CMEMS
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Resolution
-
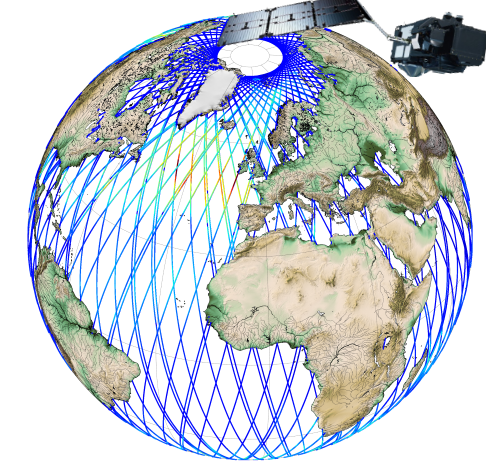
Hauteurs significatives de vagues (SWH) et vitesse du vent, mesurées le long de la trace par les satellites altimétriques CFOSAT (nadir), Sentinel-3A et Sentinel-3B, Jason-3, Saral-AltiKa, Cryosat-2 et HY-2B, en temps quasi-réel (NRT), sur une couverture globale (-66°S/66+N pour Jason-3, -80°S/80°N pour Sentinel-3A et Saral/AltiKa). Un fichier contenant les SWH valides est produit pour chaque mission et pour une fenêtre de temps de 3 heures. Il contient les SWH filtrées (VAVH), les SWH non filtrées (VAVH_UNFILTERED) et la vitesse du vent (wind_speed). Les mesures de hauteurs de vagues sont calculées à partir du front de montée de la forme d'onde altimétrique. Pour Sentinel-3A et 3B, elles sont déduites de l'altimètre SAR.
-

'''DEFINITION''' Heat transport across lines are obtained by integrating the heat fluxes along some selected sections and from top to bottom of the ocean. The values are computed from models’ daily output. The mean value over a reference period (1993-2014) and over the last full year are provided for the ensemble product and the individual reanalysis, as well as the standard deviation for the ensemble product over the reference period (1993-2014). The values are given in PetaWatt (PW). '''CONTEXT''' The ocean transports heat and mass by vertical overturning and horizontal circulation, and is one of the fundamental dynamic components of the Earth’s energy budget (IPCC, 2013). There are spatial asymmetries in the energy budget resulting from the Earth’s orientation to the sun and the meridional variation in absorbed radiation which support a transfer of energy from the tropics towards the poles. However, there are spatial variations in the loss of heat by the ocean through sensible and latent heat fluxes, as well as differences in ocean basin geometry and current systems. These complexities support a pattern of oceanic heat transport that is not strictly from lower to high latitudes. Moreover, it is not stationary and we are only beginning to unravel its variability. '''CMEMS KEY FINDINGS''' The mean transports estimated by the ensemble global reanalysis are comparable to estimates based on observations; the uncertainties on these integrated quantities are still large in all the available products. Note: The key findings will be updated annually in November, in line with OMI evolutions. '''DOI (product):''' https://doi.org/10.48670/moi-00245
-

'''DEFINITION''' Variations of the Mediterranean Outflow Water at 1000 m depth are monitored through area-averaged salinity anomalies in specifically defined boxes. The salinity data are extracted from several CMEMS products and averaged in the corresponding monitoring domain: * IBI-MYP: IBI_MULTIYEAR_PHY_005_002 * IBI-NRT: IBI_ANALYSISFORECAST_PHYS_005_001 * GLO-MYP: GLOBAL_REANALYSIS_PHY_001_030 * CORA: INSITU_GLO_TS_REP_OBSERVATIONS_013_002_b * ARMOR: MULTIOBS_GLO_PHY_TSUV_3D_MYNRT_015_012 The anomalies of salinity have been computed relative to the monthly climatology obtained from IBI-MYP. Outcomes from diverse products are combined to deliver a unique multi-product result. Multi-year products (IBI-MYP, GLO,MYP, CORA, and ARMOR) are used to show an ensemble mean and the standard deviation of members in the covered period. The IBI-NRT short-range product is not included in the ensemble, but used to provide the deterministic analysis of salinity anomalies in the most recent year. '''CONTEXT''' The Mediterranean Outflow Water is a saline and warm water mass generated from the mixing processes of the North Atlantic Central Water and the Mediterranean waters overflowing the Gibraltar sill (Daniault et al., 1994). The resulting water mass is accumulated in an area west of the Iberian Peninsula (Daniault et al., 1994) and spreads into the North Atlantic following advective pathways (Holliday et al. 2003; Lozier and Stewart 2008, de Pascual-Collar et al., 2019). The importance of the heat and salt transport promoted by the Mediterranean Outflow Water flow has implications beyond the boundaries of the Iberia-Biscay-Ireland domain (Reid 1979, Paillet et al. 1998, van Aken 2000). For example, (i) it contributes substantially to the salinity of the Norwegian Current (Reid 1979), (ii) the mixing processes with the Labrador Sea Water promotes a salt transport into the inner North Atlantic (Talley and MacCartney, 1982; van Aken, 2000), and (iii) the deep anti-cyclonic Meddies developed in the African slope is a cause of the large-scale westward penetration of Mediterranean salt (Iorga and Lozier, 1999). Several studies have demonstrated that the core of Mediterranean Outflow Water is affected by inter-annual variability. This variability is mainly caused by a shift of the MOW dominant northward-westward pathways (Bozec et al. 2011), it is correlated with the North Atlantic Oscillation (Bozec et al. 2011) and leads to the displacement of the boundaries of the water core (de Pascual-Collar et al., 2019). The variability of the advective pathways of MOW is an oceanographic process that conditions the destination of the Mediterranean salt transport in the North Atlantic. Therefore, monitoring the Mediterranean Outflow Water variability becomes decisive to have a proper understanding of the climate system and its evolution (e.g. Bozec et al. 2011, Pascual-Collar et al. 2019). The CMEMS IBI-OMI_WMHE_mow product is aimed to monitor the inter-annual variability of the Mediterranean Outflow Water in the North Atlantic. The objective is the establishment of a long-term monitoring program to observe the variability and trends of the Mediterranean water mass in the IBI regional seas. To do that, the salinity anomaly is monitored in key areas selected to represent the main reservoir and the three main advective spreading pathways. More details and a full scientific evaluation can be found in the CMEMS Ocean State report Pascual et al., 2018 and de Pascual-Collar et al. 2019. '''CMEMS KEY FINDINGS''' The absence of long-term trends in the monitoring domain Reservoir (b) suggests the steadiness of water mass properties involved on the formation of Mediterranean Outflow Water. Results obtained in monitoring box North (c) present an alternance of periods with positive and negative anomalies. The last negative period started in 2016 reaching up to the present. Such negative events are linked to the decrease of the northward pathway of Mediterranean Outflow Water (Bozec et al., 2011), which appears to return to steady conditions in 2020 and 2021. Results for box West (d) reveal a cycle of negative (2015-2017) and positive (2017 up to the present) anomalies. The positive anomalies of salinity in this region are correlated with an increase of the westward transport of salinity into the inner North Atlantic (de Pascual-Collar et al., 2019), which appear to be maintained for years 2020-2021. Results in monitoring boxes North and West are consistent with independent studies (Bozec et al., 2011; and de Pascual-Collar et al., 2019), suggesting a westward displacement of Mediterranean Outflow Water and the consequent contraction of the northern boundary. Note: The key findings will be updated annually in November, in line with OMI evolutions. '''DOI (product):''' https://doi.org/10.48670/moi-00258
-

'''Short description:''' For the Baltic Sea- The DMI Sea Surface Temperature reprocessed analysis provides daily gap-free sea surface temperature fields, referred as L4 product, at 0.02deg. x 0.02deg. horizontal resolution. It is produced by the DMI Optimal Interpolation (DMIOI) system (Høyer and She, 2007) to provide a high resolution (1/50deg. - approx. 2km grid resolution) daily analysis of the daily average sea surface temperature (SST) at 20 cm depth. It uses satellite data from infra-red radiometers, from the ESA SST_cci v3.0 (Embury et al., 2024) and Copernicus C3S projects, namely L2P data from (A)ATSRs, SLSTR and AVHRR for the period 1982-2021, L3U data from SLSTR and AVHRR for 2022-July 19 2024 and L2P data from SLSTR and AVHRR from July 20 2024 onward. For the Sea Ice Concentration it uses the Baltic high resolution sea ice concentration data from the Copernicus Marine Service SI TAC (SEAICE_BAL_PHY_L4_MY_011_019). '''DOI (product) :''' https://doi.org/10.48670/moi-00156
-
North Atlantic Ocean Colour Plankton, Reflectance, Transparency and Optics L3 NRT daily observations

'''Short description: ''' For the '''Atlantic''' Ocean '''Satellite Observations''', ACRI-ST company (Sophia Antipolis, France) is providing '''Bio-Geo-Chemical (BGC)''' products based on the '''Copernicus-GlobColour''' processor. * Upstreams: SeaWiFS, MODIS, MERIS, VIIRS-SNPP & JPSS1, OLCI-S3A & S3B for the '''""multi""''' products, and S3A & S3B only for the '''""olci""''' products. * Variables: Chlorophyll-a ('''CHL'''), Gradient of Chlorophyll-a ('''CHL_gradient'''), Phytoplankton Functional types and sizes ('''PFT'''), Suspended Matter ('''SPM'''), Secchi Transparency Depth ('''ZSD'''), Diffuse Attenuation ('''KD490'''), Particulate Backscattering ('''BBP'''), Absorption Coef. ('''CDM''') and Reflectance ('''RRS'''). * Temporal resolutions: '''daily'''. * Spatial resolutions: '''1 km''' and a finer resolution based on olci '''300 meters''' inputs. * Recent products are organized in datasets called Near Real Time ('''NRT''') and long time-series (from 1997) in datasets called Multi-Years ('''MY'''). To find the '''Copernicus-GlobColour''' products in the catalogue, use the search keyword '''""GlobColour""'''. '''DOI (product) :''' https://doi.org/10.48670/moi-00284
-

'''Short description:''' Altimeter satellite along-track sea surface heights anomalies (SLA) computed with respect to a twenty-year [1993, 2012] mean with a 1Hz (~7km) sampling. It serves in delayed-time applications. This product is processed by the DUACS multimission altimeter data processing system. It processes data from all altimeter missions available (e.g. Sentinel-6A, Jason-3, Sentinel-3A, Sentinel-3B, Saral/AltiKa, Cryosat-2, Jason-1, Jason-2, Topex/Poseidon, ERS-1, ERS-2, Envisat, Geosat Follow-On, HY-2A, HY-2B, etc). The system exploits the most recent datasets available based on the enhanced GDR/NTC production. All the missions are homogenized with respect to a reference mission. Part of the processing is fitted to the European Sea area. (see QUID document or http://duacs.cls.fr [http://duacs.cls.fr] pages for processing details). The product gives additional variables (e.g. Mean Dynamic Topography, Dynamic Atmospheric Correction, Ocean Tides, Long Wavelength Errors) that can be used to change the physical content for specific needs (see PUM document for details) “’Associated products”’ A time invariant product https://resources.marine.copernicus.eu/product-detail/SEALEVEL_GLO_PHY_NOISE_L4_STATIC_008_033/INFORMATION describing the noise level of along-track measurements is available. It is associated to the sla_filtered variable. It is a gridded product. One file is provided for the global ocean and those values must be applied for Arctic and Europe products. For Mediterranean and Black seas, one value is given in the QUID document. '''DOI (product):''' https://doi.org/10.48670/moi-00139
-

'''Short description:''' IBI Seas - near real-time (NRT) in situ quality controlled observations, hourly updated and distributed by INSTAC within 24-48 hours from acquisition in average '''DOI (product) :''' https://doi.org/10.48670/moi-00043
-

'''DEFINITION''' Estimates of Ocean Heat Content (OHC) are obtained from integrated differences of the measured temperature and a climatology along a vertical profile in the ocean (von Schuckmann et al., 2018). The products used include three global reanalyses: GLORYS, C-GLORS, ORAS5 (GLOBAL_MULTIYEAR_PHY_ENS_001_031) and two in situ based reprocessed products: CORA5.2 (INSITU_GLO_PHY_TS_OA_MY_013_052) , ARMOR-3D (MULTIOBS_GLO_PHY_TSUV_3D_MYNRT_015_012). Additionally, the time series based on the method of von Schuckmann and Le Traon (2011) has been added. The regional OHC values are then averaged from 60°S-60°N aiming i) to obtain the mean OHC as expressed in Joules per meter square (J/m2) to monitor the large-scale variability and change. ii) to monitor the amount of energy in the form of heat stored in the ocean (i.e. the change of OHC in time), expressed in Watt per square meter (W/m2). Ocean heat content is one of the six Global Climate Indicators recommended by the World Meterological Organisation for Sustainable Development Goal 13 implementation (WMO, 2017). '''CONTEXT''' Knowing how much and where heat energy is stored and released in the ocean is essential for understanding the contemporary Earth system state, variability and change, as the ocean shapes our perspectives for the future (von Schuckmann et al., 2020). Variations in OHC can induce changes in ocean stratification, currents, sea ice and ice shelfs (IPCC, 2019; 2021); they set time scales and dominate Earth system adjustments to climate variability and change (Hansen et al., 2011); they are a key player in ocean-atmosphere interactions and sea level change (WCRP, 2018) and they can impact marine ecosystems and human livelihoods (IPCC, 2019). '''CMEMS KEY FINDINGS''' Since the year 2005, the upper (0-2000m) near-global (60°S-60°N) ocean warms at a rate of 0.9 ± 0.1 W/m2. Note: The key findings will be updated annually in November, in line with OMI evolutions. '''DOI (product):''' https://doi.org/10.48670/moi-00235
-

'''Short description:''' This product provides daily (nighttime), merged multi-sensor (Level-3S, L3S) maps of foundation Sea Surface Temperature (SST) - that is, the SST free from diurnal warming - over the Mediterranean Sea, at high (HR, 1/16°) and ultra-high (UHR, 1/100°) spatial resolutions, covering the period from 2008 to present. Each map represents nighttime SST values and is produced by the Italian National Research Council – Institute of Marine Sciences (CNR-ISMAR). L3S maps are generated by selecting only the highest-quality SST observations from upstream Level-2 (L2) data acquired within a short local nighttime window, in order to minimize cloud contamination and avoid the effects of the diurnal cycle. The main L2 sources currently ingested include SLSTR from Sentinel-3A and -3B, VIIRS from NOAA-21, NOAA-20, and Suomi-NPP, AVHRR from Metop-B and -C, and SEVIRI. These L3S data serve as input to an optimal interpolation procedure used to generate gap-free Level-4 (L4) SST fields, as implemented in product 010_004 (Buongiorno Nardelli et al., 2013). '''DOI (product) :''' https://doi.org/10.48670/moi-00171
-

'''DEFINITION''' Significant wave height (SWH), expressed in metres, is the average height of the highest third of waves. This OMI provides global maps of the seasonal mean and trend of significant wave height (SWH), as well as time series in three oceanic regions of the same variables and their trends from 2002 to 2020, calculated from the reprocessed global L4 SWH product (WAVE_GLO_PHY_SWH_L4_MY_014_007). The extreme SWH is defined as the 95th percentile of the daily maximum SWH for the selected period and region. The 95th percentile is the value below which 95% of the data points fall, indicating higher than normal wave heights. The mean and 95th percentile of SWH (in m) are calculated for two seasons of the year to take into account the seasonal variability of waves (January, February and March, and July, August and September). Trends have been obtained using linear regression and are expressed in cm/yr. For the time series, the uncertainty around the trend was obtained from the linear regression, while the uncertainty around the mean and 95th percentile was bootstrapped. For the maps, if the p-value obtained from the linear regression is less than 0.05, the trend is considered significant. '''CONTEXT''' Grasping the nature of global ocean surface waves, their variability, and their long-term interannual shifts is essential for climate research and diverse oceanic and coastal applications. The sixth IPCC Assessment Report underscores the significant role waves play in extreme sea level events (Mentaschi et al., 2017), flooding (Storlazzi et al., 2018), and coastal erosion (Barnard et al., 2017). Additionally, waves impact ocean circulation and mediate interactions between air and sea (Donelan et al., 1997) as well as sea-ice interactions (Thomas et al., 2019). Studying these long-term and interannual changes demands precise time series data spanning several decades. Until now, such records have been available only from global model reanalyses or localised in situ observations. While buoy data are valuable, they offer limited local insights and are especially scarce in the southern hemisphere. In contrast, altimeters deliver global, high-quality measurements of significant wave heights (SWH) (Gommenginger et al., 2002). The growing satellite record of SWH now facilitates more extensive global and long-term analyses. By using SWH data from a multi-mission altimetric product from 2002 to 2020, we can calculate global mean SWH and extreme SWH and evaluate their trends, regionally and globally. '''KEY FINDINGS''' From 2002 to 2020, positive trends in both Significant Wave Height (SWH) and extreme SWH are mostly found in the southern hemisphere (a, b). The 95th percentile of wave heights (q95), increases faster than the average values, indicating that extreme waves are growing more rapidly than average wave height (a, b). Extreme SWH’s global maps highlight heavily storms affected regions, including the western North Pacific, the North Atlantic and the eastern tropical Pacific (a). In the North Atlantic, SWH has increased in summertime (July August September) but decreased in winter. Specifically, the 95th percentile SWH trend is decreasing by 2.1 ± 3.3 cm/year, while the mean SWH shows a decrease of 2.2 ± 1.76 cm/year. In the south of Australia, during boreal winter, the 95th percentile SWH is increasing at 2.6 ± 1.5 cm/year (c), with the mean SWH increasing by 0.5 ± 0.66 cm/year (d). Finally, in the Antarctic Circumpolar Current, also in boreal winter, the 95th percentile SWH trend is 3.2 ± 2.14 cm/year (c) and the mean SWH trend is 1.7 ± 0.84 cm/year (d). These patterns highlight the complex and region-specific nature of wave height trends. Further discussion is available in A. Laloue et al. (2024). '''DOI (product):''' https://doi.org/10.48670/mds-00352
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA