*
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Service types
Scale
Resolution
-
-
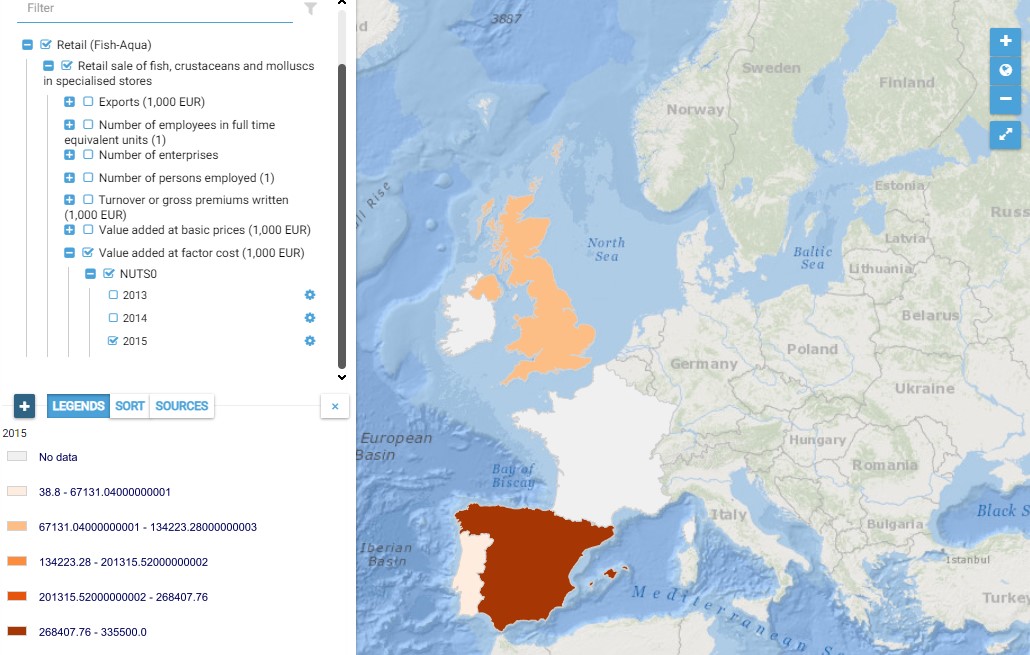
This map presents all layers corresponding to "Retail sale of fish, crustaceans and molluscs in specialised stores" activities in the Atlantic area. For more information about this NACE code : https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/ramon/nomenclatures/index.cfm?TargetUrl=DSP_NOM_DTL_VIEW&StrNom=NACE_REV2&StrLanguageCode=EN&IntPcKey=18511064&IntKey=18511154&StrLayoutCode=HIERARCHIC&IntCurrentPage=1 Indicators collected are : Business indicators per country
-
-
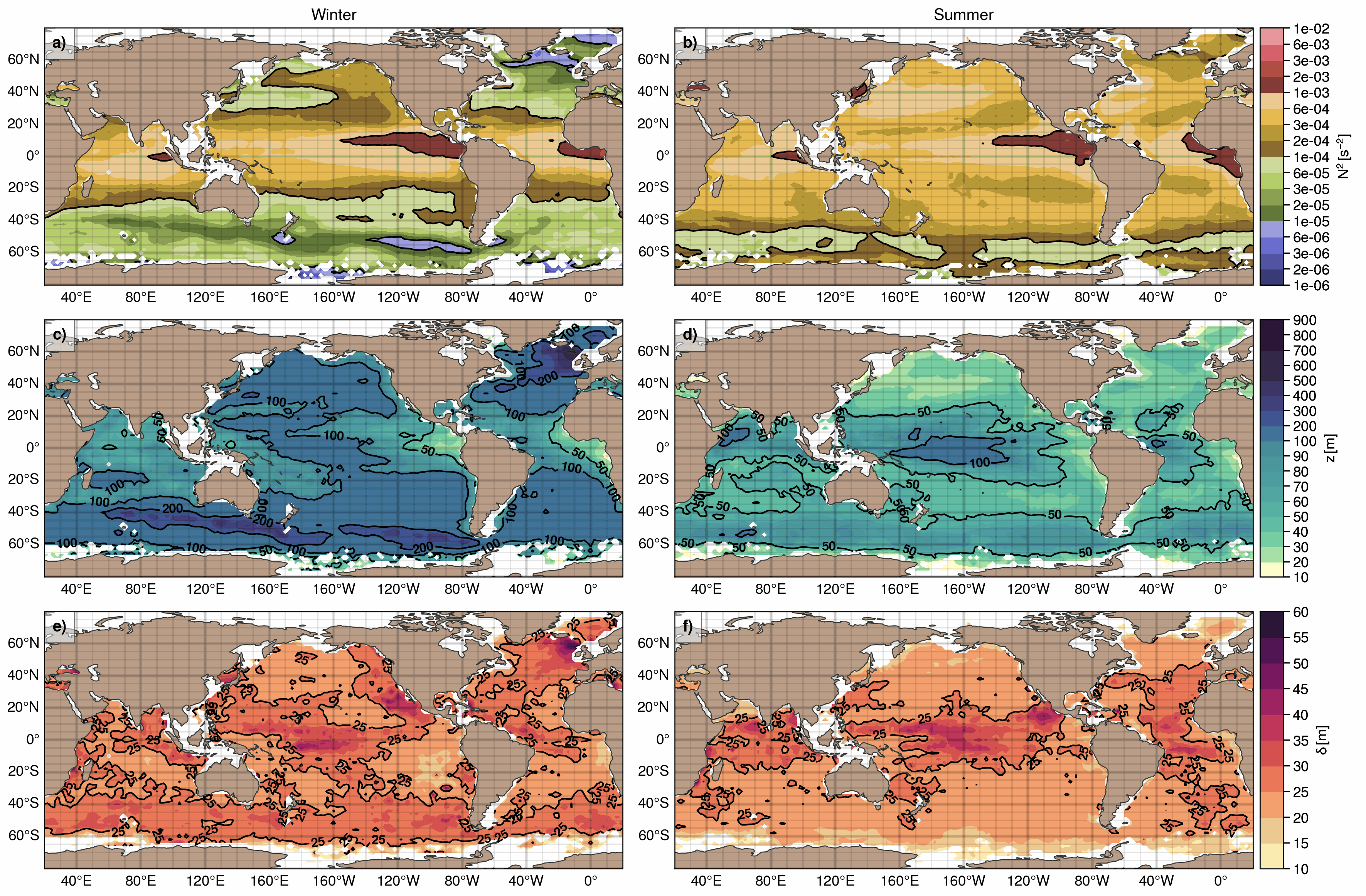
The upper ocean pycnocline (UOP) monthly climatology is based on the ISAS20 ARGO dataset containing Argo and Deep-Argo temperature and salinity profiles on the period 2002-2020. Regardless of the season, the UOP is defined as the shallowest significant stratification peak captured by the method described in Sérazin et al. (2022), whose detection threshold is proportional to the standard deviation of the stratification profile. The three main characteristics of the UOP are provided -- intensity, depth and thickness -- along with hydrographic variables at the upper and lower edges of the pycnocline, the Turner angle and density ratio at the depth of the UOP. A stratification index (SI) that evaluates the amount of buoyancy required to destratify the upper ocean down to a certain depth, is also included. When evaluated at the bottom of the UOP, this gives the upper ocean stratification index (UOSI) as discussed in Sérazin et al. (2022). Three mixed layer depth variables are also included in this dataset, including the one using the classic density threshold of 0.03 kg.m-3, along with the minimum of these MLD variables. Several statistics of the UOP characteristics and the associated quantities are available in 2°×2° bins for each month of the year, whose results were smoothed using a diffusive gaussian filter with a 500 km scale. UOP characteristics are also available for each profile, with all the profiles sorted in one file per month.
-

-

'''DEFINITION''' Heat transport across lines are obtained by integrating the heat fluxes along some selected sections and from top to bottom of the ocean. The values are computed from models’ daily output. The mean value over a reference period (1993-2014) and over the last full year are provided for the ensemble product and the individual reanalysis, as well as the standard deviation for the ensemble product over the reference period (1993-2014). The values are given in PetaWatt (PW). '''CONTEXT''' The ocean transports heat and mass by vertical overturning and horizontal circulation, and is one of the fundamental dynamic components of the Earth’s energy budget (IPCC, 2013). There are spatial asymmetries in the energy budget resulting from the Earth’s orientation to the sun and the meridional variation in absorbed radiation which support a transfer of energy from the tropics towards the poles. However, there are spatial variations in the loss of heat by the ocean through sensible and latent heat fluxes, as well as differences in ocean basin geometry and current systems. These complexities support a pattern of oceanic heat transport that is not strictly from lower to high latitudes. Moreover, it is not stationary and we are only beginning to unravel its variability. '''CMEMS KEY FINDINGS''' The mean transports estimated by the ensemble global reanalysis are comparable to estimates based on observations; the uncertainties on these integrated quantities are still large in all the available products. Note: The key findings will be updated annually in November, in line with OMI evolutions. '''DOI (product):''' https://doi.org/10.48670/moi-00245
-
Auteur(s): Thomas Michel , Projet de création d'un centre voué à la culture musicale dans l'enceinte du Palais Gallien, ruine de l'amphithéâtre gallo romain, seul vestige de la présence romaine à Bordeaux
-
-
Auteur(s): Darracq Alain, Desmoulins Christian , Proposition pour la reconversion d'une ancienne minoterie en en lieu de création artistique et artisanale
-
The three digital maps provided in this product aim to assess the degree of Offshore windfarm siting suitability existing over a geographical area with a focal point where waters of France and Spain meet in Biscay Bay on 500 m depth. The maps display respectively the spatial distribution of the average and lowest windfarm siting suitability scores along with the average wind speed distribution over a time period of 10 years. They are part of a process set up to assess the fit for use quality of the currently available datasets to support a preliminary selection of potential offshore sites for wind energy development. To build these maps, GIS tools were applied to several key spatial datasets from the 5 data type domains considered in the project: Air, Marine Water, Riverbed/Seabed, Biota/Biology and Human Activities, collated during the initial stages of the project. Initially, each selected dataset was formatted and clipped to the study area extent and spatially classified according to suitability scores, to define raster layers with the variables depicting levels of current anthropogenic and environmental spatial occupation of activities, seabed depth and slope, distances to shoreline, shipping intensity, mean significant wave height, and substrate type. These pre-processed layers were employed as inputs for applying a spatial multi-criteria model using a wind farming suitability classification based on a discrete 5 grades index, ranging from Very Low up to Very High suitability. In adition to suitability maps, an average wind speed spatial distribution map for a 10 years period, at 10 m height, was obtained over the study area from the raster processing of a wind speed time series of monthly means available from daily wind analysis data. The characteristics of the datasets used in this exercise underwent an appropriateness evaluation procedure based on a comparison between their measured quality and those specified for the product. All the spatial information made available in these maps and from the subsequent appropriateness analysis of the datasets, contributes to a clearer overview of the amount of public-access baseline knowledge currently existing for the North Atlantic basin area.
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA