Human activities
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
Resolution
-
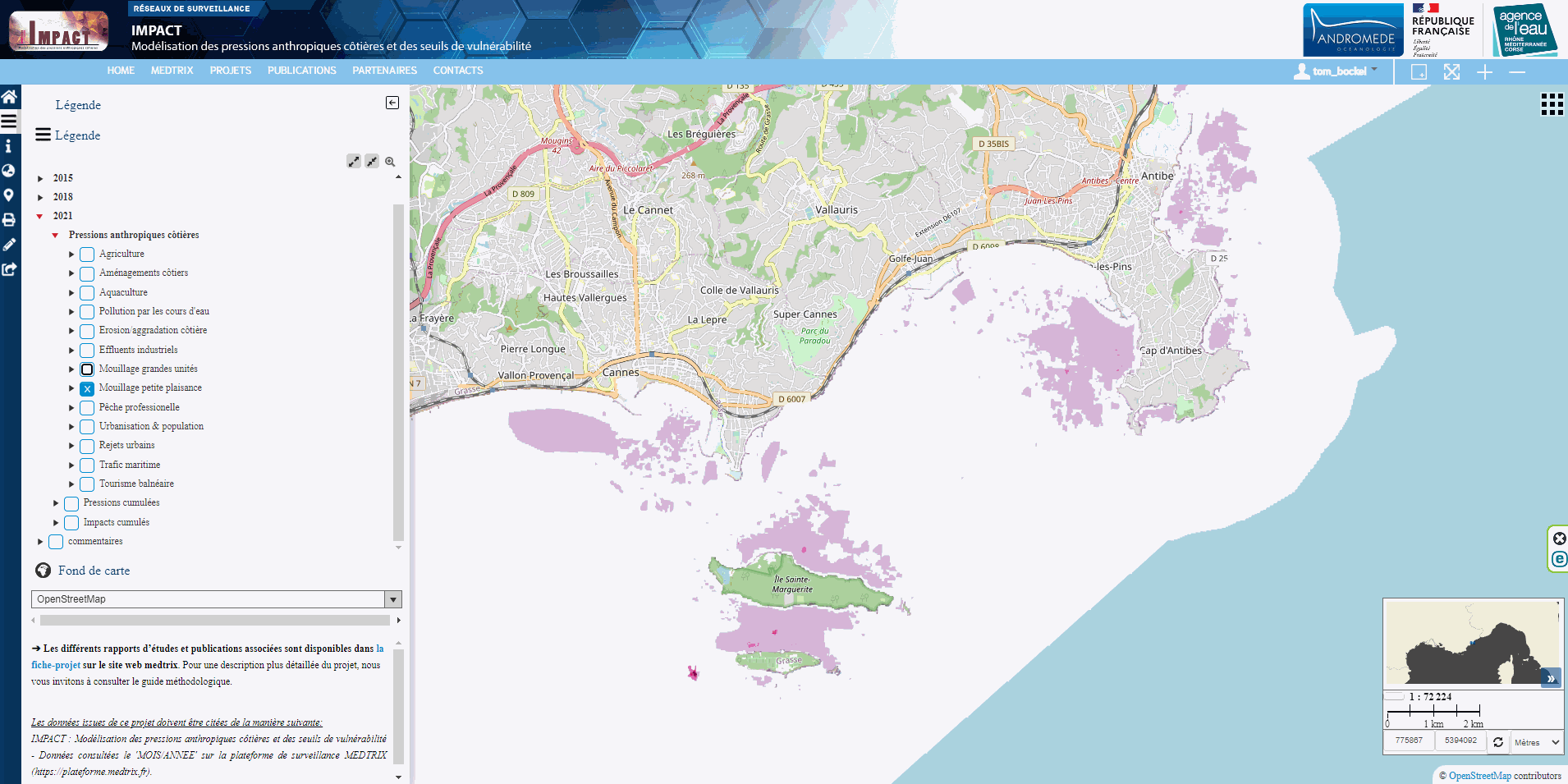
This dataset contains maps of 13 anthropogenic pressures (one pressure per map), modeled according to the methodology used by Holon et al. (2015), and updated with the latest available data on human activities in 2021. This dataset is available for visualization on the Medtrix cartographic platform (http://www.medtrix.fr, free access after registration). More details can be found on the methodology and modeling approach on the medtrix website (https://medtrix.fr/en/portfolio_page/impact-2/) and on the 2018 IMPACT update report (only available in French at the moment). The modeling and mapping was performed using R software V 4.0. Table 1 lists the modeled anthropogenic pressures, the modeling approach and the data used. The spatial resolution of the raster layers is 500 m, the coordinate reference system (CRS) of the raster layers is RGF93 / Lambert-93 (EPSG 2154). The values of each layer range from 0 (no pressure) to 1 (max modeled pressure over the study area), and is unitless. All pressures are modeled over the spatial extent of the French mediterranean coastal habitat map (www.medtrix.fr, “DONIA expert” project), except for professional fishing and marine traffic, that are modeled over the entire French Mediterranean sea. The ZIP archive contains a tif raster composed of 13 layers corresponding to the 13 modeled pressures. All data acquired are publicly accessible without any restriction (under CC-BY licence).
-
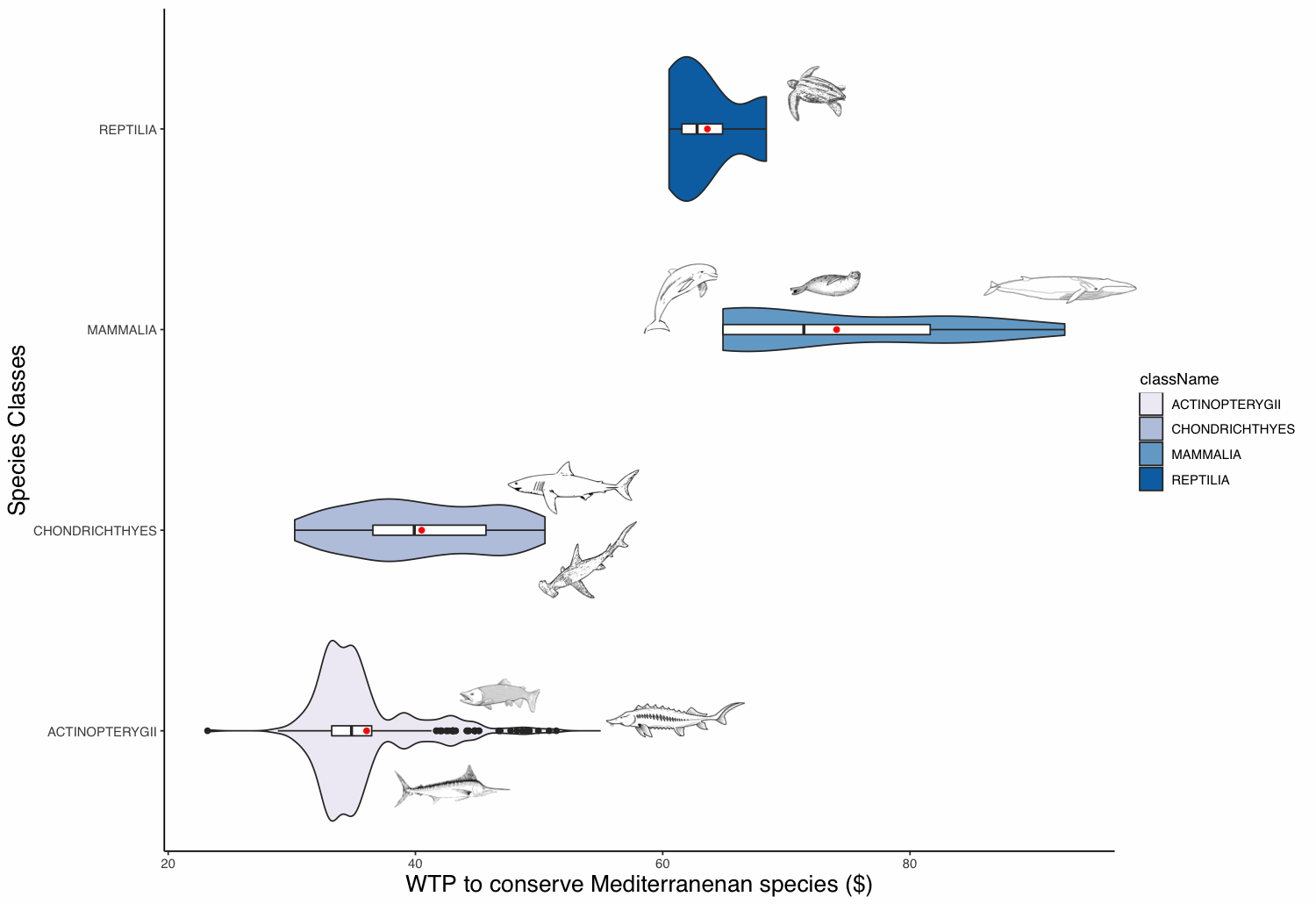
The willingness to pay (WTP) of people to protect animal populations can be used as a tool for these populations’ conservation. The WTP reflects the non-use value of animals, which can be significant for charismatic species. This value can be used as an economic criterion for decision-makers in order to recommend protective measures. The definition of the WTP to protect a species is challenging, as valuation methods are time-consuming and expensive. To overcome these limitations, we built a benefit transfer function based on 112 valuation studies and apply it to 440 Mediterranean marine species. We extracted these species from the IUCN database and retrieved some required parameters from, amongst others, the FishBase database. Marine mammals appear to have the highest WTP value followed in order by sea turtles, sharks and rays, and ray-finned fishes. Commercial fish species appear to have the highest values amongst the fish class.
-
List of fish stocks referenced for the year 2018. The repository includes 477 stocks. Each stock is identified by a unique key in accordance with the ICES codification in use. Each record contains a stock identifier, a species or group of species identifier according to the ASFIS/FAO classification, the English stock name, the Latin name of the species, the assessment area according to the FAO codification of fishing sectors. When the stock assessment area groups a series of sectors, the first and last sectors in the series are separated by a dash.
-
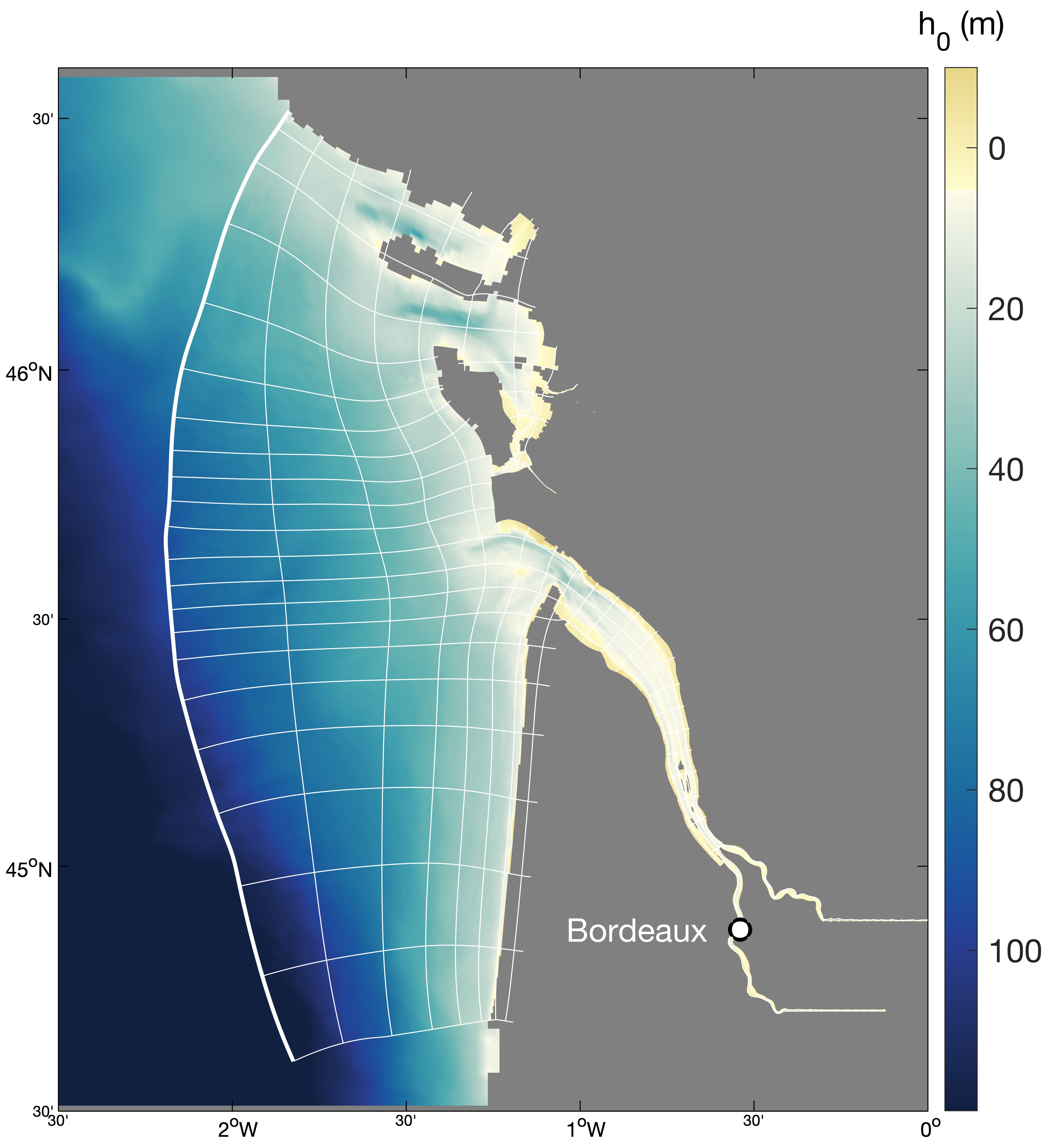
Hydrodynamics and sediment dynamics hindcast in the Gironde Estuary (France), produced by coupling the hydrodynamics model MARS3D (with sediment dynamics module MUSTANG) and wave spectral model WAVEWATCH III®.
-
-

-

-
We have to create an account on medtrix and then download the data ( request online)
-
-
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA