2017
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Service types
Scale
Resolution
-

The Joint WMO-IOC Technical Commission for Oceanography and Marine Meteorology Observing Programmes Support Centre, provides technical coordination at international level for the sustained elements of the Global Ocean Observing System. The Centre monitors in real-time the status of the observing networks and provides a toolbox to evaluate their performance and optimize their implementation and data flow. Currently OceanOPS monitors the Argo profiling floats, the DBCP surface drifters, coastal and tropical moorings, ice buoys, tsunami buoys, the OceanSITES moorings time-series, the GO-SHIP hydrographic reference lines, the SOT mat/ocean ship based observations and the GLOSS sea level tide gauges. A number of other observing systems are being added gradually, including ocean gliders, polar systems, marine mammals and potentially HF radars.
-
Temporal series (annual mean values) and Long Term Average (LTA) of sediment load for each river mouth where in situ data is available. Different sources can be mixed if any.
-
Temporal series (annual mean values) and long term average (LTA) of temperature for each river mouth.
-
Temporal series (annual mean values) with error of estimation and Long Term Average (LTA) with error of estimation of total nitrogen load for each river mouth where in situ data is available. Different sources can be mixed if any.
-
Temporal series (annual mean values) with error of estimation and Long Term Average (LTA) with error of estimation of total nitrogen load for each river mouth where in situ data is available. Different sources can be mixed if any.
-
Temporal series (annual mean values) and Long term Average (LTA) of water discharge for each river mouth where in situ data is available. Different sources can be mixed if any.
-
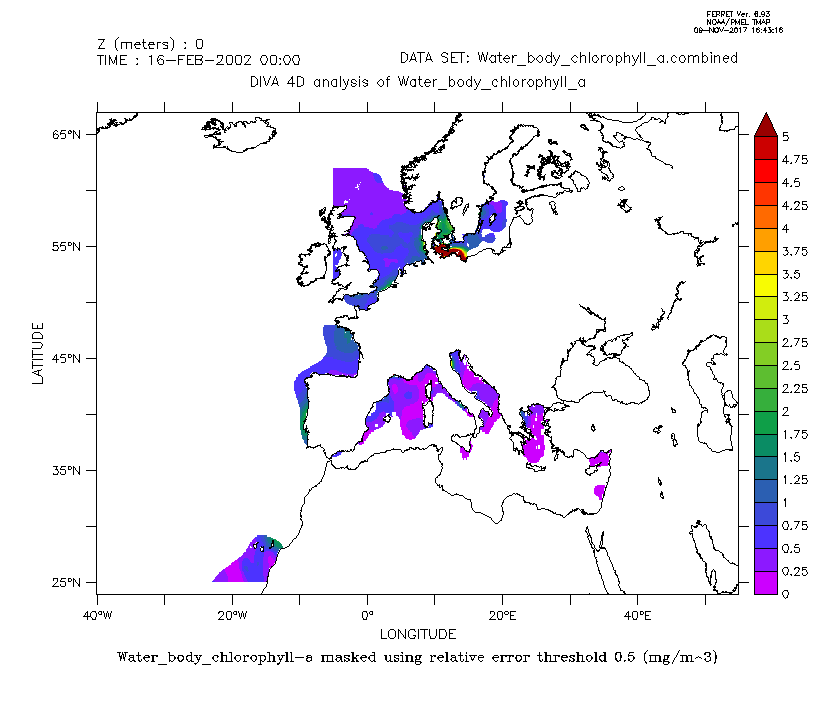
Combined product of Water body chlorophyll a based on DIVA 4D 10-year analysis on five regions : Northeast Atlantic Ocean, North Sea, Baltic Sea, Black Sea, Mediterranean Sea. The boundaries and overlapping zones between these five regions were filtered to avoid any unrealistic spatial discontinuities. This combined Water body chlorophyll a product is masked using the relative error threshold 0.5. Units: mg/m^3. Created by 'University of Liege, GeoHydrodynamics and Environment Research (ULg-GHER)'.
-

Nature de l'occupation du sol par commune et en m².
-
Temporal series (annual mean values) and Long Term Average (LTA) of sediment load for each river mouth where in situ data is available. Different sources can be mixed if any.
-
Cartographie historique des écluses à poissons sur l'île de Ré.
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA