/Environment/Habitat
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
status
Scale
Resolution
-
Accredited through the MEDIN partnership, and core-funded by the Department for the Environment, Food and Rural Affairs (Defra) and the Scottish Government, DASSH provides tools and services for the long-term curation, management and publication of marine species and habitats data, within the UK and internationally. Below are a selection of projects, outputs and deliverables that DASSH and the MBA Data Team have been involved in recently. - NE Data Management: DASSH have been contracted by the Marine team at Natural England (NE) to support NE data dissemination. We have been digitising datasets used in Article 17 reporting and helping them input data to Marine Recorder and MEDIN guidelines. In addition, DASSH is running a 2-day workshop with the marine data team in October 2014 on data management and standards. The aims of the workshop are to present MEDIN data guidelines and standards and to run practicals on quality assurance (QA) issues with data, creating MEDIN formatted data, and creation of MEDIN metadata. - MCZ Data Archiving: DASSH staff have been working with Defra, JNCC, Natural England, Cefas and the other MEDIN DAC's in the development and implementation of a strategy for the archiving and dissemination of MCZ survey data. This involves the archives of many terrabytes of data from the survey work undertaken at 127 sites. DASSH is currently working with the other DACs archiving the data from several MCZ sites before taking delivery of the complete survey catalogue. - Non-Natives Data Management: DASSH staff work with other members of the KE team to help deliver the MBA contribution to the GB Non-native Species Information Portal. The data team ensure the validation of records submitted and raise alerts when records of Invasive Non-Native Species of concern and in disseminating information about species distribution via DASSH and the NBN. DASSH staff continue to liaise with organisations to ensure the prompt flow of marine non-native species distribution data to the public domain. The KE team facilitated the identification of two new marine invasive non-native species in 2014 and have subsequently created the identification sheet for these species. Hemigrapsus sanguineus (from volunteer records sent in for identification) and Hemigrapsus takanoi (first recorded by the John Bishop Group survey team). - EMODNet Biology: The Data Team are part of a consortium led by the Flanders Marine Institute (VLIZ) for the biological data component of EMODNet (European Marine Observation and Data Network). The Data Team will lead a work package relating to biological traits and indicator species as identified for Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD) reporting, bringing an additional €130k of funding. - VALMER: The Data Team led a key work package in a £3.7 million (ca. €260k for the MBA) INTERREG project to "Develop, trial and refine methodologies that will be used to quantify and communicate the value (economical, social and environmental) of marine and coastal ecosystem services". The research identified an operational framework to value marine ecosystem services, and which could be used to enhance marine planning and policy decisions.
-
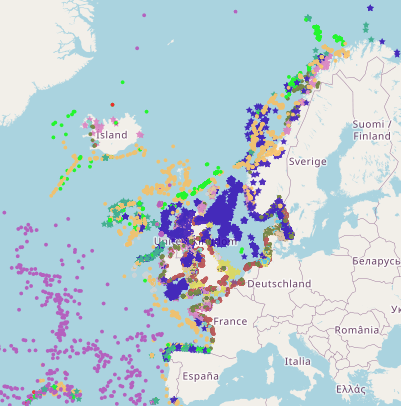
This is a compilation of OSPAR habitat point data for the northeast Atlantic submitted by OSPAR contracting parties. The compilation is coordinated by the UK's Joint Nature Conservation Committee, working with a representative from each of the OSPAR coastal contracting parties. This public dataset does not contain records relating to sensitive species (e.g. Ostrea edulis) in specific areas, or where data are restricted from public release by the owner's use limitations. This version (v2020) was published in July 2021.
-
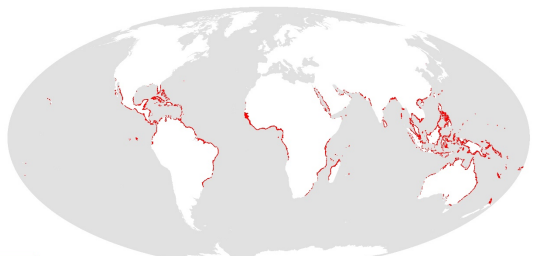
This dataset shows the global distribution of mangroves, and was produced as joint initiatives of the International Tropical Timber Organization (ITTO), International Society for Mangrove Ecosystems (ISME), Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), UN Environment World Conservation Monitoring Centre (UNEP-WCMC), United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization’s Man and the Biosphere Programme (UNESCO-MAB), United Nations University Institute for Water, Environment and Health (UNU-INWEH) and The Nature Conservancy (TNC). Major funding was provided by ITTO through a Japanese Government project grant; the project was implemented by ISME.
-
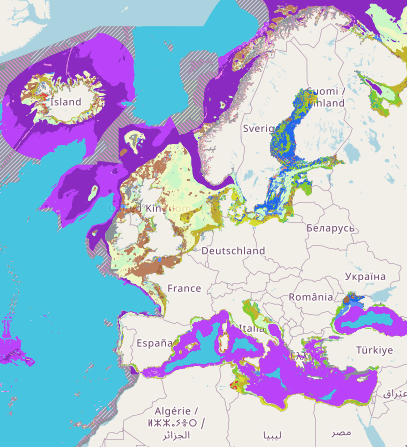
Output of the 2019 EUSeaMap broad-scale predictive model, produced by EMODnet Seabed Habitats and aggregated into the Benthic Broad Habitat Types of the Marine Strategy Framework Directive (as defined in the Commission Decision 17 May 2017). The extent of the mapped area includes the Mediterranean Sea, Black Sea, Baltic Sea, and areas of the North Eastern Atlantic extending from the Canary Islands in the south to the Barents Sea in the north. The map was produced using a "top-down" modelling approach using classified habitat descriptors to determine a final output habitat. Habitat descriptors differ per region but include: - Biological zone - Energy class - Oxygen regime - Salinity regime - Seabed substrate - Riverine input Habitat descriptors (excepting Substrate) are calculated using underlying physical data and thresholds derived from statistical analyses or expert judgement on known conditions.
-

This layer shows the current known extent and distribution of live hard coral cover in European waters, collated by EMODnet Seabed Habitats. The polygons portion was last updated in 2019. The points were added in Sept 2021. Lophelia pertusa and Coral gardens are both on the OSPAR List of threatened and/or declining species and habitats. The purpose was to produce a data product that would provide the best compilation of evidence for the essential ocean variable (EOV) known as Hard coral cover and composition (sub-variable: Live hard coral cover and extent), as defined by the Global Ocean Observing System (GOOS). This data product should be considered a work in progress and is not an official product.
-
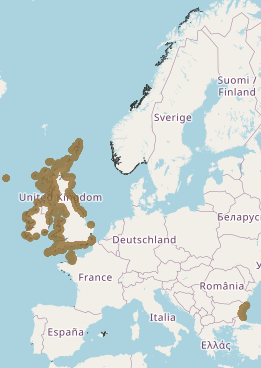
This layer shows the current known extent and distribution of macroalgal canopy in European waters, collated by EMODnet Seabed Habitats. The polygons portion was last updated in 2019. The points were added in Sept 2021. The purpose was to produce a data product that would provide the best compilation of evidence for the essential ocean variable (EOV) known as Macroalgal canopy cover and composition (sub-variable: Areal extent), as defined by the Global Ocean Observing System (GOOS). Kelp and fucoid brown algae are the dominant species that comprise macroalgal forests. This data product should be considered a work in progress and is not an official product.
-

Seabed Habitats was one of seven themes of the European Marine Observation and Data Network (EMODnet) initiative, funded by the European Maritime and Fisheries Fund. Since its inception in 2009, EMODnet Seabed Habitats developed, improved and gradually increased the coverage of a broad-scale seabed habitat map for Europe's seabed, also known as EUSeaMap. In addition, EMODnet Seabed Habitats continued the work started by MESH and MESH Atlantic projects in collating and making available seabed habitat maps from surveys, through the EMODnet Seabed Habitats map viewer. In it's third Phase (2017-2019), EMODnet Seabed Habitats collated and provided habitat point data and the outputs of habitat distribution modelling, and the third phase has now been extended to 2021. The extended third phase of the project will: - Continue to grow Europe's only comprehensive library of habitat maps from surveys and collection of survey sample points - Create new composite data products to add to those for the Essential Ocean Variable habitats and OSPAR threatened and/or declining habitats - Update the EMODnet broad-scale seabed habitat map for Europe (EUSeaMap) using the next seabed substrate update from EMODnet Geology - Update web content with extra resources for habitat mapping, including a catalogue highlighting all the most useful data products
-

Portal to view and download observations of Vulnerable Marine Ecosystem (VME) indicators and habitats in the North Atlantic. A central portal for data on the distribution and abundance of Vulnerable Marine Ecosystems (VMEs), (and organisms considered to be indicators of VMEs) across the North Atlantic has been set up by the Joint ICES/NAFO Working Group on Deep-water Ecology (WGDEC). Criteria used to select habitats and indicators for inclusion in the database were those described in the FAO International Guidelines for the Management of Deep-sea Fisheries in the High Seas (FAO, 2009). The database is comprised of: - 'VME habitats' that are records for which there is unequivocal evidence for a VME, e.g. ROV observations of a coral reef - 'VME indicators' which are records that suggest the presence of a VME with varying degrees of uncertainty. For VME indicators a weighting system of vulnerability and uncertainty is provided as part of the database to aid interpretation. The VME database may be used for many purposes. ICES uses it when providing scientifically-robust advice on the distribution of VMEs and recommending possible management solutions such as bottom fishing closures within North East Atlantic Fisheries Commission (NEAFC) waters to protect VMEs.
-
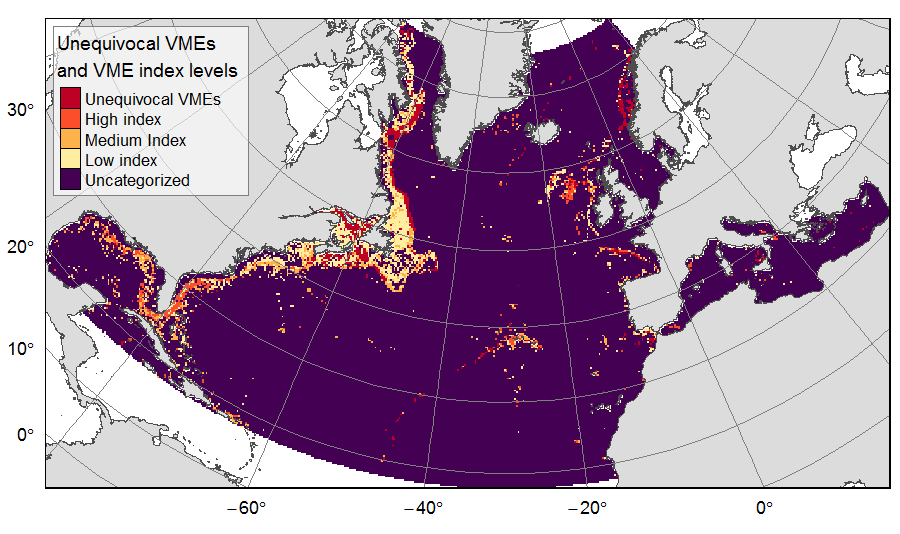
Distribution of unequivocal Vulnerable Marine Ecosystems (VMEs) and VME likelihood based on indicator taxa records, on the North Atlantic (18°N to 76°N and 36°E to 98°W). Several datasets, originating from public databases, literature review and data call to ATLAS partners, were gathered to compute the presence of unequivocal VME habitats in 25km * 25 km cells for the ATLAS work package 3. One layer displays the unequivocal VMEs (value=4) and the assigned high (value=3), medium (value=2) or low (value=1) likelihood of gridsquares to host VMEs, indexed on indicator taxa records from public databases with the method detailed in Morato et al (2018). The second displays the confidence associated to the VME likelihood score, indexed on data quality as detailed in Morato et al (2018) (values for unequivocal VMEs thus 100% confidence=4; high confidence=3; medium confidence=2; low confidence=1). This dataset was built to feed a basin-wide spatial conservation planning exercise, targeting the deep sea of the North Atlantic. The goal of this approach was to identify conservation priority areas for Vulnerable Marine Ecosystems (VMEs) and deep fish species, based on the distribution of species and habitats, human activities and current spatial management.
-

The Sea Around Us is a research initiative at The University of British Columbia (located at the Institute for the Oceans and Fisheries, formerly Fisheries Centre) that assesses the impact of fisheries on the marine ecosystems of the world, and offers mitigating solutions to a range of stakeholders. The Sea Around Us was initiated in collaboration with The Pew Charitable Trusts in 1999, and in 2014, the Sea Around Us also began a collaboration with The Paul G. Allen Family Foundation to provide African and Asian countries with more accurate and comprehensive fisheries data. It provides data and analyses through View Data, articles in peer-reviewed journals, and other media (News). We regularly update our products at the scale of countries’ Exclusive Economic Zones, Large Marine Ecosystems, the High Seas and other spatial scales, and as global maps and summaries. It emphasises catch time series starting in 1950, and related series (e.g., landed value and catch by flag state, fishing sector and catch type), and fisheries-related information on every maritime country (e.g., government subsidies, marine biodiversity). Information is also offered on sub-projects, e.g., the historic expansion of fisheries, the performance of Regional Fisheries Management Organizations, or the likely impact of climate change on fisheries. The information and data presented on this website is freely available to any user, granted that its source is acknowledged. We are aware that this information may be incomplete. Please let us know about this via the feedback options available on this website.
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA