Habitats and biotopes
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
Resolution
-

Vibrio bacteria sampled from juvenile oysters and seawater collected in Thau Lagoon (Languedoc-Roussillon, France) in October 2015 during a mortality event were genotyped using hsp60, rctB, topA and mreB protein-coding genes
-

This dataset consists of metatranscriptomic sequencing reads corresponding to coastal micro-eukaryote communities sampled in Western Europe in 2018 and 2019.
-
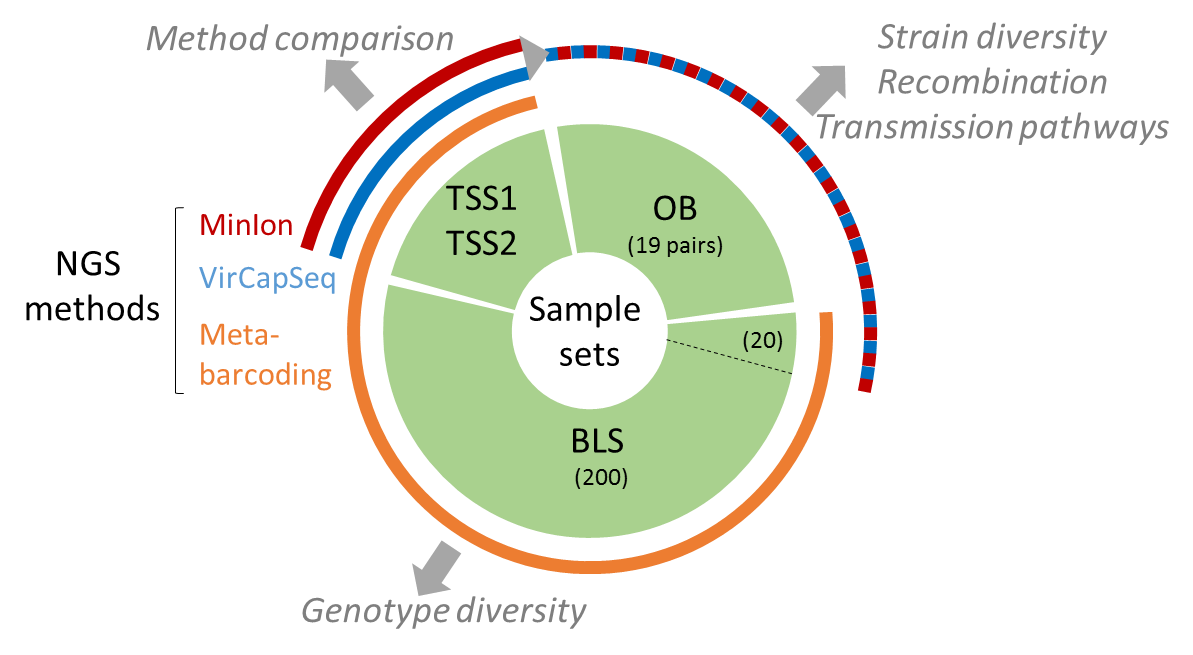
The present data set concerne metabarcoding raw reads produced using 4 different PCR targeting polymerase or capside coding region of the genoyupe I and II of norovirus. Test samples of norovirus with serial dilutions in pure water and after a bio-accumulation in oysters. Sequencing was made after VirCapSeq-VERT approach.
-

WGS for Iatlantic projet ( ) for assessing past and present connectivity
-
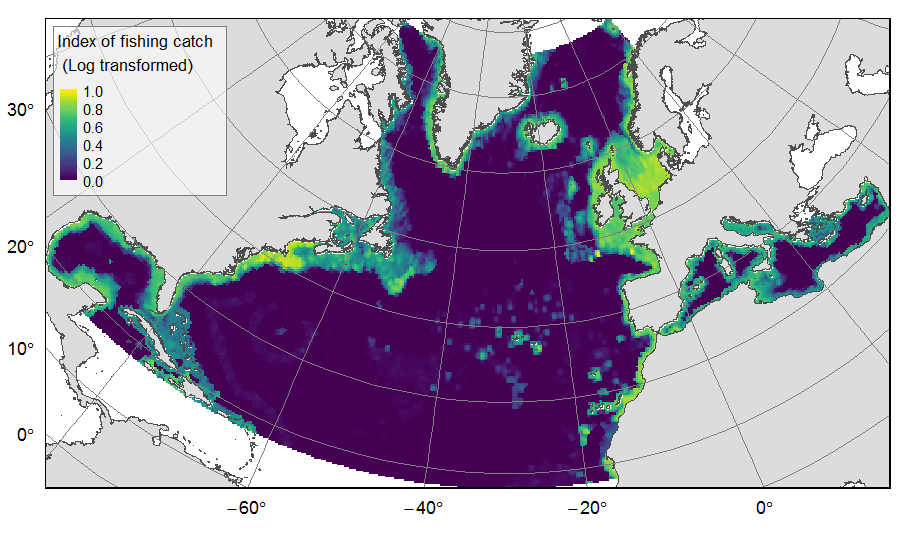
Distribution of catch from deep-sea impacting fishing on the North Atlantic (18°N to 76°N and 36°E to 98°W), for the period 2010-2015. The average of yearly fishing catch for the period 2010-2015 is displayed as an index on the ATLAS grid of 25km * 25km resolution. Source data originated from the Global Fisheries Landings V4.0 database. The dataset was filtered to select only the fishing gears that have an impact on large areas of the seafloor (dredges, bottom trawls, and Danish seines). Within each cell, all remaining catch records were summed to get the total catch rate of the considered year. This dataset was built to feed a basin-wide spatial conservation planning exercise, targeting the deep sea of the North Atlantic. The goal of this approach was to identify conservation priority areas for Vulnerable Marine Ecosystems (VMEs) and deep fish species, based on the distribution of species and habitats, human activities and current spatial management.
-

160 whole genomes sequences obtained from 160 individual fish samples representing about 100 different species present in Gulf of Lion, and bay of Biscay.
-
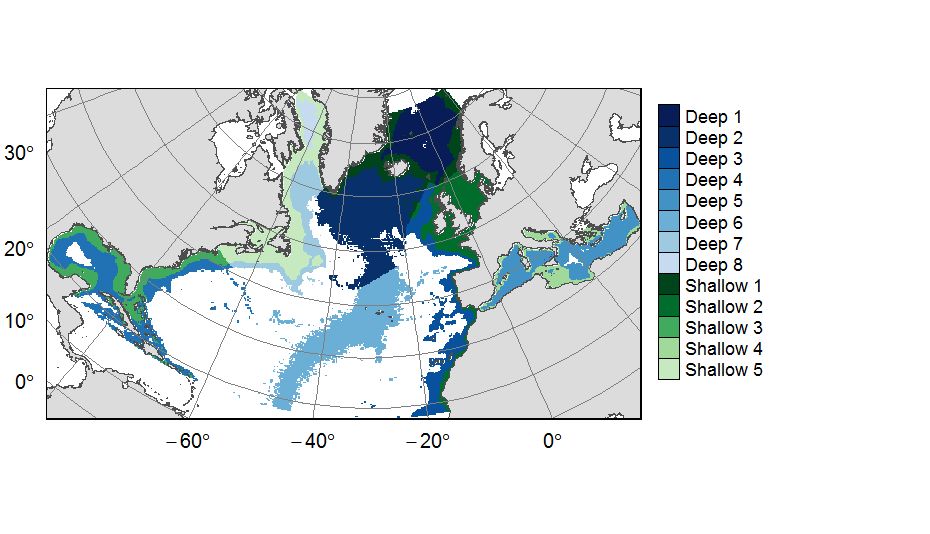
Planning units layers used for ATLAS EU prioritization scenarios on the North Atlantic (18°N to 76°N and 36°E to 98°W). This raster layer is designed on a grid of 25km * 25km resolution, that served to extract all the spatial data used prioritization. The 31 518 planning units (cells with value) corresponded to areas containing depths shallower or equal to 3500m, even if they could also contain deeper areas locally. For connectivity scenarios, only the planning units matching with the extent of available connectivity data were selected. One layer allocates planning units to the 13 geographical provinces (values ranging from 1 to 13) created for the purpose of prioritization. This dataset was built to feed a basin-wide spatial conservation planning exercise, targeting the deep sea of the North Atlantic. The goal of this approach was to identify conservation priority areas for Vulnerable Marine Ecosystems (VMEs) and deep fish species, based on the distribution of species and habitats, human activities and current spatial management.
-

The eleven collected wild strains of T. lutea were compared phenotypically, in particular with regard to their pigment and lipid profiles. The genome of each T. lutea strain was also sequenced to investigate the genetic structure and genome organisation of this species. Collected data were summarized in a genome browser to provide easy-to-use support for the scientific community (https://genomes-catalog.ifremer.fr). This provides an important resource- to understand, exploit and predict the biodiversity of this species.
-

This study aims to compare different metabarcoding sequences of commercially fished shrimps collected by tree counties on the North Brazil Shelf Large Marine Ecosystem
-

Dart Seq data gathered on Blue Shark in the framework of the PSTBS-IO project supported by funding from FAO, CSIRO Oceans and Atmosphere, AZTI Tecnalia, Institut de recherche pour le développement (IRD), and Research Institute for Tuna Fisheries (RITF) and financial assistance of the European Union (GCP/INT/233/EC – Population structure of IOTC species in the Indian Ocean), and POPSIZE project supported by FEAMP (2014-2020 UE N°508/2014), and Institut français de recherche pour l'Exploitation de la mer (Ifremer).
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA