0.25 degree
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Resolution
-
-
Water body silicate - Monthly Climatology for the European Seas for the period 1960-2020 on the domain from longitude -45.0 to 70.0 degrees East and latitude 24.0 to 83.0 degrees North. Data Sources: observational data from SeaDataNet/EMODnet Chemistry Data Network. Description of DIVA analysis: The computation was done with the DIVAnd (Data-Interpolating Variational Analysis in n dimensions), version 2.7.2, using GEBCO 30sec topography for the spatial connectivity of water masses. Horizontal correlation length and vertical correlation length vary spatially depending on the topography and domain. Depth range: 0.0, 5.0, 10.0, 15.0, 20.0, 25.0, 30.0, 35.0, 40.0, 45.0, 50.0, 55.0, 60.0, 65.0, 70.0, 75.0, 80.0, 85.0, 90.0, 95.0, 100.0, 125.0, 150.0, 175.0, 200.0, 225.0, 250.0, 275.0, 300.0, 325.0, 350.0, 375.0, 400.0, 425.0, 450.0, 475.0, 500.0, 550.0, 600.0, 650.0, 700.0, 750.0, 800.0, 850.0, 900.0, 950.0, 1000.0, 1050.0, 1100.0, 1150.0, 1200.0, 1250.0, 1300.0, 1350.0, 1400.0, 1450.0, 1500.0, 1550.0, 1600.0, 1650.0, 1700.0, 1750.0, 1800.0, 1850.0, 1900.0, 1950.0, 2000.0, 2100.0, 2200.0, 2300.0, 2400.0, 2500.0, 2600.0, 2700.0, 2800.0, 2900.0, 3000.0, 3100.0, 3200.0, 3300.0, 3400.0, 3500.0, 3600.0, 3700.0, 3800.0, 3900.0, 4000.0, 4100.0, 4200.0, 4300.0, 4400.0, 4500.0, 4600.0, 4700.0, 4800.0, 4900.0, 5000.0, 5100.0, 5200.0, 5300.0, 5400.0, 5500.0 m. Units: umol/l. The horizontal resolution of the produced DIVAnd analysis is 0.25 degrees.
-
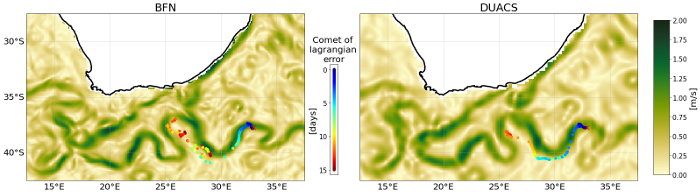
This dataset provides Level 4 total current including geostrophy and a data-driven approach for Ekman and near-inertial current, based on a convolution between drifter observation and wind history, to fit empirically a complex and time-lag dependant transfert function between ERA5 wind stress and current The data are available through HTTP and FTP; access to the data is free and open. In order to be informed about changes and to help us keep track of data usage, we encourage users to register at: https://forms.ifremer.fr/lops-siam/access-to-esa-world-ocean-circulation-project-data/ This dataset was generated by Datlas and is distributed by Ifremer / CERSAT in the frame of the World Ocean Circulation (WOC) project funded by the European Space Agency (ESA).
-
A Group for High Resolution Sea Surface Temperature (GHRSST) global Level 4 sea surface temperature analysis produced daily on a 0.25 degree grid at the NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information. This product uses optimal interpolation (OI) by interpolating and extrapolating SST observations from different sources, resulting in a smoothed complete field. The sources of data are satellite (AVHRR) and in situ platforms (i.e., ships and buoys), and the specific datasets employed may change over. At the marginal ice zone, sea ice concentrations are used to generate proxy SSTs. A preliminary version of this file is produced in near-real time (1-day latency), and then replaced with a final version after 2 weeks. Note that this is the AVHRR-ONLY (AVHRR-OI), available from September 1, 1981, but there is a companion SST product that includes microwave satellite data, available from June 2002.
-
A Group for High Resolution Sea Surface Temperature (GHRSST) global Level 4 sea surface temperature analysis is produced daily on a 0.25 degree grid at the NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information. This product uses optimal interpolation (OI) by interpolating and extrapolating SST observations from different sources, resulting in a smoothed complete field. The sources of data are satellite (AVHRR) and in situ platforms (i.e., ships, buoys, and Argo floats above 5m depth), and the specific datasets employed may change over time. In the regions with sea-ice concentration higher than 30%, freezing points of seawater are used to generate proxy SSTs. A preliminary version of this file is produced in near-real time (1-day latency), and then replaced with a final version after 2 weeks. The v2.1 is updated from the AVHRR_OI-NCEI-L4-GLOB-v2.0 data. Major improvements include: 1) In-Situ ship and buoy data changed from the NCEP Traditional Alphanumeric Codes (TAC) to the NCEI merged TAC + Binary Universal Form for the Representation (BUFR) data, with large increase of buoy data included to correct satellite SST biases; 2) Addition of Argo float observed SST data as well, for further correction of satellite SST biases; 3) Satellite input from the METOP-A and NOAA-19 to METOP-A and METOP-B, removing degraded satellite data; 4) Revised ship-buoy SST corrections for improved accuracy; and 5) Revised sea-ice-concentration to SST conversion to remove warm biases in the Arctic region (Banzon et al. 2020). These updates only apply to granules after Jan. 1st, 2016. The data pre 2016 are still the same as v2.0 except for metadata upgrades.
-
-
The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) Microwave Imager (TMI) is a well calibrated passive microwave radiometer, similar to the Special Sensor Microwave Imager (SSM/I), that contains lower frequency channels required for sea surface temperature (SST) retrievals. The TRMM is part of the NASA's mission to planet Earth, and is a joint venture between NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) to measure precipitation, water vapor, sea surface temperature (SST) and surface wind in the global tropical regions and was launched in 27 November 1997 from the Tanegashima Space Center in Tanegashima, Japan. The TRMM satellite travels west to east in a 402 km altitude semi-equatorial processing orbit that results in day-to-day changes in the observation time of any given earth location between 38S and 38N. Remote Sensing Systems (REMSS) has produced a Version-7.1a TMI SST dataset for the Group for High Resolution Sea Surface Temperature (GHRSST) by applying an algorithm to the 10.7 GHz channel through a removal of surface roughness effects. In contrast to infrared SST observations, microwave retrievals can be measured through clouds, which are nearly transparent at 10.7 GHz. Microwave retrievals are also insensitive to water vapor and aerosols. The algorithm for retrieving SSTs from radiometer data is described in "AMSR Ocean Algorithm."
-

-
A Group for High Resolution Sea Surface Temperature (GHRSST) global Level 4 sea surface temperature analysis is produced daily on a 0.25 degree grid at the NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information. This product uses optimal interpolation (OI) by interpolating and extrapolating SST observations from different sources, resulting in a smoothed complete field. The sources of data are satellite (AVHRR) and in situ platforms (i.e., ships, buoys, and Argo floats above 5m depth), and the specific datasets employed may change over time. In the regions with sea-ice concentration higher than 30%, freezing points of seawater are used to generate proxy SSTs. A preliminary version of this file is produced in near-real time (1-day latency), and then replaced with a final version after 2 weeks. The v2.1 is updated from the AVHRR_OI-NCEI-L4-GLOB-v2.0 data. Major improvements include: 1) In-Situ ship and buoy data changed from the NCEP Traditional Alphanumeric Codes (TAC) to the NCEI merged TAC + Binary Universal Form for the Representation (BUFR) data, with large increase of buoy data included to correct satellite SST biases; 2) Addition of Argo float observed SST data as well, for further correction of satellite SST biases; 3) Satellite input from the METOP-A and NOAA-19 to METOP-A and METOP-B, removing degraded satellite data; 4) Revised ship-buoy SST corrections for improved accuracy; and 5) Revised sea-ice-concentration to SST conversion to remove warm biases in the Arctic region (Banzon et al. 2020). These updates only apply to granules after Jan. 1st, 2016. The data pre 2016 are still the same as v2.0 except for metadata upgrades. Version Description:
-
Water body phosphate - Monthly Climatology for the European Seas for the period 1960-2020 on the domain from longitude -45.0 to 70.0 degrees East and latitude 24.0 to 83.0 degrees North. Data Sources: observational data from SeaDataNet/EMODnet Chemistry Data Network. Description of DIVA analysis: The computation was done with the DIVAnd (Data-Interpolating Variational Analysis in n dimensions), version 2.7.2, using GEBCO 30sec topography for the spatial connectivity of water masses. Horizontal correlation length and vertical correlation length vary spatially depending on the topography and domain. Depth range: 0.0, 5.0, 10.0, 15.0, 20.0, 25.0, 30.0, 35.0, 40.0, 45.0, 50.0, 55.0, 60.0, 65.0, 70.0, 75.0, 80.0, 85.0, 90.0, 95.0, 100.0, 125.0, 150.0, 175.0, 200.0, 225.0, 250.0, 275.0, 300.0, 325.0, 350.0, 375.0, 400.0, 425.0, 450.0, 475.0, 500.0, 550.0, 600.0, 650.0, 700.0, 750.0, 800.0, 850.0, 900.0, 950.0, 1000.0, 1050.0, 1100.0, 1150.0, 1200.0, 1250.0, 1300.0, 1350.0, 1400.0, 1450.0, 1500.0, 1550.0, 1600.0, 1650.0, 1700.0, 1750.0, 1800.0, 1850.0, 1900.0, 1950.0, 2000.0, 2100.0, 2200.0, 2300.0, 2400.0, 2500.0, 2600.0, 2700.0, 2800.0, 2900.0, 3000.0, 3100.0, 3200.0, 3300.0, 3400.0, 3500.0, 3600.0, 3700.0, 3800.0, 3900.0, 4000.0, 4100.0, 4200.0, 4300.0, 4400.0, 4500.0, 4600.0, 4700.0, 4800.0, 4900.0, 5000.0, 5100.0, 5200.0, 5300.0, 5400.0, 5500.0 m. Units: umol/l. The horizontal resolution of the produced DIVAnd analysis is 0.25 degrees.
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA