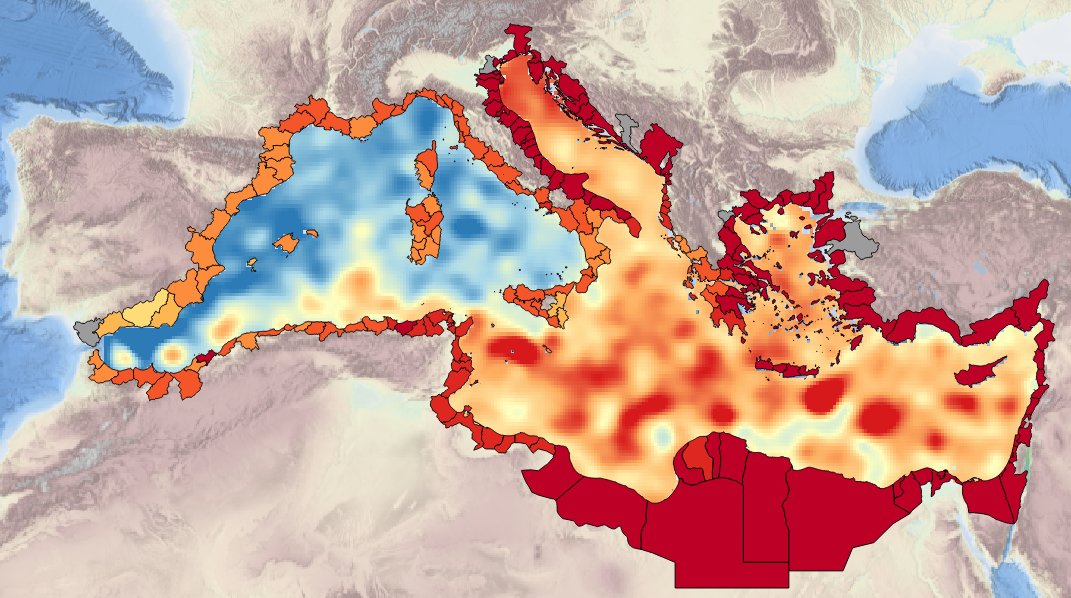
Description ot the spatial layers attributes of sea level trend for the last 50 and 100 years for the Mediterranean basin and for each NUTS3 region along the coast.
-

-

-
-
Today's normative and regulatory requirements to assess the producible energy from wind rely on in situ measurements (mast with anemometric sensors), which are extremely costly to Implement offshore. However, proof should be provided that hindcast model results are highly reliable, in order to provide an equivalent assessment. Very high resolution models is also the key issue in decision making for a proper siting that is relaying on the consistency of all datasets provided in the assessment. In this tender the products of the FP7 MARINA project will be used. 10-year (2001-2010) highresolution atmospheric, wave, tidal and ocean current simulations will be used. The model outputs are at high resolution (0.05x0.05 degree horizontal resolution, 1-hour time resolution, 5-vertical levels at 10,40,80,120,180 m). The wave parameters are co-located with the meteorological output fields. Satellite altimetry data from ENVISAT and JASON satellites have been assimilated in the system. Other wind and wave satellite data sets will be also analyzed (Synthetic Aperture Radars-SAR for example). At the same co-located points the tidal and ocean current data together with bathymetry are available. For preselected points in the North Western Mediterranean (Spain-France-ltaly areas) directional wave spectra data have been saved and are available. From SKIRON meteorological model available parameters are: WIND SPEED (m/s), WIND DIRECTION (deg), AIR PRESSURE (hPa), AIR DENSITY (Kgr/m3), TEMPERATURE (K), MODEL SEAMASK From the wave model available parameters: SIGNIFICANT WAVE HEIGHT (m), MEAN WAVE DIRECTION (deg), WAVE MEAN PERIOD (s), PEAK WAVE PRERIOD (s), SWELL WAVE HEIGHT (m), MEAN SWELL PERIOD (s), MEAN DIRECTIONAL SPREAD, WINDSEA MEAN DIRECTIONAL SPREAD, SWELL MEAN DIRECTIONAL SPREAD, MAXIMUM WAVE HEIGHT (m)
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA