2015
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Service types
Scale
Resolution
-
The vision of the AtlantOS project was to improve and innovate Atlantic observing by using the Framework of Ocean Observing to obtain an international, more sustainable, more efficient, more integrated, and fit-for-purpose system contributing to the Trans-Atlantic Research Alliance, the GEO (Group on Earth Observations) global initiative Blue Planet, and GOOS (Global Ocean Observing Systems). Hence, the AtlantOS project will have a long-lasting and sustainable contribution to the societal, economic and scientific benefit arising from this integrated approach. This will be achieved by improving the value for money, extent, completeness, quality and ease of access to Atlantic Ocean data required by industries, product supplying agencies, scientists and citizens. The overarching target of the AtlantOS initiative was to deliver an advanced framework for the development of an integrated Atlantic Ocean Observing System that goes beyond the state-of–the-art, and leaves a legacy of sustainability after the life of the project (see AtlantOS High-Level Strategy and find out more about the AtlantOS program). The legacy derived from the AtlantOS aims: - to improve international collaboration in the design, implementation and benefit sharing of ocean observing, - to promote engagement and innovation in all aspects of ocean observing, - to facilitate free and open access to ocean data and information, - to enable and disseminate methods of achieving quality and authority of ocean information, - to strengthen the Global Ocean Observing System (GOOS) and to sustain observing systems that are critical for the Copernicus Marine Environment Monitoring Service and its applications and - to contribute to the aims of the Galway Statement on Atlantic Ocean Cooperation The project was organized along work packages on: i) observing system requirements and design studies, ii) enhancement of ship-based and autonomous observing networks, iii) interfaces with coastal ocean observing systems, iv) integration of regional observing systems, v) cross-cutting issues and emerging networks, vi) data flow and data integration, vii) societal benefits from observing /information systems, viii) system evaluation and resource sustainability. Engagement with wider stakeholders including end-users of Atlantic Ocean observation products and services was also key throughout the project. The AtlantOS initiative contributed to achieving the aims of the Galway Statement on Atlantic Ocean Cooperation that was signed in 2013 by the EU, Canada and the US, launching a Transatlantic Ocean Research Alliance to enhance collaboration to better understand the Atlantic Ocean and sustainably manage and use its resources.
-
Specification of the desirable and recommended product attributes for generating time series of annual average sea level (units: mm) from tide gauges over periods of 50 years (1963-2012) and 100 years (1913-2012), to characterize and assess average annual sea-level rise relative to the land.
-
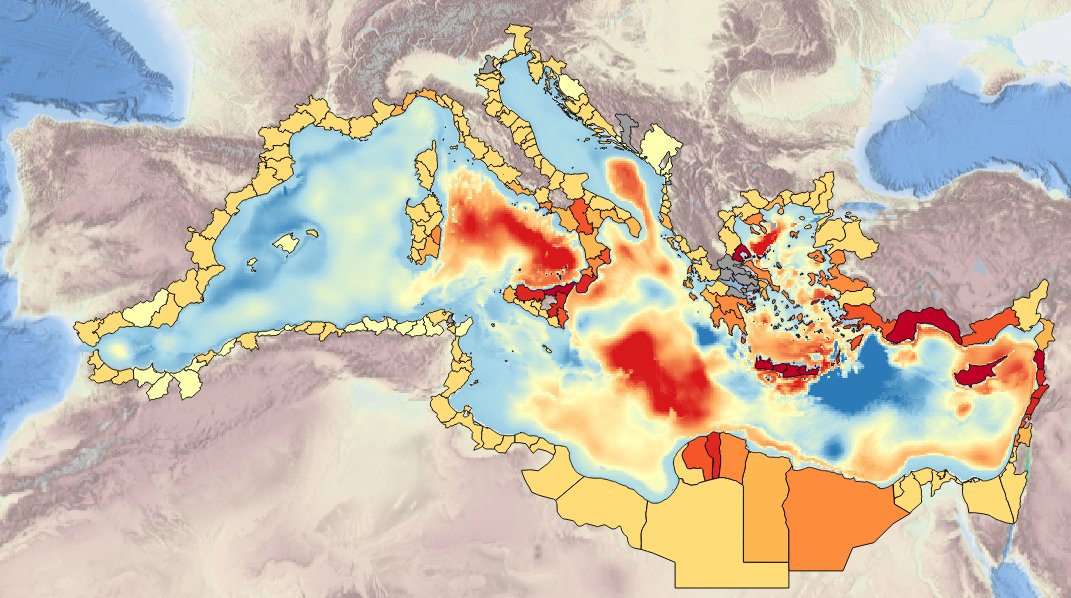
Specification of the desirable and recomended product attributes for generating spatial layers of sea surface temperature trend for the last 10, 50, 100 years for the Mediterranean basin and for each NUTS3 region along the coast.
-

L’étalement urbain est une forme d’urbanisation qui s’est développée autour des agglomérations. Il entraine une artificialisation des sols qui produit des impacts sur l’environnement, sur le paysage et sur l’organisation des territoires. La lutte contre l’étalement urbain et l’artificialisation des sols au profit de formes urbaines denses et compactes est une priorité régionale qui implique de mettre en oeuvre une politique globale de maîtrise de la consommation des espaces naturels, agricoles et forestiers. L’Aquitaine est une région vaste et davantage artificialisée que la France métropolitaine. La densité de population est faible et l’Aquitaine arrive en 8ème position des régions occupant le plus d’espace artificialisé par habitant. Son fort dynamisme démographique accroît les pressions sur le foncier disponible, notamment autour des pôles d’emploi. Dans plusieurs aires urbaines, les sols s’artificialisent à un rythme bien supérieur à l’évolution de la population.
-
Specification of the desirable and recommended product attributes for generating spatial layers of annual avergae internal energy for the last 20 years.
-
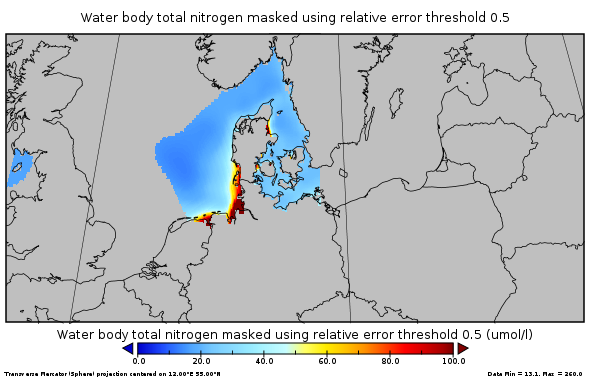
This gridded product visualizes 1960 - 2014 water body total nitrogen concentration (umol/l) in the North Sea domain, for each season (winter: December – February; spring: March – May; summer: June – August; autumn: September – November). It is produced as a Diva 4D analysis, version 4.6.11: a reference field of all seasonal data between 1960-2014 was used; results were logit transformed to avoid negative/underestimated values in the interpolated results; error threshold masks L1 (0.3) and L2 (0.5) are included as well as the unmasked field. Every step of the time dimension corresponds to a 10-year moving average for each season. The depth dimension allows visualizing the gridded field at various depths.
-
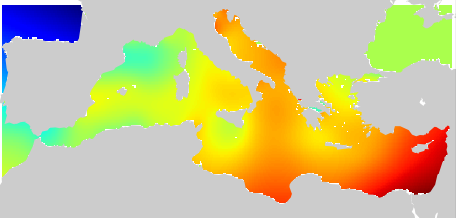
Mediterranean Sea Climatology computed from the SeaDataNet V1.1 aggregated dataset . The version used for the DIVA software is the 4.6.9. The period covers 1900-2013. For data access please register at http://www.marine-id.org
-

Description of attributes for time series of annual average sea level (units: mm) from tide gauges over periods of 50 years (1963-2012) and 100 years (1913-2012), to characterize and assess average annual sea-level rise relative to the land.
-
Specification of the desirable and recommended products attributes for generating spatial layers of sea surface temperature for the last 10, 50 and 100 years for the Mediterranean basin and for each NUTS3 region along the coast.
-

The Copernicus Marine Service (or Copernicus Marine Environment Monitoring Service) is the marine component of the Copernicus Programme of the European Union. It provides free, regular and systematic authoritative information on the state of the Blue (physical), White (sea ice) and Green (biogeochemical) ocean, on a global and regional scale. It is funded by the European Commission (EC) and implemented by Mercator Ocean International. It is designed to serve EU policies and International legal Commitments related to Ocean Governance, to cater for the needs of society at large for global ocean knowledge and to boost the Blue Economy across all maritime sectors by providing free-of-charge state-of-the-art ocean data and information. It provides key inputs that support major EU and international policies and initiatives and can contribute to: combating pollution, marine protection, maritime safety and routing, sustainable use of ocean resources, developing marine energy resources, blue growth, climate monitoring, weather forecasting, and more. It also aims to increase awareness amongst the general public by providing European and global citizens with information about ocean-related issues.
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA