transportation
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
Resolution
-

-

-

"Traffic Separation Schemes" product contains a description of TSS in French maritime spaces. A TSS is a routeing measure aimed at the separation of opposing streams of traffic by appropriate means and notably by the establishment of traffic lanes. The measures taken aim at improving navigation safety in areas where navigation is threatened by the density of traffic associated with various natural difficulties. Several classes of objects constitute this product, the acronyms used are those of IHO standard S-57: - Traffic separation scheme lane part (TSSLPT): area of a traffic lane in which the direction of flow of traffic is uniform; - Traffic separation scheme boundary (TSSBND): outer limit of a traffic lane part or a traffic separation scheme roundabout; - Traffic separation line (TSELNE): common boundary between two traffic lanes, or between one traffic lane and one inshore traffic zone; - Traffic separation zone (TSEZNE): separation areas between two traffic lanes, or between one traffic lane and one inshore traffic zone, or to the central area of a roundabout; - Inshore traffic zone (ISTZNE): area between the landward boundary of a traffic separation scheme and the adjacent coast; - Precautionary area (PRCARE): area, within defined limits, where ships must navigate with particular caution, and within which the direction of traffic flow may be recommended; - Deep water route part (DWRTPT): sections within which the flow of traffic either follows one defined direction for one-way traffic, or follows one defined direction and its reciprocal for two-way traffic. A deep-water route is a route in a designated area within defined limits which has been accurately surveyed for clearance of sea bottom and submerged obstacles to a minimum indicated depth of water; - Two-way route part (TWRTPT): sections within which traffic flows in two directions along one bearing and its reciprocal. These route parts are generally two-way, but some may be restricted to one-way traffic flow; - Radio calling-in line (RDOCAL_lne) : positions at which vessels are required to report to a traffic control centre.
-

-

"Regulation - Navigation" product contains 18 object classes, the acronyms used are those of IHO standard S-57 - International Hydrographic Organization – (https://iho.int/): - Anchorage area (ACHARE): an area in which vessels anchor or may anchor. - Anchor berth (ACHBRT): a designated area of water where a single vessel, sea plane, etc. may anchor. - Administration Area (Named) (ADMARE) - Cable area (CBLARE) - Coastguard station (CGUSTA) - Cargo transhipment area (CTSARE) - Distance mark (DISMAR): mark indicating the distance on canals or rivers. - Dumping ground (DMPGRD): sea area where dredged material or other potentially more harmful material e.g. explosives, chemical waste, is deliberately deposited. - Fairway (FAIRWY): part of a river, harbour etc. where the main navigable channel for vessels of larger size lies. It is also the usual course followed by vessels entering or leaving harbours and sometimes called "ship channel". - Ice area (over land or water) (ICEARE) - Local magnetic anomaly (LOCMAG): anomaly of the magnetic field of the earth, extending over a relatively small area, due to local magnetic influences. - Marine farm/culture (MARCUL) - Navigation line (NAVLNE): a line generally passing through two clearly defined charted landmarks, and along part of which a vessel can approach safely. - Pipeline area (PIPARE) - Recommended track (RECTRC): track of undefined width, recommended to all or only certain vessels. - Restricted area (RESARE): specified area designated by an appropriate authority within which navigation is restricted in accordance with certain specified conditions. - Sea-plane landing area (SPLARE) Detailed definitions of each of these object classes can be found in the S-57 standard (https://iho.int/en/standards-and-specifications). An online catalog is available at http://www.s-57.com/. Some of the symbols used for display on data.shom.fr portal have been adapted from icons from the OpenSeaMap open library (https://github.com/OpenNauticalChart/). For reasons of readability, not all the characteristics of the objects are systematically displayed. All available information can be consulted by querying this layer.
-
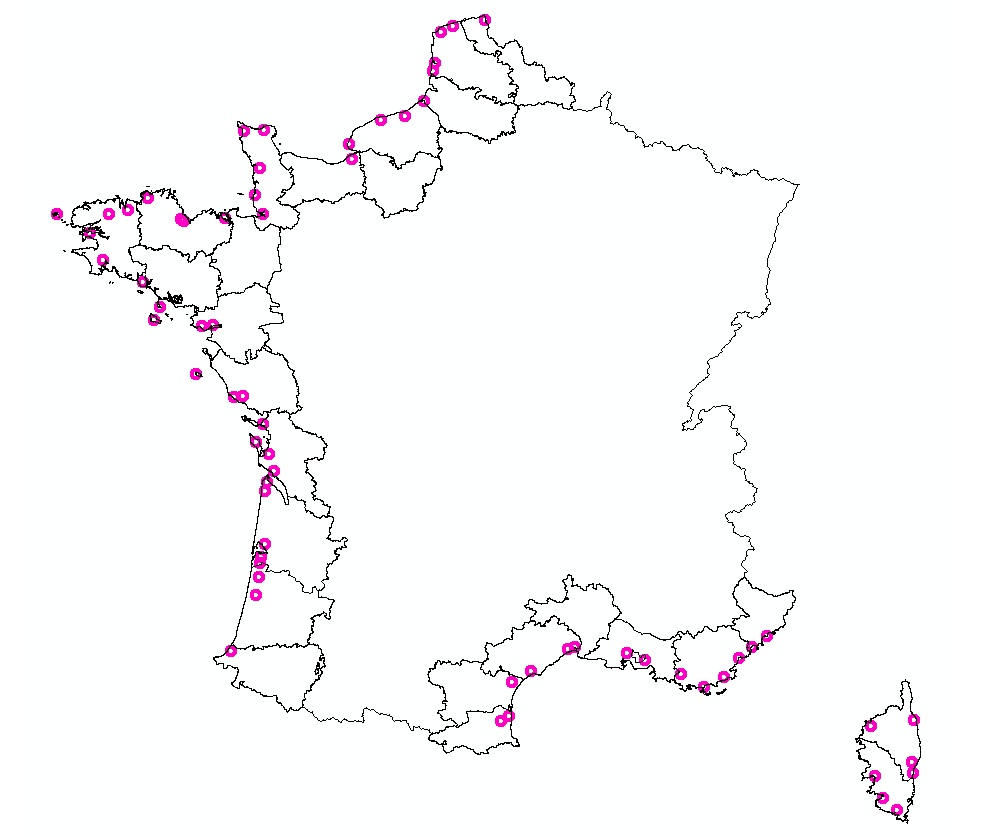
Cette couche représente les aérodromes civils présents sur la façade littorale métropolitaine.
-
Ce jeu de données ponctuelles issu du Système d'Aide à l'Exploitation et d'Information des Voyageurs (SAEIV) représente l'emplacement des arrêts de bus physiques du réseau TBM de la Métropole Bordelaise sur lesquels les usagers peuvent monter ou descendre d'un véhicule.
-
Eléments de description physique et géographique caractérisant les modalités du déplacement urbain sur la voie publique. Ces éléments représentent les pistes cyclables sous forme de lignes, les sens uniques sous forme de points orientés et les zones réglementaires (aires piétonnes, zone 30) sous forme de surfaciques.
-
Appartiennent au mobilier urbain. Ensemble des objets ou dispositifs publics ou privés installés dans l'espace public et liés à une fonction ou à un service offert par la collectivité. Date de Publication : 2009
-
Stationnements vélo installés/projetés par Limoges Métropole.
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA