*
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Service types
Scale
Resolution
-
Assessment of the confidence limits of the data base by means of evaluation of the two involved numerical models: The wave model WAM (Parameter: Significant wave height Hs) and the Atmospheric model SKIRON (Parameter: Wind Speed 10m)
-

'''This product has been archived''' For operationnal and online products, please visit https://marine.copernicus.eu '''Short description:''' For the Global Ocean- In-situ observation delivered in delayed mode. This In Situ delayed mode product integrates the best available version of in situ oxygen, chlorophyll / fluorescence and nutrients data '''DOI (product) :''' https://doi.org/10.17882/86207
-
Description of de desirable and recomended attributes for generating time-series of sea surface annual average temperature for the last 10, 50 and 100 yrs for the Mediterranean basin and for each NUTS region along the coast.
-
Auteur(s): Cha Lucie , Analyse des paysages de méga évènements sur des sites internationaux. Historique de l'évolution de expositions géantes. Projet d'aménagement de la ville de Bordeaux qui a posé sa candidature pour l'Exposition universelle de 2025
-
Auteur(s): Dorgambide Jacques, Desmoulins Christian , Pouvoir apporter à tous ceux qui vont vers le sport un lieu d'accueil favorisant : l'initiation donc la connaissance des gestes sportifs, la prévention donc la connaissance de ses moyens et le risque encouru par la pratique du sport, l'animation donc ouvrir vers une très large participation, l'information donc la relation de sportif néophyte (enfants, adultes, parents)
-

'''Short description:''' For the Global Ocean - The product contains daily L3 gridded sea surface wind observations from available scatterometers with resolutions corresponding to the L2 swath products: *0.5 degrees grid for the 50 km scatterometer L2 inputs, *0.25 degrees grid based on 25 km scatterometer swath observations, *and 0.125 degrees based on 12.5 km scatterometer swath observations, i.e., from the coastal products. Data from ascending and descending passes are gridded separately. The product provides stress-equivalent wind and stress variables as well as their divergence and curl. The NRT L3 products follow the NRT availability of the EUMETSAT OSI SAF L2 products and are available for: *The ASCAT scatterometers on Metop-A (discontinued on 15/11/2021), Metop-B and Metop-C at 0.125 and 0.25 degrees; *The OSCAT scatterometer on Scatsat-1 (discontinued on 28/02/2021) and Oceansat-3 at 0.25 and 0.5 degrees; *The HSCAT scatterometer on HY-2B, HY-2C and HY-2D at 0.25 and 0.5 degrees In addition, the product includes European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) operational model forecast wind and stress variables collocated with the scatterometer observations at L2 and processed to L3 in exactly the same way as the scatterometer observations. '''DOI (product) :''' https://doi.org/10.48670/moi-00182
-
Auteur(s): Darracq Alain, Desmoulins Christian , Proposition pour la reconversion d'une ancienne minoterie en en lieu de création artistique et artisanale
-
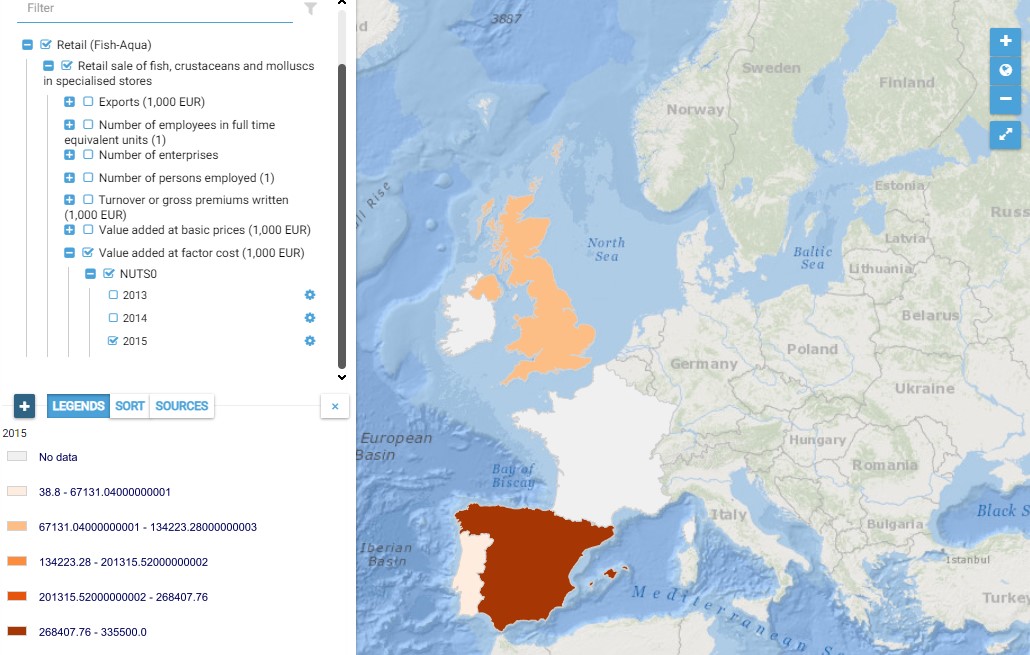
This map presents all layers corresponding to "Retail sale of fish, crustaceans and molluscs in specialised stores" activities in the Atlantic area. For more information about this NACE code : https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/ramon/nomenclatures/index.cfm?TargetUrl=DSP_NOM_DTL_VIEW&StrNom=NACE_REV2&StrLanguageCode=EN&IntPcKey=18511064&IntKey=18511154&StrLayoutCode=HIERARCHIC&IntCurrentPage=1 Indicators collected are : Business indicators per country
-

-
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA