notPlanned
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
Resolution
-

The coastal topobathymetric DEM of Ré Island's surroundings, with a resolution of 0.00005° (~5 meters), was created by Shom as part of the HOMONIM-3 project. It covers the coast of the municipalities of Ars-en-Ré and Saint-Clément-des-Baleines, extending offshore to a depth of about 20 meters, to the west of the Phare des Baleines lighthouse. This DEM is designed for use in hydrodynamic models to enhance the modeling of coastal processes, particularly forecasting submersion risk. The product complements the coastal topobathymetric DEM of the Pertuis-Charentais, with a resolution of 0.0002° (~20 meters), and the bathymetric DEM of the Atlantic coast, with a resolution of 0.001° (~100 meters). It is available in the vertical reference of the Lowest Astronomical Tide (LAT) or the Mean Sea Level (MSL).
-

-

-
-

-

This metadata refers to a dataset that shows the percentage of cities' administrative area (core city based on the Urban Morphological Zones dataset) inundated by the sea level rise of 2 metres, without any coastal flooding defences present for a series of individual coastal European cities (included in Urban Audit). The dataset has been computed using the CReSIS (Centre for Remote Sensing of Ice Sheets) dataset for 2018.
-
-
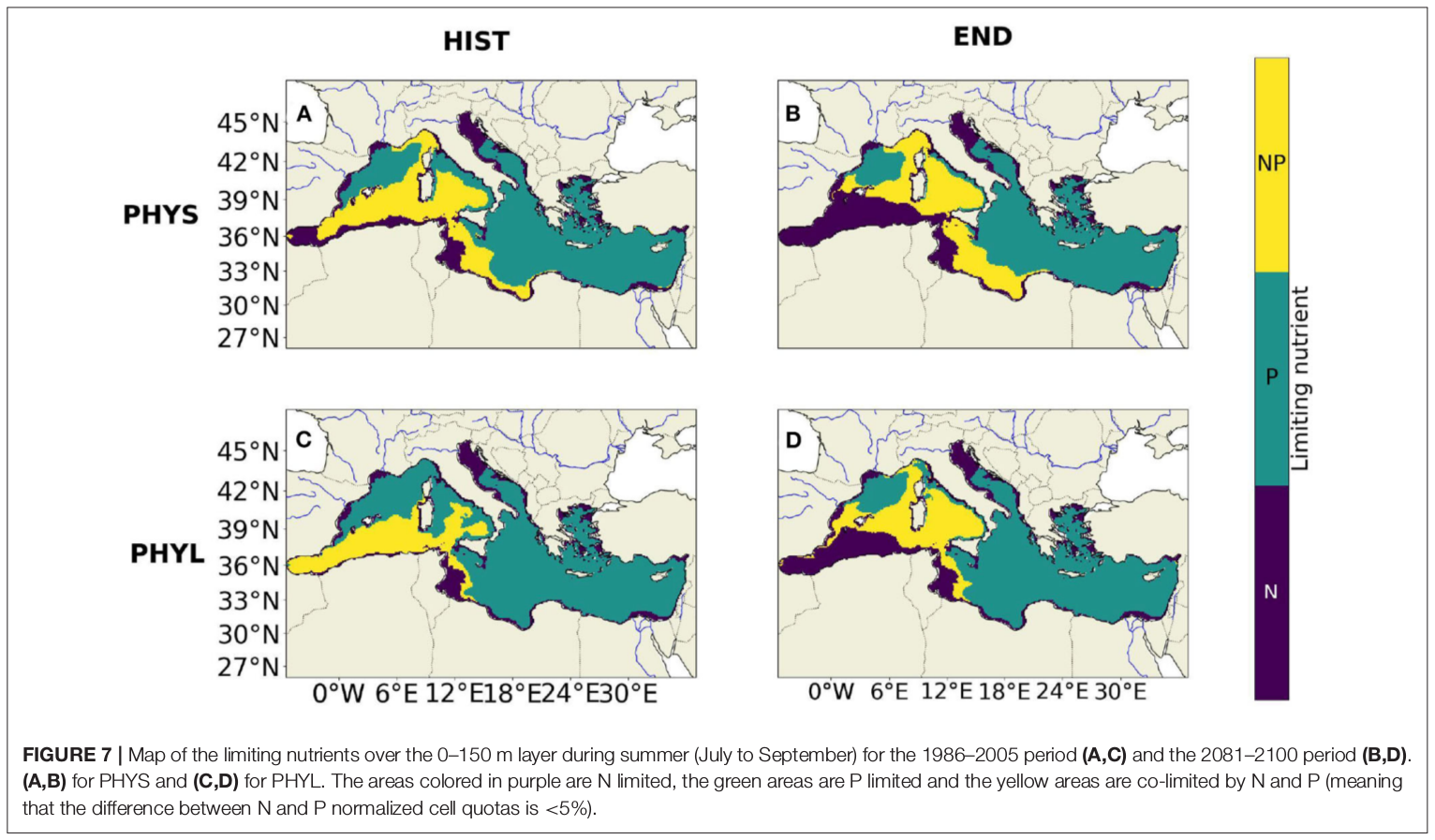
"Towards an integrated prediction of Land & Sea Responses to global change in the Mediterranean Basin" The LaSeR-Med project aims at investigating the effects of climate change and of mediterranean population growth on some major indicators of the Mediterranean Sea (primary production, carbon export, zooplankton biomass available for small pelagic fishes, pH, dissolved oxygen) using and integrated model encompassing a socio-economic model, a continental model of agro-ecosystems, and a physical ocean-atmosphere model coupled to a biogeochemical model of the ocean. Last, a model for the widespread species of jellyfish Pelagia Noctiluca (Berline et al., 2013) uses biogeochemical outputs as food forcing for the jellyfish. In this project, our aim was first to investigate the large-scale and long-term impacts of variations in river inputs on the biogeochemistry of the Mediterranean Sea over the last decades (see Pages et al., 2020a). In the second phase, a climate scenario (RCP8.5) alone (Pages et al., 2020b) or combined with a “land-use” scenario derived to ensure the same level of food availability as today in 2050 have been run to investigate its effect on these indicators and to analyze the observed changes on the structure and the functioning of planktonic food web. This interdisciplinary project provided the framework for joint discussions on each of the sub-models that constitute the integrated model, namely the socio-economic model (Ami et al., in prep., Mardesic et al., in prep.) created ex nihilo by researchers from AMSE, INRA and GREQAM, the continental agro-ecosystem model LPJmL (Bondeau et al., 2007) worked on at IMBE so as to include the nitrogen and phosphorous cycles in the frame of the present project, and the ocean biogeochemical model Eco3M-Med developed at MIO (Baklouti et al., 2006; Alekseenko et al. 2014, Guyennon et al., 2015; Pagès et al., 2020a), forced by ocean physics, either using the ocean model NEMO-Med12 forced by atmosphere at IPSL (simulation NM12-FREE run with the NEMO-MED12 model and used for our hindcast simulation, see below) or a coupled ocean-atmosphere model at CNRM (physical forcing provided by CNRM-RCSM4, see below). Details on the CNRM-RCSM4 model The CNRM-RCSM4 simulates the main components of the Mediterranean regional climate system and their interactions. It includes four different components: (i) The atmospheric regional model ALADIN-Climate (Radu et al., 2008; Colin et al., 2010; Herrmann et al., 2011) characterized by a 50 km horizontal resolution, 31 vertical levels, and a time step of 1800 s, (ii) the ISBA (Interaction between Soil Biosphere and Atmosphere) land-surface model (Noilhan and Mahfouf, 1996) at a 50 km horizontal resolution, (iii) the TRIP (Total Runoff Integrating Pathways) river routing model (Oki and Sud, 1998), used to convert the runoff simulated by ISBA into rivers (Decharme et al., 2010; Szczypta et al., 2012; Voldoire et al., 2013), and (iv) the Ocean general circulation model NEMO (Nucleus for European Modeling of the Ocean, Madec and NEMO-Team, 2016) in its NEMO-MED8 regional configuration (Beuvier et al., 2010). NEMO-MED8 is characterized by a horizontal resolution of 1/8° (grid cells size from 6 to 12 km), a vertical resolution of 43 vertical levels (cell height ranging from 6 to 200 m), and a time step of 1200 s. More details about the CNRM-RCSM4 model can be found in Sevault et al. (2014). Keywords: - Mediterranean Sea, river inputs, chlorophyll, nutrients, phytoplankton, bacteria, zooplankton, dissolved and particulate organic detrital matter Citation: Pagès, R., Baklouti, M., Barrier, N., Richon, C., Dutay, J.-C., and Moutin, T. (2020a). Changes in rivers inputs during the last decades significantly impacted the biogeochemistry of the eastern Mediterranean basin: a modelling study. Prog. Oceanogr. 181:102242. doi:10.1016/j.pocean.2019.102242 Pagès, R., Baklouti, M., Barrier, N., Ayache, M., Sevault, F., Somot, S. and Moutin, T. (2020b). Projected Effects of Climate-Induced Changes in Hydrodynamics on the Biogeochemistry of the Mediterranean Sea Under the RCP 8.5 Regional Climate Scenario. Front. Mar. Sci. 7:563615. doi:10.3389/fmars.2020.563615 Ayache, M., Bondeau, A., Pagès, R., Barrier, N., Ostberg, S. and Baklouti, M. (2020). LPJmL-Med – Modelling the dynamics of the land-sea nutrient transfer over the Mediterranean region–version 1: Model description and evaluation. Geoscientific Model Development Discussions, Copernicus Publ.
-

-
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA