Celtic Seas
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
Resolution
-

Ireland’s Marine Atlas is developed and maintained by the Marine Institute with funding by the Government of Ireland. This work is part supported by the Irish Government and the European Maritime & Fisheries Fund as part of the EMFF Operational Programme for 2014-2020. The atlas provides a one-stop-shop to view and download marine environmental data relevant to reporting under Ireland’s Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD). The aim of the European Union’s MSFD directive is to protect more effectively the marine environment across Europe through the establishment of “good marine waters”. Data in Ireland’s Marine Atlas has been guided by the European Directive on harmonising environmental data across Europe within a spatial data infrastructure known as INSPIRE. INSPIRE Data Specifications (Data Models) have been used to manage data to the categories visible under THEMES in the atlas. Many of the layers displayed in the Atlas are also used in the National Marine Planning Framework (NMPF). This framework aims to bring together all marine-based human activities, outlining the government’s vision, objectives and marine planning policies for each marine activity. The NMPF report details how these marine activities will interact with each other in an ocean space that is under increasing spatial pressure, ensuring the sustainable use of our marine resources to 2040. Please read the following information carefully as it sets out the terms and conditions that govern the use of products and services on this website. Once you have read these terms and conditions click the "Agree" button at the bottom of the page to proceed. By clicking the "Agree" button you will be deemed to have accepted the terms and conditions, our legal notices and privacy statement.
-
Excel file containing CPR data from Standard Areas B4,C3,C4,D3,D4,D5,E4,F4 for the plankton Calanus finmarchicus and helgolandicus, total traverse (small) copepods, total large copepods, Phytoplankton Colour Index and Cnidaria (presence denoted by a 1, absence by a zero). All taxa are from 1980, except Cnidaria which are from 2011. Dataset is in the format of sample level data, with each row being a discrete sample, with a sample being 3m3 filtered seawater, and 10nm of tow. For each row, a sample has the following information, starting at column a: Standard area of sample, sample id, latitude (decimal degrees) of sample mid point, longitude (decimal degrees) of sample midpoint, sample midpoint date and local time, year of sample, month of sample, then plankton abundance values (or PCI index or cnidaria presence/absence). All taxa have been looked for during the period this dataset spans, so zero values represent true absence.
-
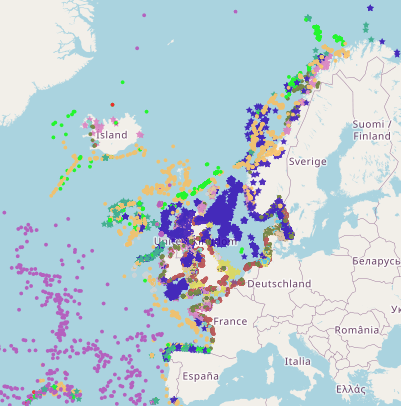
This is a compilation of OSPAR habitat point data for the northeast Atlantic submitted by OSPAR contracting parties. The compilation is coordinated by the UK's Joint Nature Conservation Committee, working with a representative from each of the OSPAR coastal contracting parties. This public dataset does not contain records relating to sensitive species (e.g. Ostrea edulis) in specific areas, or where data are restricted from public release by the owner's use limitations. This version (v2020) was published in July 2021.
-

OSPAR is the mechanism by which 15 Governments & the EU cooperate to protect the marine environment of the North-East Atlantic. OSPAR started in 1972 with the Oslo Convention against dumping and was broadened to cover land-based sources of marine pollution and the offshore industry by the Paris Convention of 1974. These two conventions were unified, up-dated and extended by the 1992 OSPAR Convention. The new annex on biodiversity and ecosystems was adopted in 1998 to cover non-polluting human activities that can adversely affect the sea. The fifteen Governments are Belgium, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Iceland, Ireland, Luxembourg, The Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland and United Kingdom. OSPAR is so named because of the original Oslo and Paris Conventions ("OS" for Oslo and "PAR" for Paris). OSPAR Data & Information Management System (ODIMS) is a fully featured platform for accessing OSPAR's geospatial maps, data and metadata. 61 Maps and 254 layers regarding: - Cables and pipelines - Comprehensive atmospheric monitoring programme - Discharges of radionuclides from the non-nuclear sectors - Discharges, spills and emissions from offshore oil and gas installations - Dumping and placement of wastes or other matter at sea - Environmental monitoring of radioactive substances - Fishing for litter - Vulnerable marine ecosystems - etc.
-
Intermediate Assessment 2017 - Seabed Litter - Litter is widespread on the seafloor across the area assessed, with plastic being the predominant material encountered. In the areas assessed, higher amounts of litter are found in the Eastern Bay of Biscay, Southern Celtic Seas and English Channel relative to the north of the Greater North Sea and Celtic Seas.
-
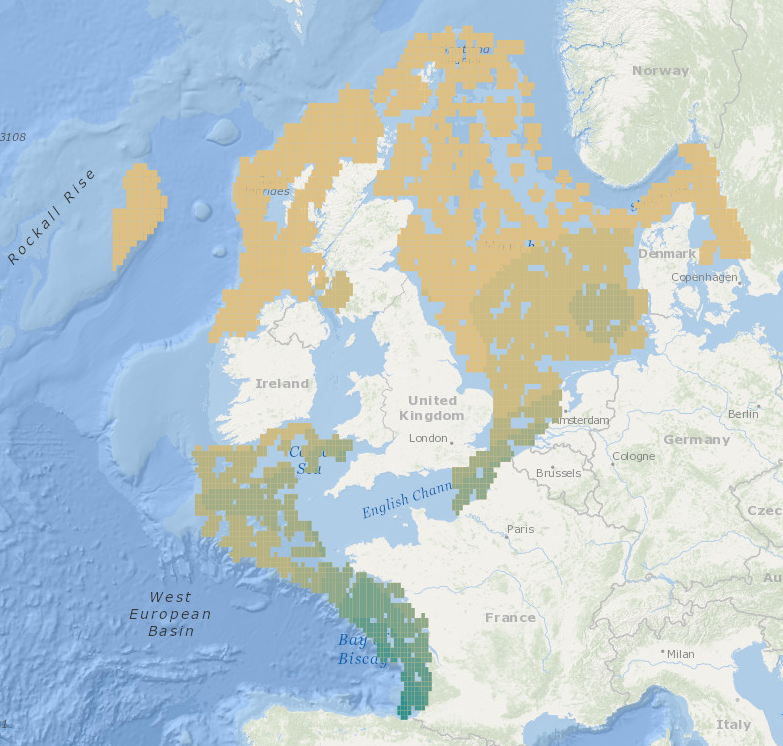
Output of the 2019 EUSeaMap broad-scale predictive model, produced by EMODnet Seabed Habitats and aggregated into the Benthic Broad Habitat Types of the Marine Strategy Framework Directive (as defined in the Commission Decision 17 May 2017). The extent of the mapped area includes the Mediterranean Sea, Black Sea, Baltic Sea, and areas of the North Eastern Atlantic extending from the Canary Islands in the south to the Barents Sea in the north. The map was produced using a "top-down" modelling approach using classified habitat descriptors to determine a final output habitat. Habitat descriptors differ per region but include: - Biological zone - Energy class - Oxygen regime - Salinity regime - Seabed substrate - Riverine input Habitat descriptors (excepting Substrate) are calculated using underlying physical data and thresholds derived from statistical analyses or expert judgement on known conditions.
-

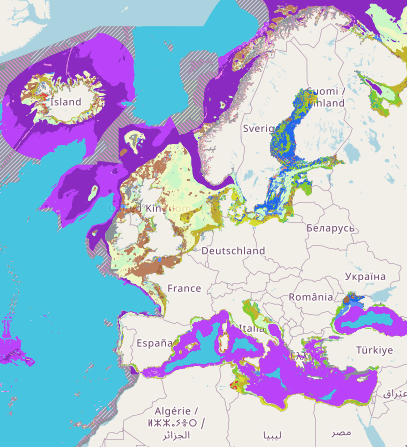
This layer shows the current known extent and distribution of live hard coral cover in European waters, collated by EMODnet Seabed Habitats. The polygons portion was last updated in 2019. The points were added in Sept 2021. Lophelia pertusa and Coral gardens are both on the OSPAR List of threatened and/or declining species and habitats. The purpose was to produce a data product that would provide the best compilation of evidence for the essential ocean variable (EOV) known as Hard coral cover and composition (sub-variable: Live hard coral cover and extent), as defined by the Global Ocean Observing System (GOOS). This data product should be considered a work in progress and is not an official product.
-
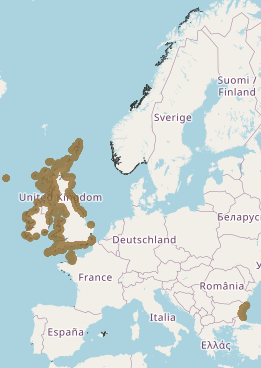
This layer shows the current known extent and distribution of macroalgal canopy in European waters, collated by EMODnet Seabed Habitats. The polygons portion was last updated in 2019. The points were added in Sept 2021. The purpose was to produce a data product that would provide the best compilation of evidence for the essential ocean variable (EOV) known as Macroalgal canopy cover and composition (sub-variable: Areal extent), as defined by the Global Ocean Observing System (GOOS). Kelp and fucoid brown algae are the dominant species that comprise macroalgal forests. This data product should be considered a work in progress and is not an official product.
-
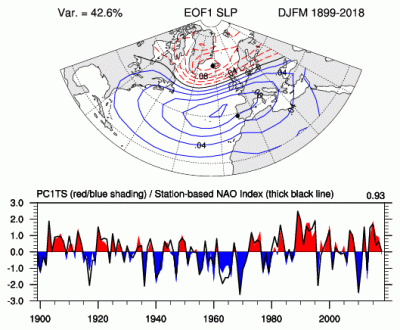
The principal component (PC)-based indices of the North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO) are the time series of the leading Empirical Orthogonal Function (EOF) of SLP anomalies over the Atlantic sector, 20°-80°N, 90°W-40°E. These indices are used to measure the NAO throughout the year, tracking the seasonal movements of the Icelandic low and Azores high. These movements are illustrated in the Figures on this page. Positive values of the NAO index are typically associated with stronger-than-average westerlies over the middle latitudes, more intense weather systems over the North Atlantic and wetter/milder weather over western Europe.
-

Seabed Habitats was one of seven themes of the European Marine Observation and Data Network (EMODnet) initiative, funded by the European Maritime and Fisheries Fund. Since its inception in 2009, EMODnet Seabed Habitats developed, improved and gradually increased the coverage of a broad-scale seabed habitat map for Europe's seabed, also known as EUSeaMap. In addition, EMODnet Seabed Habitats continued the work started by MESH and MESH Atlantic projects in collating and making available seabed habitat maps from surveys, through the EMODnet Seabed Habitats map viewer. In it's third Phase (2017-2019), EMODnet Seabed Habitats collated and provided habitat point data and the outputs of habitat distribution modelling, and the third phase has now been extended to 2021. The extended third phase of the project will: - Continue to grow Europe's only comprehensive library of habitat maps from surveys and collection of survey sample points - Create new composite data products to add to those for the Essential Ocean Variable habitats and OSPAR threatened and/or declining habitats - Update the EMODnet broad-scale seabed habitat map for Europe (EUSeaMap) using the next seabed substrate update from EMODnet Geology - Update web content with extra resources for habitat mapping, including a catalogue highlighting all the most useful data products
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA