Geology
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
Resolution
-
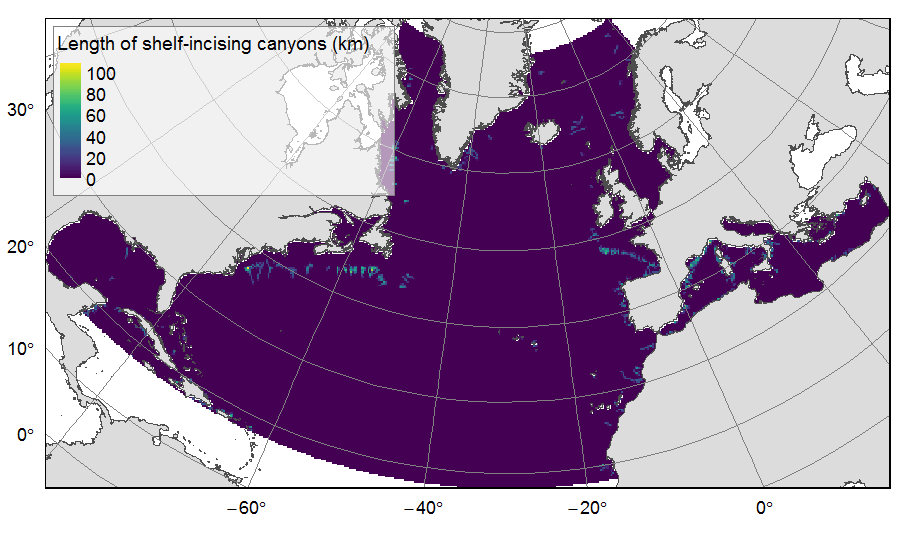
Distribution of three geomorphologic features (fracture zones, canyons, and seamounts) on the North Atlantic (18°N to 76°N and 36°E to 98°W). Source vector data originated from the GEBCO Gazetteer of Undersea Features Names for fractures, Harris & Whiteway (2011) for canyons, and Yesson et al. (2011) for seamounts. The presence (value=1) of fracture zones or seamounts and the total length of canyons (in km, independently for shelf-incising or blind canyons) was extracted in 25km * 25km gridsquares. This dataset was built to feed a basin-wide spatial conservation planning exercise, targeting the deep sea of the North Atlantic. The goal of this approach was to identify conservation priority areas for Vulnerable Marine Ecosystems (VMEs) and deep fish species, based on the distribution of species and habitats, human activities and current spatial management.
-
Specification of the desirable and recommended product attributes for sediment mass budget at the coast for the last 10, 50 and 100 years for the Mediterranean basin and for each NUTS3 region along the coast.
-
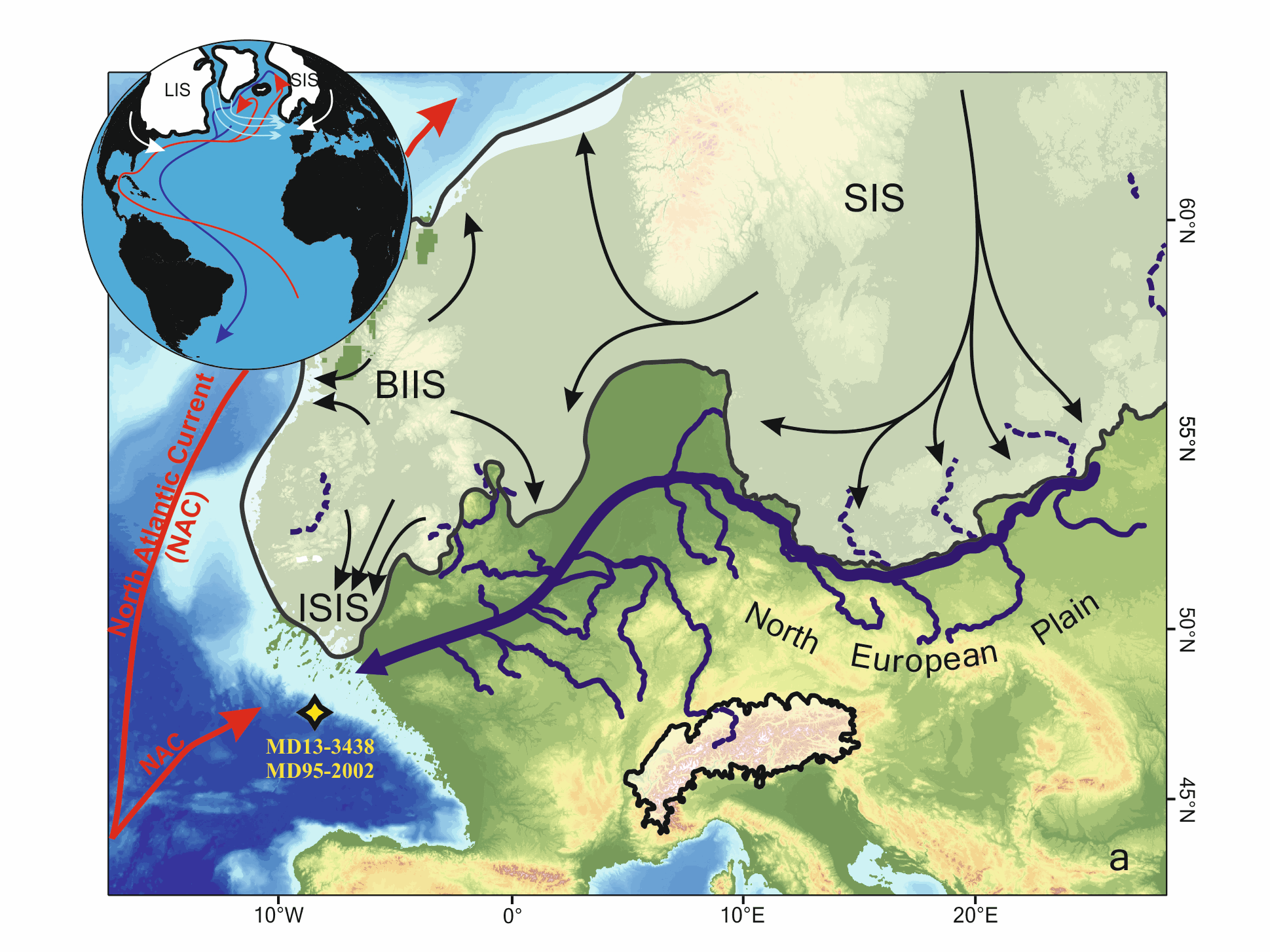
Marine microfossils (dinoflagellate cysts and planktonic foraminifera) and geochemical (XRF-Ti/Ca)-based climatic records from a core located off the Fleuve Manche (FM) paleo-mouth (MD13-3438) have revealed that sustained warm summer sea surface temperatures (SSTs) during sub-millennial climate changes within HS1 (~18–14.7 ka) may have played a key role in the FM regime related to the European Ice Sheet (EIS) melting rate. In this study, we have analyzed the MD13-3438 pollen content over the HS1 at a mean resolution of ~50 years to test whether vegetation-based air temperatures were coupled to SSTs face to this rapid climate variability. First, our results highlight two major phases of pollen sources at site MD13-3438, preventing the pollen record to be interpreted as a continuous record of the evolution of vegetation and climate occupying a single watershed across HS1. The first phase, i.e. the HS1-a interval (~18–16.8 ka), is marked by strong occurrences of boreal pollen taxa (especially Picea-Abies). Considering their spatial distribution and the coalescence of the British and Scandinavian ice sheets into the North Sea during the Last Glacial Maximum, these taxa probably originated from the North European Plain, i.e., eastern FM tributaries (east of the Rhine River), where cool-humid conditions generally prevailed. Then, the second phase, i.e. the HS1-b interval (~16.8–14.7 ka BP), is characterized by a deceleration of the EIS retreat and the drop of boreal pollen values at site MD13-3438 further signing a less influence of the upstream FM drainage system and thus a better characterization of pollen sources related with western FM tributaries. Superimposed to these two HS1 main phases, pollen fluctuations are concomitant with sub-millennial variability in the EIS deglaciation intensity. During the early HS1 (HS1-a), we discussed two short-term increases in the ratio between deciduous trees (Quercus-Corylus-Alnus) and herbaceous plants (Plantago-Amaranthaceae-Artemisia). These events were coeval with phases of increasing FM meltwater runoff and SST seasonality (i.e., dinocyst-based summer SST amplification). We associated these events with lower contribution of the upstream FM catchment as well as, possibly, atmospheric warming and regional sea-level positive oscillations. The HS1-b is composed of three main phases that appear more influenced by the downstream FM drainage system. HS1-b1 (16.8–16.3 ka BP) corresponds to the driest and coldest conditions west of the Rhine River. HS1-b2 (16.3–15.6 ka BP) is coeval with large arrivals of iceberg from the Hudson strait in the Bay of Biscay and thus likely to a major sea-level positive oscillation associated with a phase of FM valley reworking. HS1-b3 (15.6–14.7 ka BP) corresponds to persistent arid conditions that preceded the subsequent more humid conditions recorded from 14.7 ka BP at the start of the Bölling-Alleröd.
-
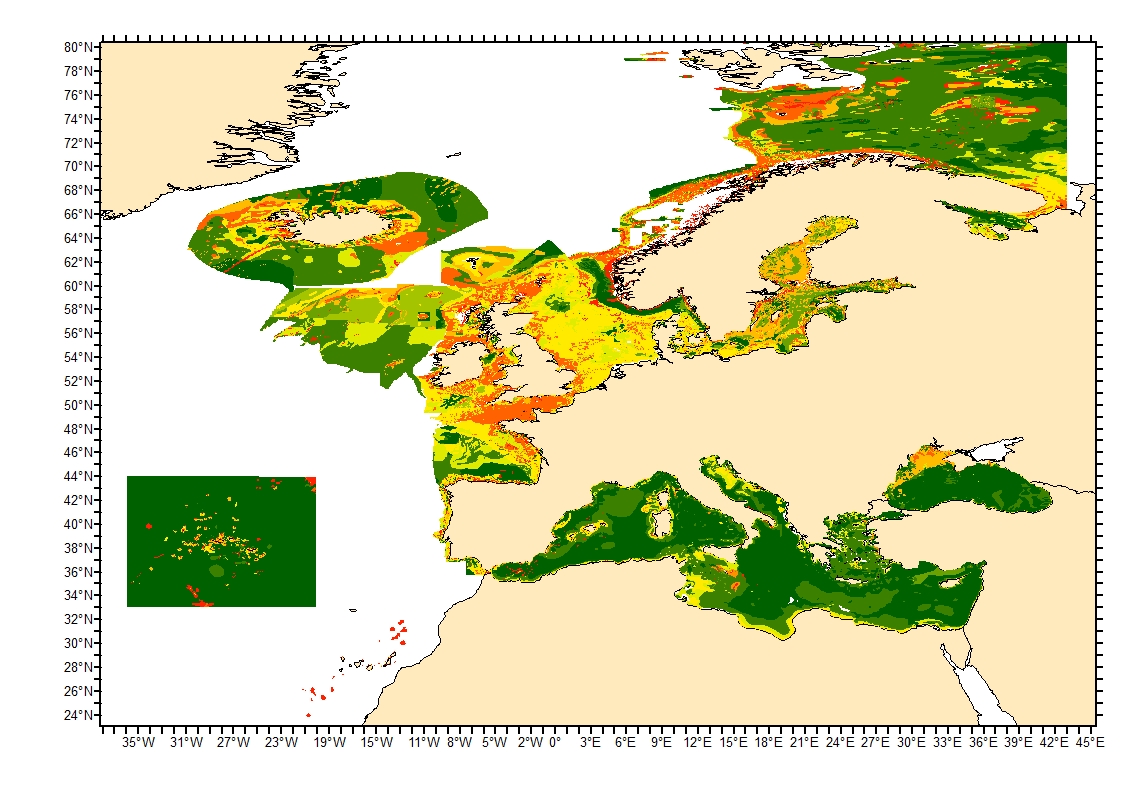
Sediment average grain size in the European North-East Atlantic and Mediterranean waters was generated from Euseamap 2023 sediment categories. This rough granulometry estimate may be used for habitat models at meso- and large scale.
-

Description of attributes for sediment mass budget at the coast for the last 10, 50 and 100 years for the Mediterranean basin and for each NUTS3 region along the coast.
-
Cadre géologique des Pyrénées-Atlantiques. La numérisation a été réalisée à partir d’une carte produite par le BRGM.
-

-
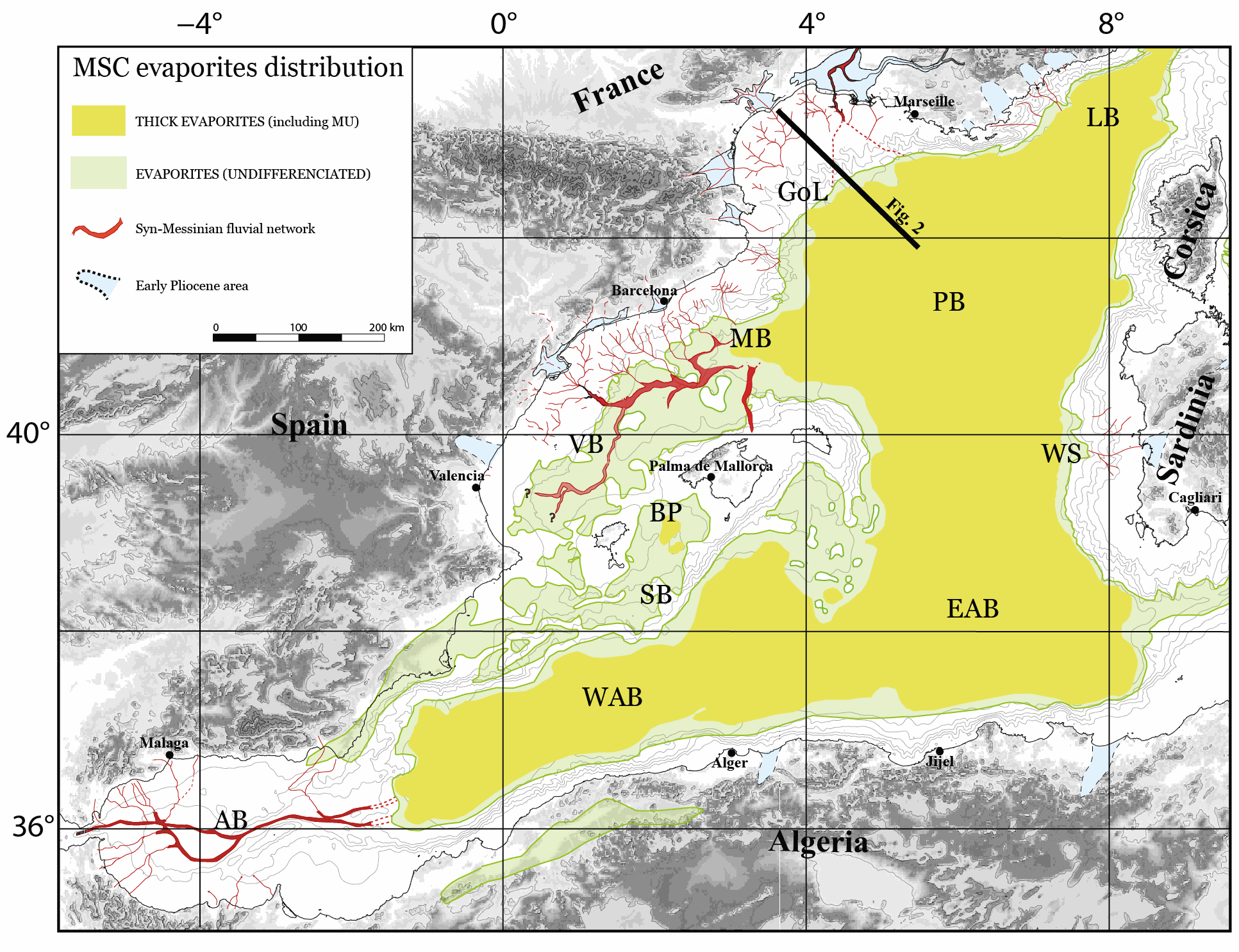
The Western Mediterranean Sea is a natural laboratory to address questions about the formation and evolution of continental margins and the relationship between surface and deep processes. The evaporites deposited during the late Miocene’s Messinian Salinity Crisis (MSC) strongly impact its sedimentological and geomorphological evolution. Hereafter, we present a compilation of some of the main regional seismic stratigraphic markers throughout the Western Mediterranean Sea. We provide in xyz format (z in second twt) the original, not interpolated, points interpretation of the following horizons: i) Acoustic basement, ii) Base and Top of the MSC salt, also known as Mobile Unit (MU), iii) base Pliocene and iv) Seafloor. The available reflection seismic dataset, coming from a collaboration between French, Spanish, Algerian and Italian research institutes, covers most of the Western Mediterranean sub-basins with the exception of the Ligurian Basin. This compilation is currently the most comprehensive and updated available in literature and provides a useful contribution to the scientific community working in sedimentary, tectonics and geodynamics studies in the Western Mediterranean Sea.
-

-

 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA